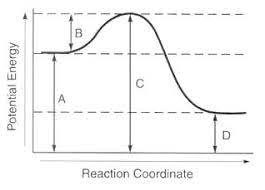
Which line represents the products?
Which line represents the activation energy?
Products is line D
Activation energy is line B
When extra NH3 is added to the following system at equilibrium:
3 H2(g) + N2(g) <--> 2 NH3(g)
which reaction (forward/reverse) will be favored?
Reverse
In the reaction
A + heat <--> B
what is the effect of cooling the system down?
reaction will shift to the left/favor backward reaction
What is necessary in order to have an effective collision?
Sufficient energy and proper orientation
Identify as exothermic or endothermic
A + B --> C + heat
EXOTHERMIC
Which line represents the heat of reaction?
Which line represents activation energy?
Line 4 represents the heat of reaction
Line 3 represents activation energy.
Complete: "Le Chatelier's Principle states that when a _________ is applied to a system in equilibrium, it will adjust to counter the effect of such change and restore the ________."
Stress, equilibrium
When the pressure is decreased on the following system at equilibrium:
3 H2(g) + N2(g) <--> 2 NH3(g)
which reaction will be favored?
backward/shift to the left
How does a catalyst speed up a reaction?
Catalysts speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy
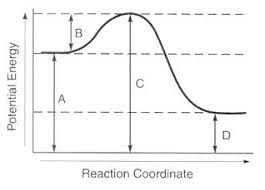
Identify as endothermic or exothermic. Explain.
Exothermic: products have less energy than reactants or line D < line A
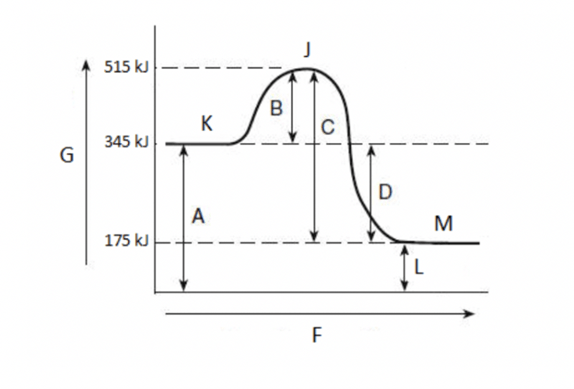
Activation energy?
Heat of reaction?
Endothermic or exothermic?
activation energy is 170 kJ
heat of reaction is -170 kJ
exothermic
2 NO2 (g) <---> N2O4 (g) ΔH = -58.0 kJ
Name four ways to favor the forward reaction.
add NO2
remove N2O4
increase pressure
decrease temperature
Name three ways to speed up a reaction.
increase temperature
increase concentration of reactants
increase surface area
add a catalyst
Upon mixing chemical A and B inside a beaker, white precipitates settled at the bottom and it became cold. What type of reaction happened?
ENDOTHERMIC
The heat of the reactants is:
The heat of the products is:
heat of reactants: 50 kJ
heat of products: 100 kJ
What are equal in a system that is in chemical equilibrium?
the rate of forward and backward reaction
CO (g) + H2 (g) ↔ C(s) + H2O(g)
For this reaction, which direction will the shift occur when pressure increases? explain.
When pressure increases, the system shifts to the side with fewer moles of gas.
2 moles <---> 1 mole (note carbon is a solid)
Shifts RIGHT
Which of the following would decrease the rate of a reaction?
a. increase the surface area of the reactants
b. decrease temperature
c. increase the temperature
d. decrease the surface area of the reactants
e. adding a catalyst
b. decrease temperature
d. decrease surface area of the reactants
The activation energy is:
The heat of the reaction is:
The activation energy is 200 kJ.
The heat of the reaction is 50 kJ.
CH4 (g) + 2H2S (g) ↔ CS2 (g) + 4H2 (g)
The reaction is endothermic.
If the temperature is increased, what happens to the concentration of CS2? Explain
Energy + CH4 (g) + 2H2S (g) ↔ CS2 (g) + 4H2 (g)
Energy will be a reactant so if temperature increases, forward reaction will be favored and the concentration of CS2 increases.
Of the following, which shifts RIGHT when pressure is increased?
a) A + B <---> C + D
b) 2A + B <---> 2C
c) A + B <---> C
Pressure increases, shifts to side with smaller number of moles
a) 2 moles <---> 2 moles no shift
b) 3 moles <---> 2 moles shift right
c) 2 moles <---> 1 mole shift right
Answer: B and C
What is activation energy?
Activation energy is the minimum energy required for a reaction to take place.