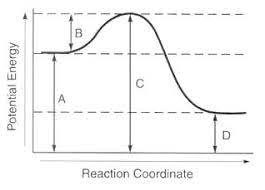
Which line represents the products?
Which line represents the activation energy?
Products is line D
Activation energy is line B
Complete: "Le Chatelier's Principle states that when a _________ is applied to a system in equilibrium, it will adjust to counter the effect of such change and restore the ________."
Stress, equilibrium
In the reaction
A + heat <--> B
what is the effect of cooling the system down?
reaction will shift to the left/favor backward reaction
What is necessary in order to have an effective collision?
Sufficient energy and proper orientation
Which line represents the heat of reaction?
Which line represents activation energy?
Line 4 represents the heat of reaction
Line 3 represents activation energy.
When extra NH3 is added to the following system at equilibrium:
3 H2(g) + N2(g) <--> 2 NH3(g)
which reaction (forward/backward) will be favored?
BACKWARD
When the pressure is decreased on the following system at equilibrium:
3 H2(g) + N2(g) <--> 2 NH3(g)
which reaction will be favored?
backward/shift to the left
How does a catalyst speed up a reaction?
Catalysts speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy
Identify as exothermic or endothermic
A + B --> C + heat
EXOTHERMIC
The heat of the reactants is:
The heat of the products is:
heat of reactants: 50 kJ
heat of products: 100 kJ
Of the following, which shifts left when pressure is increased? (A B C and D are all gasses)
a) A + B <---> C + D
b) 2A + B <---> 2C
c) A + B <---> C
Pressure increases, shifts to side with smaller number of moles
a) 2 moles <---> 2 moles no shift
b) 3 moles <---> 2 moles shift right
c) 2 moles <---> 1 mole shift right
Answer: NONE shift left
Name three ways to speed up a reaction.
increase temperature
increase concentration of reactants
increase surface area
add a catalyst
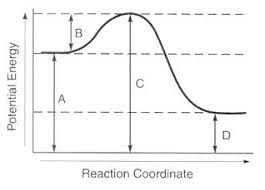
Identify as endothermic or exothermic. Explain.
Exothermic: products have less energy than reactants or line D < line A
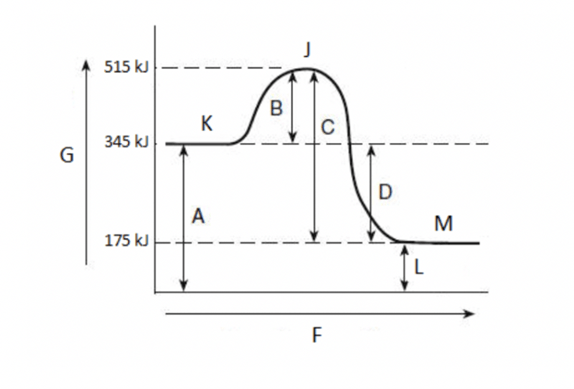
Activation energy?
Heat of reaction?
Endothermic or exothermic?
activation energy is 170 kJ
heat of reaction is -170 kJ
exothermic
What are equal in a system that is in chemical equilibrium?
the rate of forward and backward reaction
2 NO2 (g) <---> N2O4 (g) ΔH = -58.0 kJ
Name four ways to favor the forward reaction.
add NO2
remove N2O4
increase pressure
decrease temperature
Which of the following would decrease the rate of a reaction?
a. increase the surface area of the reactants
b. decrease temperature
c. increase the temperature
d. decrease the surface area of the reactants
e. adding a catalyst
b. decrease temperature
d. decrease surface area of the reactants
Upon mixing chemical A and B inside a beaker, white precipitates settled at the bottom and it became cold. What type of reaction happened?
ENDOTHERMIC
The activation energy is:
The heat of the reaction is:
The activation energy is 200 kJ.
The heat of the reaction is 50 kJ.
CH4 (g) + 2H2S (g) ↔ CS2 (g) + 4H2 (g)
The reaction is endothermic.
If the temperature is increased, what happens to the concentration of CS2? Explain
Energy + CH4 (g) + 2H2S (g) ↔ CS2 (g) + 4H2 (g)
Energy will be a reactant so if temperature increases, forward reaction will be favored and the concentration of CS2 increases.
CO (g) + H2 (g) ↔ C(s) + H2O(g)
For this reaction, which direction will the shift occur when pressure increases? explain.
When pressure increases, the system shifts to the side with fewer moles of gas.
2 moles <---> 1 mole (note carbon is a solid)
Shifts RIGHT
What is activation energy?
Activation energy is the minimum energy required for a reaction to take place.