What is Chemistry?
What is an atom?
Smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction
The S orbital is what shape?
Spherical
What is an atomic orbital (electron)?
Describes the probability of finding an electron at various locations around the nucleus
What are valence electrons?
Electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element's atoms
What are the three states of matter? (describe each at the molecular level)
What are the three subatomic particles?
Proton, Neutron, and Electron
Atom comes from what Greek word and what does it mean?
-Atomos
-Unable to be cut
How are elements arranged on a periodic table?
Based on atomic number
Explain the difference between an anion and cation. How is each formed?
Anion - negatively charged (gains electron)
Cation - positively charged (loses electron)
Explain the difference between a homogenous and heterogenous mixture.
Homogenous - composition is uniform throughout, evenly distributed
(air, vinegar, salt water)
Heterogenous - composition is not uniform throughout
(Chicken noodle soup, chocolate chip cookie)
Explain the difference between the atomic number and mass number of an atom.
Atomic number - # of protons
Mass number - # of protons and neutrons
P orbitals are what shape?
Dumbbell
The first column of the periodic table are the
Alkali Metals
What is an alloy?
A mixture of tow or more elements, at least of of which is a metal
Explain the difference between an element and compound?
Element - the simplest form of matter that has a unique set of properties
Compound - A substance that contains two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed proportion
What is an isotope?
A form of a chemical element with the same number protons, but a different number of neutrons
How does salt melt ice?
Salt ions (Na, Cl) disrupt the water molecules from forming a crystalline structure (get in the way)
In regard to orbitals, principal energy level 2 can contain a maximum of how many electrons?
Explain ionic bonding.
Electrostatic force that holds ions together (positive and negative)
Explain the difference between a physical and chemical change.
During a chemical change, the composition of the matter always changes. During a physical change, the composition of the matter never changes
What discovery did Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment lead to? How did he know/discover it?
-Protons
-Nucleus of gold was positive and deflected positive alpha particles (some directly back at him)
Which of argon's three isotope is most abundant: argon-36, argon-38, argon-40? The atomic mass of argon is 39.948.
Argon-40 (Closest to atomic mass)
An atom of an element has two electrons in the first energy level and five electrons in the second energy level. Write the electron configuration for this atom and name the element. How many unpaired electrons does an atom of this element have?
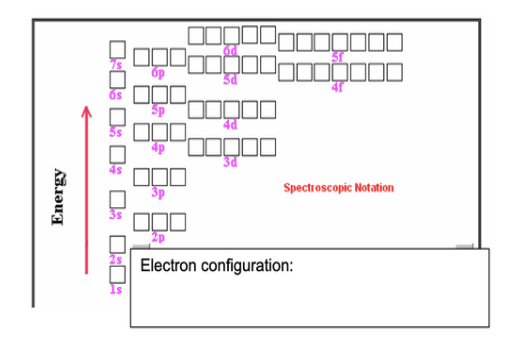
- 1s22s22p3
- Nitrogen
- 3 unpaired electrons
Explain metallic bonding.
-Forces of attraction between the free floating valence electrons and the positively charged metal ions