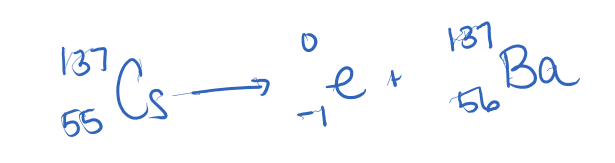Define Arrhenius acid and provide an example.
A substance that produces H+ ions when dissolved in water; examples: acetic acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, etc. (OR can list more common names like vinegar, oranges, lemons, etc.)
Define Arrhenius base and provide an example.
A substance the produces OH- ions when dissolved in water; examples: sodium hydroxide, ammonia, etc. (OR can list more common names like bleach, Windex, soap, etc.)
The oxidation state of any uncombined/free element is ________.
zero
When hydrogen is bonded to a nonmetal, it always takes an oxidation state of _______.
+1
Nuclear chemistry is different than most other areas of chemistry because it involves studying changes in the _______________ of an atom.
nucleus
List/describe three characteristics of acids.
Taste sour; are in many of the foods we eat; corrosive/caustic; conduct electricity; pH less than 7; react with metals to form hydrogen gas; neutralize bases
List/describe three characteristics of bases.
Define oxidation, and describe what happens to a substance's oxidation state when it is oxidized.
the loss of electrons; increases
Define reduction, and describe what happens to a substances oxidation state when it is reduced.
The gain of electrons; decreases
Define radioisotope and explain what makes an isotope radioactive.
An isotope of an element that emits radiation; an unbalanced ratio of neutrons to protons
Name the following substances (assume they are aqueous): HF, KOH, H2SO4.
hydrofluoric acid; potassium hydroxide; sulfuric acid
NaOH and NH3 are both classified as Arrhenius ___________ and turn phenolphthalein ____________________.
bases; pink
The oxidation state of nitrogen in the compound NaNO3 is ______.
+5
Consider the following reaction:
3Mg (s) + 2AlCl3 (aq) --> 2Al (s) + 3MgCl2 (aq)
In this reaction, the solid magnesium is ____________ (oxidized or reduced) as it reacts to form magnesium chloride.
oxidized
Define transmutation and describe the difference between natural and artificial transmutation.
The conversion of an atom of one element to an atom of a different element. Natural transmutation: decay; one reactant. Artificial transmutation: an isotope is bombarded with a high energy particle; two reactants.
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between nitric acid and sodium metal.
2HNO3 (aq) + 2Na (s) --> 2NaNO3 (aq) + H2 (g)
Write a balanced chemical reaction for the neutralization reaction between HBr (aq) and Mg(OH)2 (aq).
2HBr (aq) + Mg(OH)2 (aq) --> MgBr2 (aq) + 2HOH (l)
Consider the diagram below. When the switch is closed, the zinc metal is oxidized to zinc ions. Based on this information, you can conclude that the zinc is the _______________ (anode or cathode) and electrons flow _______________(left to right or right to left) through the wire.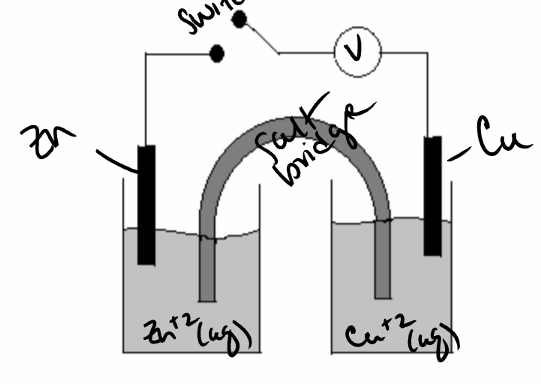
anode; left to right
A voltaic cell is composed of a lead cathode and an aluminum anode. Calculate the Eocell value.
+1.53 V
Define/describe nuclear fission and fusion. What do these two types of nuclear reactions have in common?
Fission: the splitting of a large, unstable nucleus into two smaller nuclei. Fusion: the combining of two small nuclei into one larger nucleus. Both of these reactions convert a portion of the atoms' mass into LARGE amounts of energy.
A sample of LiOH (aq) is titrated with HF (aq). The indicator used in thymol blue. Describe the color change that will take place as HF (aq) is added to LiOH (aq).
blue to yellow
A 15-mL sample of hydrochloric acid of unknown concentration is titrated with 0.500 M sodium hydroxide. The initial volume reading in the buret containing sodium hydroxide was 4.75 mL and the final volume was 22.10 mL. Calculate the molarity of the hydrochloric acid.
0.58 M (+/- one sig fig)
Does the electrochemical cell in the diagram below represent a voltaic or electrolytic cell? Provide evidence for your answer.
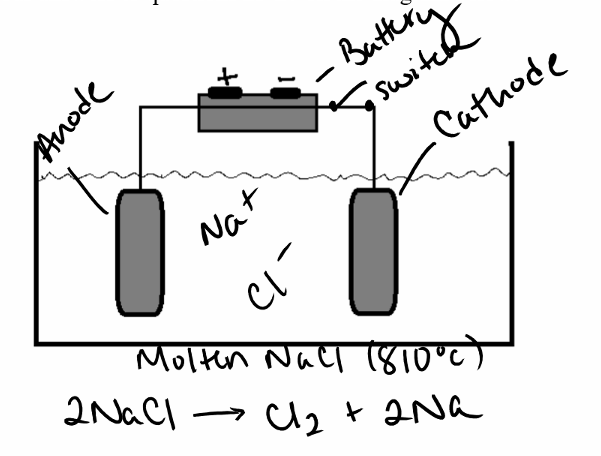
Electrolytic; has a battery, is in one container
In an electrolytic cell, a chloride ion will naturally migrate toward the _____________ (anode or cathode). Explain your response.
Anode; the anode is positively charged in an electrolytic cell, so a negatively charged ion (like chloride) will be attracted to it.
Write a balanced nuclear reaction for the decay of Cs-137.