CO2 has two regions of negative charge around the central atom. What shape will it take and what is the bond angle between these regions?

Linear --> 180o
A colourless liquid is suspected to be an amine. Three identification tests are available - Red litmus paper, Blue litmus paper, and Bromine Water. Which of these tests will return a positive result and what will be observed.
Red litmus paper / It will turn blue as an amine is a base
The reaction of an alkene with hydrogen (H2) is an addition reaction. Explain what an addition reaction is and why this reaction qualifies.
An addition reaction involves the breaking of a double bond and adding one atom or group to each carbon of where the double bond was.
In this case, the double bond breaks and a H atom is added to each carbon of the double bonding carbons.
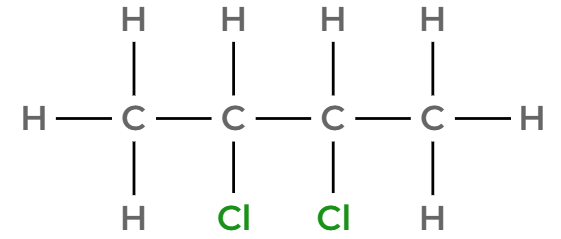
Draw 2,3-dichlorobutane
Molecular covalent substances have strong ______ bonds between atoms inside the molecule and weak ________ ________ between the molecules.
Covalent / Intermolecular forces
Ammonia (NH3) has 4 regions of negative charge around the central atom. 3 of these are bonding regions and 1 is a non bonding region. What shape will ammonia take and what is the bond angle?

Trigonal Pyramidal --> 109o
A scientist mixed up two bottles of organic solutions. One was known to be an alkane and one was known to be an alkene. What test could be performed to distinguish between the two and what would be observed.
Bromine Water Test
The alkene would react immediately changing from orange to colourless quickly.
The alkane would react slowly changing from orange to colourless over a time.
This is an elimination reaction. Two atoms or groups from neighbouring carbons (in this case OH & H) are removed and a double bond is formed between these carbons.
Name this molecule
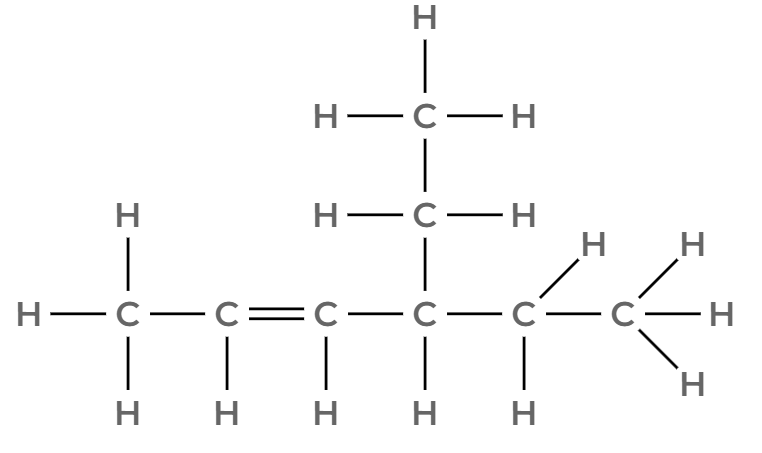
4-ethylhex-2-ene
Covalent network substances are giant 3D networks of atoms connected by strong covalent bonds. There are three covalent network structures we have learned about. What are these three?
Graphite / Diamond / Silicon Dioxide
CCl3F has four regions of negative charge surrounding the central carbon atom. All of these are bonding regions. What shape will CCl3F take and what will the bond angle be?
Tetrahedral --> 109o
A scientist lost all of their litmus paper and universal indicator. They do however, have some metal and metal carbonates. How can this be used to check if the product he made is a carboxylic acid?
When an acid reacts with a metal or metal carbonate, bubbles would be observed as gaseous products are created. With a metal the gas formed is hydrogen gas and with a carbonate the gas created is carbon dioxide
The reaction of propan-2-ol with SOCl2 is a substitution reaction. Explain why this is a substitution reaction and name the product formed.
This is a substitution reaction because one atom/group has been substituted for another atom/group. In this case the OH group has been swapped for a Cl atom.
The product formed is 2-chloropropane
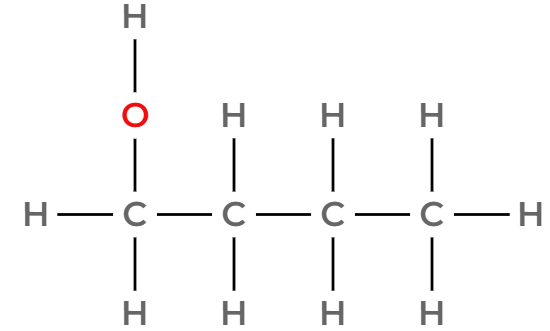
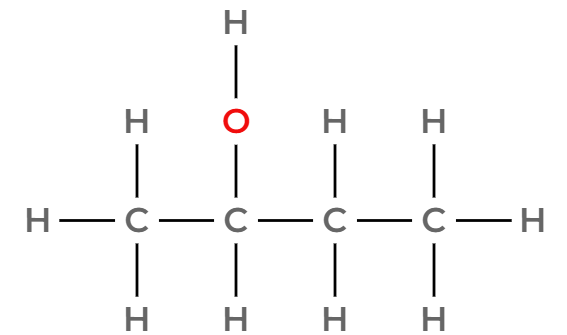
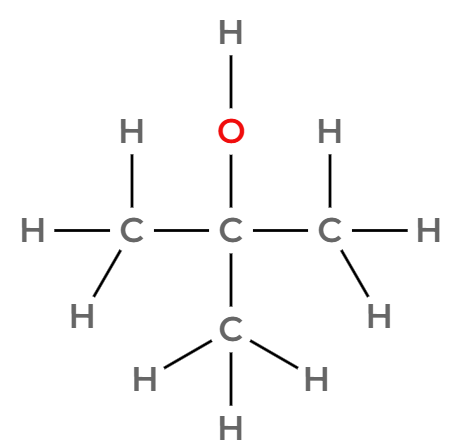
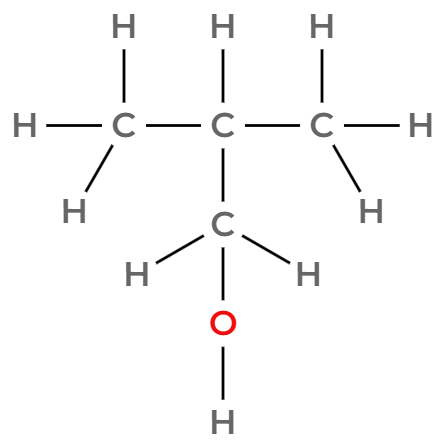
Draw three of the four isomers of C4H9OH
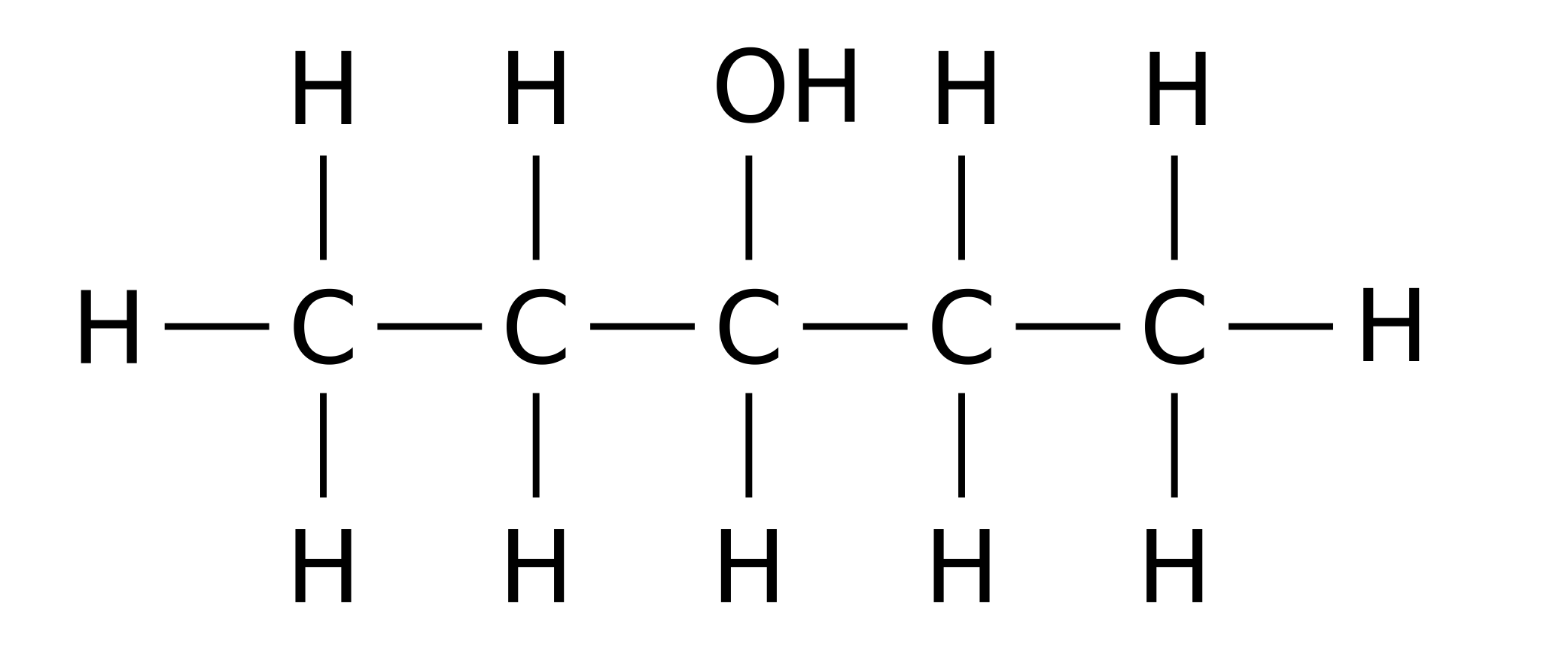
Name 2 physical properties that ionic substances possess
Brittle / Soluble in water / Conductive of electricity in solution / Conductive of electricity in molten
BF3 has three regions of negative charge around the central atom. All of these are bonding regions. What shape will BF3 take and what will the bond angle be?
Trigonal Planar --> 120o
I lost all my labels again for my organic solution bottles. I want to find out which one of my bottles is a primary alcohol and which one is an alkene. I have permanganate and dichromate available to test with. What will be observed when I test both unknown bottles with permanganate and dichromate.
With a primary alcohol, permaganate will turn from purple to colourless and dichromate will turn from orange to green.
With an alkene, permanganate will turn from purple to colourless and with dichromate it will stay orange.
There is nothing I love more than watching a reaction between a primary alcohol and potassium dichromate. Identify the type of reaction occurring, the conditions required, and the colour change observed.
Draw and name the two products of the reaction pent-2-ene with H2O/H+.
Pentan-2-ol

Pentan-3-ol
Metallic substances are comprised of metal cations surrounded by delocalised electrons. Explain why metallic substances are good conductors of electricity and head in solid and liquid form.
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) has 4 regions of negative charge around the central atom. All of these are bonding regions. Using this information, identify the shape, bond angle, and polarity of this molecule.
You must explain why the shape makes it this polarity.
Tetrahedral / 109o / symmetrical shape, bond dipoles cancel out, overall molecule is non-polar
I performed multiple tests on an unknown organic solution. These were the results.
Formed a single layer when put into water
Did not react with permanganate or dichromate
Had a fishy smell
Did not change the colour of blue litmus paper
What homologous series does the solution belong to?
Amine (C 1-5)
Haloalkanes will do two different reactions with KOH depending on the conditions. Identify the type of reaction it will do with KOH(alc) and KOH(aq) and explain these reactions.
Haloalkane + KOH(alc) --> Alkene (elimination reaction)
The halogen and a neighbouring hydrogen are removed and a double bond is formed between these two neighbouring carbons.
Haloalkane + KOH(aq) --> Alcohol (substitution reaction)
The halogen is substituted for the OH group to form an alcohol.
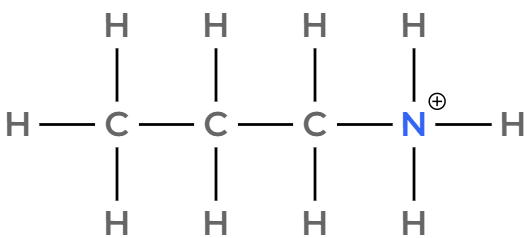
Draw and name the ion formed when propan-1-amine is dissolved in water.
Propylammonium ion
Rank the types of substances (metallic, molecular, covalent network, and ionic) in order of increasing melting and boiling point.
Explain these trends
The melting and boiling points of a molecule are determined by the strength of the attractive forces between particles. An increased MP or BP means that more energy is required to overcome the attractive forces. The strongest attractive forces in these molecules are covalent bonds which are present between atoms in network covalent molecules. The next strongest are ionic and metallic bonds present in ionic and metallic substances. The weakest attractive forces are the intermolecular forces present in molecular substances.
Molecular --> Ionic/Metallic --> Network Covalent