The acronym KMT refers to this
What is Kinetic Molecular Theory?
Used to separate iron filings from sand
What is a magnet
The process of water freezing is an example of this type of change.
What is a physical change?
Who is considered the father of atomic theory?
What is John Dalton?
Trail mix and granola
What is a mechanical mixture?
The state in which particles only vibrate and do not move randomly
What is a solid?
What is a suspension?
The amount of mass in a given volume of a substance is called this.
What is density?
Greek philosophers believed all matter was made up of these 4 elements
What is air, earth, water and fire?
A pure substance made up of at least 2 elements
What is a compound?
State of matter that has the most kinetic energy
What is a gas?
A mixture that looks the same throughout
What is a homogenous mixture?
Ability for a substance to be hammered and rolled into thin sheets
What is malleability?
Electrons circling the nucleus in orbits - give the theorist and name of model
What is the solar system model? What is Ernest Rutherford?
Energy added to a liquid spreads particles farther apart
What is evaporation?
What are atoms and molecules?
What is a pure substance?
This chemical property refers to the ability of a substance to combine with oxygen, often resulting in rusting or burning.
What is combustibility?
Discovered the neutron - give the theorist and year
What is James Chadwick, What is 1932
Addition of energy vaporizes a solid
What is sublimation?
Explanation for why liquids have no shape (use the word particles in your answer)
Liquids do not have a definite shape because the spacing between particles in liquids lets the particles slip and slide past each other, changing their position
What is stirring, increasing temperature or crushing?
8 physical properties of matter
What is colour, malleability, texture, viscosity, hardness, solubility, melting and boiling point, ability to conduct heat and electricity
What is Democritus?
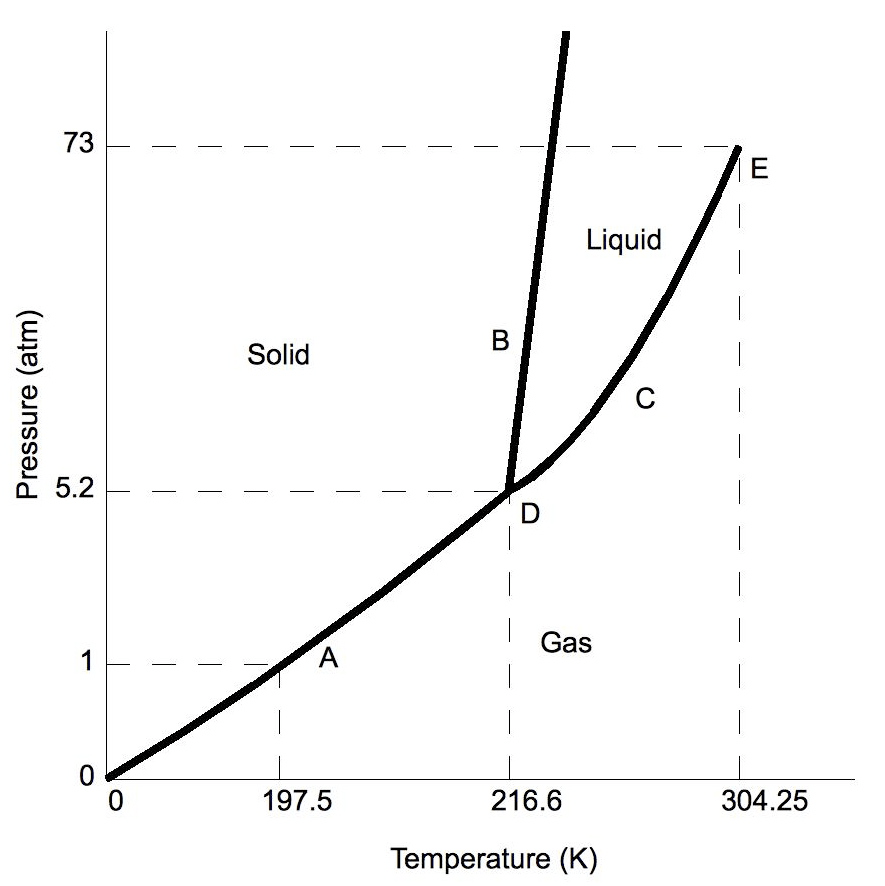
What is a phase diagram?