The subatomic particle that is almost 2000x bigger than an electron and has a charge of +1.
The type of radiation that occurs when an atom spits out the heaviest of all particles which is similar in structure to a single helium atom.
What is alpha decay/emission?
The amount of time it takes for half of a material to decay.
What is a half-life?
This is the most recognizable part for each element. Only consists of 1 capital letter and sometimes 1 lowercase letter.
What is the atomic symbol?
This kind of radiation is the most energetic and has been associated with green guys who workout.
What is gamma radiation?
The smallest subatomic particle that is attracted to the positive end of a magnet.
What is an electron?
The type of radiation that occurs when a small negatively charges particle is spit out by an atom resulting in the loss of a singular negative charge.
What is beta/electron decay/emission?
The number of half-lives that have passed if you started with 500g of material and now you have 250g.
This is the identification number of an element. It also tells you how many protons are in the element.
What is the atomic number?
The first people to theorize about the atom and make assumptions about what they are.
Because atoms naturally have the same number of electrons and protons they are said to have this kind of charge.
What is neutral/zero/no charge?
The type of radiation that occurs when a small particle similar to an electron but with a positive charge is spit out by an atom resulting in the loss of a singular positive charge.
What is positron decay/emission?
What is 25g?
This number tells you what isotope you have. It also tells you the weight of the isotope.
What is atomic mass number?
The type of nuclear reaction that occurs in the center of the sun.
What is fusion?
The name of the chart that arranges of all known elements in the universe.
What is the periodic table of elements?
When an atoms gains a negative charge from a small subatomic particle this is said to have happened.
What is electron/beta capture?
MA=M(1/2)^(t/T)
Taking all of the naturally occurring isotopes of a certain element and multiplying their atomic mass by their percent of abundance will give you this number.
The experiment that Rutherford conducted that led to the discovery of the atomic nuclei, proton, and neutron.
What is the gold foil experiment?
The area of an atom that contains 99% of it's mass and all of the atoms protons + neutrons.
What is the nucleus of an atom?
The missing part in this radiation equation.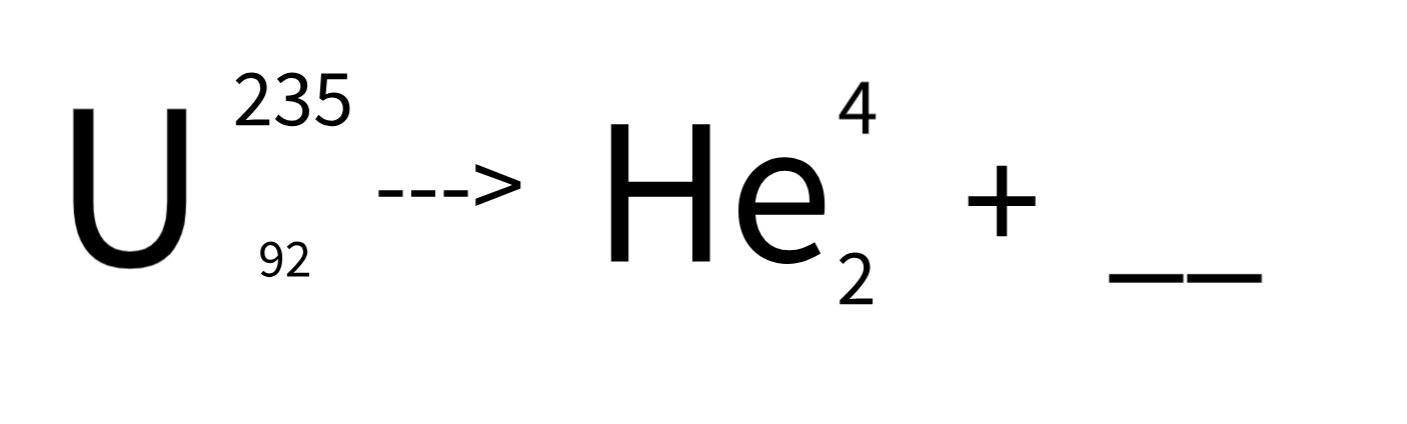
What is Thorium - 231?
When one material turns into another material it has gone through this process.
What is transmutation?
What is yttrium-89?
The law that states that material can not be created or destroyed only rearranged or changed.
What is the Law of Conservation of Mass?