What is a compound?
a substance made from more than one element joined by a chemical bond
What is Density?
Mass/Volume
Mass of a substance per unit of volume.
What is the definition for property?
particular characteristics of a material such as the materials density, melting point, or color. A change in volume, size or shape of the material does not change its properties.
What are the three states?
Which one has the highest kinetic energy?
Which has the lowest kinetic energy?
Solid, liquid, gas
Highest = gas
Lowest = solid
What is the definition of a particle?
Small structures that make up all matter.
In the molecule C16H18O5 how many elements are there?
3 elements: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
What is the density of water?
1.0 g/cm3
List two types of physical properties.
Melting point
Boiling point
Color
Malleability
Odor
State
Density
If you increase thermal energy what does this do to the motion of the particles?
Give me an example.
Ice to liquid water. Particles heat up and begin moving faster and break some of the bonds becoming a liquid.
What is the definition of malleability?
The flexibility of a material.
Name a substance that is both a molecule and a compound.
Now name a substance that is a molecule but not a compound.
Example: H2O Water
Example: O2 Oxygen gas
If something has a density of 1.2 will it sink or float?
Sink, density of water is 1.0 g/cm3
What is a chemical property?
how a material reacts with another substance
(reactivity)
Draw a container of gas particles at room temperature.
See teacher model.
What is the difference between a monomer and a polymer?
Monomer is a singular molecular subunit and a polymer is a long chain of smaller units called monomers.
What is the definition of an extended structure?
a varied number of one or more kinds of atoms bonded together to form a larger network.
Johnny measures a piece of plastic and determines it has a mass of 20 grams and a volume of 5 cm3 . What is the density of the piece of metal? Will it sink or float?
4 g/cm3
Sink
Which of the following is NOT a property that can be used to identify a material?
Flexibility
Shape
Color
Density
Shape
Use the graph below to answer this question.
This graph shows the temperature of a substance as it is heated over time from 20 to 100 degrees Celsius. This substance has a boiling point of 80 degrees Celsius. Explain what is happening at point B in the graph.
The substance is boiling, the state is changing from a liquid to a gas. The energy is going toward breaking bonds/connections to increase kinetic energy of particles and change states.
Draw a monomer. Within your monomer drawing: label an atom, chemical bond, and the monomer. Draw a polymer. Lastly, draw a cross-linked polymer.
See teacher model.
Which one is a compound?
Na
N
CO
Ca
CO
Carbon and Oxygen
Draw something of less density, equal density, and greater density.
See teacher example.
Which of these substances would be a solid at room temperature?
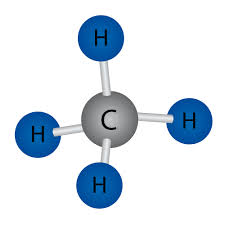
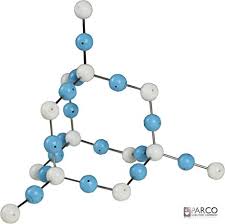

In general, large molecular or extended structures tend to be solids at room temperature.
Draw a model for the kinetic energy of gas particles when they are cooled, at room temperature, and when they are heated.
Plastics are made from:
hydrogen and carbon compounds
sand, soda ash, and limestone
water and sand
none of the above
Hydrogen and Carbon compounds.