This value is represented by the difference between the potential energy of the products and the potential energy of the reactants PE products - PEreactants
Change in Enthalpy - delta H
A species in a reaction mechanism that is consumed in an early step and then regenerated in a later step.
Catalyst (It is present at the start and regenerated at the end).
To find the instantaneous rate from a concentration versus time graph, you must calculate the slope of this line at a specific point.
The slope of the tangent line.
A reaction where the energy of the products is lower than the energy of the reactants is classified as this type of process.
Exothermic (reaction).
A species in a reaction mechanism that is produced in an early step and then consumed in a later step.
Reaction Intermediate (or simply Intermediate) (It is produced then consumed).
The vertical distance on a potential energy diagram from the energy of the reactants up to the energy of the activated complex represents this value.
Activation Energy
This is the term for the slowest step in a reaction mechanism, which determines the overall rate of product formation.
Rate-Determining Step (or Rate-Limiting Step).
This reaction would be endothermic or exothermic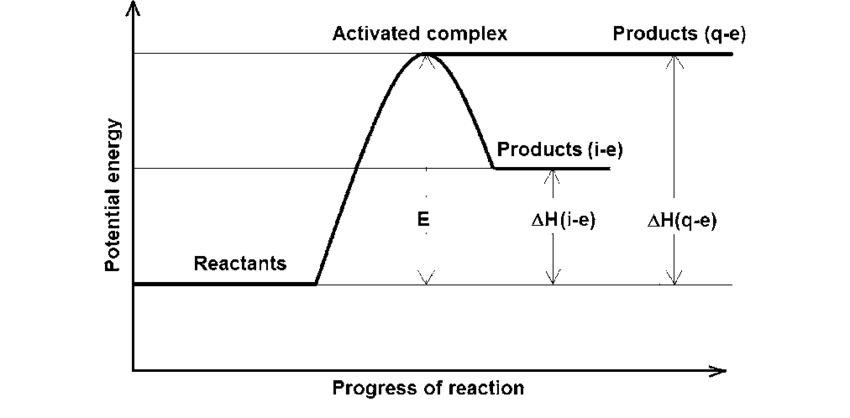
endothermic (products gained energy)
FFor the reaction mechanism
NO2+NO2----N2O4 (slow) and
N2O4+CO------ NO+CO2+NO2 (fast), this species is the catalyst.
NO2
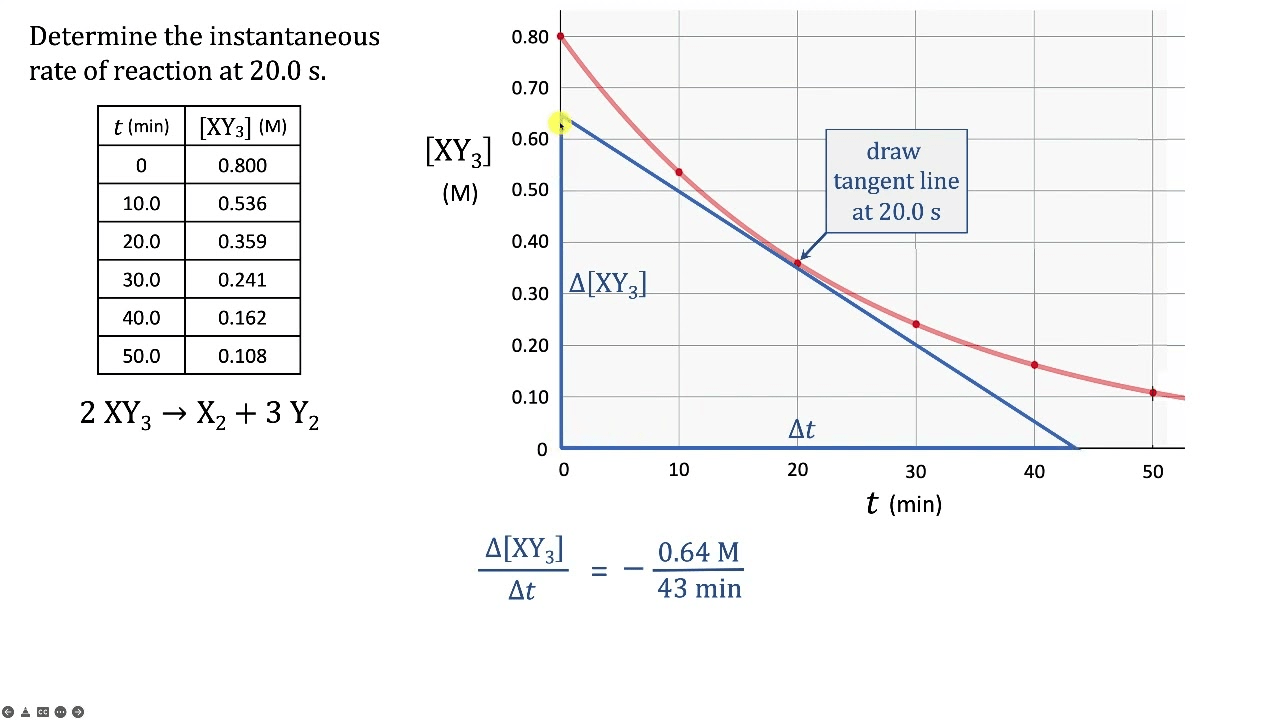
What would the average rate of this reaction be?
-0.014 M/S
Why are there two hills? 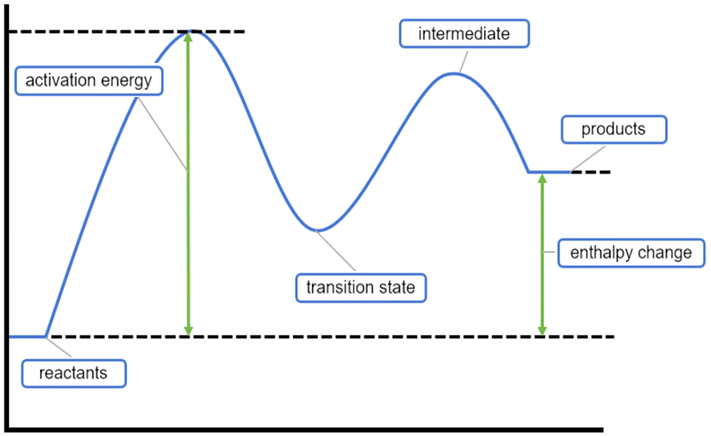
This is a two step reaction mechanism?
For an overall reaction, what the net change in concentration for both the catalyst and the reaction intermediate is.
Zero (Both the catalyst and the intermediate are consumed and produced/regenerated within the mechanism, so their net change in the overall reaction is zero).
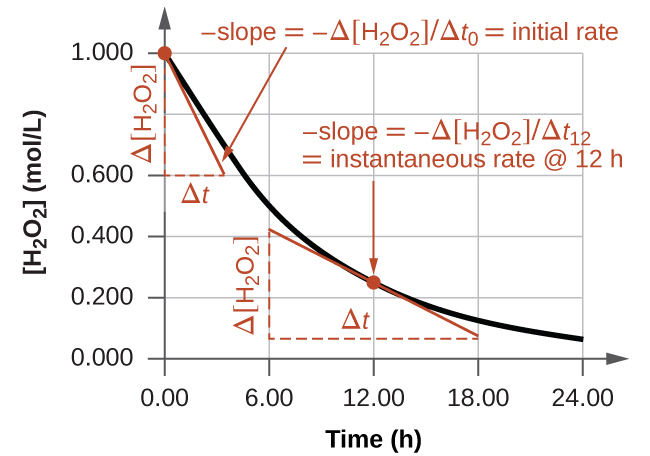
What would the instantaneous rate be at 12.00h?
around -0.033 M/s