What are the three main subatomic particles in an atom?
Protons, neutrons, and electrons
What is an isotope?
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
What are the three common states of matter?
Solid, liquid, and gas
What does the term “latent heat” mean?
The energy required for a substance to change state without changing temperature
What do the rows in the periodic table represent?
Periods — they show how many electron shells an atom has
Where are protons and neutrons located in an atom?
In the nucleus
What is an ion?
An atom that has gained or lost electrons
What happens to particle movement as temperature increases?
The particles move faster and have more kinetic energy
What is the formula for latent heat?
L = Q/m
What do the columns (groups) in the periodic table represent?
Elements with the same number of valence electrons and similar chemical properties
What does the atomic number tell you?
The number of protons in an atom
A carbon atom has 6 protons and 8 neutrons. What is its isotope notation?
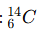
What is the process called when a solid changes directly into a gas?
Sublimation
How much energy is needed to melt 2 kg of ice if the latent heat of fusion is 334,000 J/kg
668000J
What are the elements on the far right of the periodic table called?
Noble gases
If an atom has 11 protons and 10 electrons, what is its overall charge?
+1
Sodium forms an ion with a +1 charge. What happened to its electrons?
It lost one electron
Explain what happens to temperature during melting or boiling.
Temperature stays constant while the substance changes state
Why does temperature not increase while a substance is melting?
Energy is used to break intermolecular bonds, not increase kinetic energy
Why are the alkali metals (Group 1) very reactive?
They have one valence electron that is easily lost
Explain why atoms are electrically neutral.
Because they have an equal number of protons (positive) and electrons (negative)
Chlorine has two common isotopes: Cl-35 and Cl-37. The average atomic mass is 35.45 amu. Which isotope is more abundant?
Cl-35 (because the average is closer to 35)
Compare the particle arrangement and movement in solids, liquids, and gases.
Solids – tightly packed, vibrate; Liquids – close but slide past; Gases – far apart, move freely
Water has a latent heat of vaporization of 2.26×10^6 J/kg. How much heat is needed to evaporate 0.5 kg of water?
1.13 x 10 ^6 J
Explain why elements in the same group have similar chemical properties.
They have the same number of valence electrons, causing similar bonding behavior