The energy change when an electron is added to a gaseous atom
What is electron affinity?
The lewis symbol for an atom with the electron configuration [Ne]3s23p4 is
What is  ?
?
*The element is sulfur with 6 valence electrons.
the charge the atom would have if each bonding electron pair in the molecule were shared equally between its two atoms.
What is the formal charge?
*FC = = valence electrons - 1/2 bonding electrons - nonbonding electrons
Used to predict the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms
What is the VSEPR Theory?
Suppose a Lewis structure for neutral fluorine-containing molecule results in a formal charge of +1 on the fluorine atom. What conclusion would you draw?
What is that there is probably a better choice of Lewis structure than the one chosen?
Explanation: Because the formal charges must add up to 0 and the formal charge on the F atom is +1, there must be another atom that has a formal charge of -1. Because F is the most electronegative element, we don’t expect it to carry a positive formal charge.
This analogy can be referred to what kind of phenomenon?
What is the effective nuclear charge? (Zeff = Z - S)
Explanation: The amount of light seen by the observer depends on the intensity of the light bulb and the screening by the frosted glass lampshade. Effective nuclear charge (Zeff) indicates the net positive charge a valence electron experiences in an atom
the energy required to completely separate one mole of a solid ionic compound into its gaseous ions
What is lattice energy?
The sulfate ion, SO4 2-, can be drawn in many ways. If you minimize formal charge on the sulfur, how many S-O double bonds should you draw in the lewis structure?
What is 2?

Suppose a particular AB3 molecule has a resonance structure  How many electron domains are there around the A atom?
How many electron domains are there around the A atom?
What are four electron domains?
*Two single bonds, one double bond, and one nonbonding electron domain around A. A bonding pair of electrons thus defines a region in which the electrons are most likely to be found. We will refer to such a region as an electron domain. The arrangement of electron domains about the central atom of an ABn molecule or ion is called its electron-domain geometry.
In contrast, the molecular geometry is the arrangement of only the atoms in a molecule or ion—any nonbonding pairs in the molecule are not part of the description of the molecular geometry.
How does the electronegativity of an element differ from its electron affinity?
What is electron affinity measures the energy released when an isolated atom gains an electron to form a 1- ion and has units of energy. Electronegativity has no units and is the ability of the atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself within that molecule?
Consider S, Cl, and K and their most common ions. (a) List the ions in order of increasing size. (b) Explain any differences in the orders of the atomic and ionic sizes.
What is K+ < Cl- < S2 - & The neutral K atom has the largest radius because the n-value of its outer electron is larger than the n-value of valence electrons in S and Cl. The K+ ion is the smallest because, in an isoelectronic series, the ion with the largest Z has the smallest ionic radius.
one of the atoms exerts a greater attraction for the bonding electrons than the other is known as a
What is a Polar Covalent Bond?
*If the difference in relative ability to attract electrons is large enough, an ionic bond is formed.
As the number of bonds between the carbon atoms increases, the bond length ______, and the bond enthalpy ________
What is decrease and increase?
Explanation: That is, the carbon atoms are held more closely and more tightly together. In general, as the number of bonds between two atoms increases, the bond grows shorter and stronger. Bond order can be done: the higher the bond order, the shorter the length of the bonds & the stronger.
Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular geometry of (a) O3, (b) SnCl3 -.
What are bent and trigonal-pyramidal?
To predict the molecular geometries, we draw their Lewis structures and count electron domains around the central atom to get the electron-domain geometry. We then obtain the molecular geometry from the arrangement of the domains that are due to bonds
Explanation: Two of the domains are from bonds, and one is due to a nonbonding pair. So, the molecular geometry is bent with an ideal bond angle of 120° for O3. s. A tetrahedral electron-domain geometry with three bonding and one nonbonding domains leads to a trigonal-pyramidal molecular geometry for SnCl3 -.
Although I3 - is a known ion, F3 - is not. (a) Draw the Lewis structure for I3 - (it is linear, not a triangle). (b) A classmate says F3 - does not exist because it would violate the octet rule. Is this classmate possibly correct?
What is a  and no the classmate is wrong?
and no the classmate is wrong?
Explaination: Tha capability of atoms to form does not rely on atomic radius. Instead on the number of valence electrons and atomic orbitals present, F does not have an available d orbital thereby cannot contain the extra valence electrons.
The equation for the 3rd IE of Bromine
What is Br²⁺ (g) → B³⁺ (g) + e⁻?
*Write out the first & second Ionization NRG equations.
Arrange the ionic compounds NaF, CsI, and CaO in order of increasing lattice energy?
What is CsI < NaF < CaO?
Explanation: the larger the ionic charges, the greater the energy, and & the farther apart the ions are, the lower the energy.
NaF consists of Na+ and F- ions, CsI of Cs+ and I - ions, and CaO of Ca2+ and O2- ions. Because the product Q1Q2 appears in the numerator of electrostatic PE equation the lattice energy increases dramatically when the charges increase. Thus, we expect the lattice energy of CaO, which has 2+ and 2- ions, to be the greatest of the three.
The ionic charges are the same in NaF and CsI. The difference in their lattice energies thus depends on the difference in the distance between ions in the lattice. Following the ionic radius trend with regards to the respective ions: the distance between Na+ and F- ions in NaF is less than the distance between the Cs+ and I- ions in CsI. As a result, the lattice energy of NaF should be greater than that of CsI.
Three possible Lewis structures for the thiocyanate ion, NCS-, are below. Which is the dominant Lewis structure?
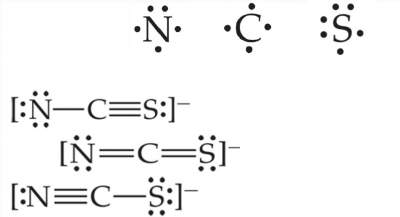
What is the second one?
Explanation: The dominant Lewis structure is generally the one in which the atoms bear formal charges closest to zero. & A Lewis structure in which any negative charges reside on the more electronegative atoms is generally more dominant than one that has negative charges on the less electronegative atoms.
N is more electronegative than C or S, therefore, we expect any negative formal charge to reside on the N atom.
A certain AB4 molecule has a square-planar molecular geometry. Which of the following statements about the molecule is or are true?
(i)The molecule has four electron domains about the central atom A.
(ii) The B¬A¬B angles between neighboring B atoms are 90°.
(iii) The molecule has two nonbonding pairs of electrons on atom A.
What is all true?
Explain:
The square planar geometry is the geometry in which the four groups are connected through an angle of 90∘ and all 5 atoms are in one plane.
It is not necessary for the molecule to have two non bonding pair of electrons on atom A but if it does have , then its parent geometry will be distorted octahedral. And if it doesn't have this non bonding pair of electrons then the geometry would be the square planar.
Thus the molecule has four electron domains about the central atom A.
Draw the Lewis structure for molecules or ions, and predict their electron-domain and molecular geometries: BrO2-
What is 2 and bent? 
Is this possible: Ar(g) + e- ----> Ar-(g)
What is no?
Explanation: The greater the attraction between an atom and an added electron, the more negative the atom’s electron affinity. For some elements, such as the noble gases, the electron affinity has a positive value, meaning that the anion is higher in energy than are the separated atom and electron. The fact that the electron affinity is positive means that an electron will not attach itself to an Ar atom; in other words the Ar- ion is unstable and does not form.
Predict the formula of the stable binary compound (a compound composed of two elements) formed when nitrogen reacts with fluorine and draw its Lewis structure
What is 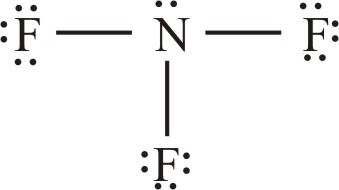 ?
?
Explanation: nitrogen has five valence electrons and fluorine has seven. We need to find a combination of the two elements that results in an octet of electrons around each atom. Nitrogen requires three additional electrons to complete its octet, and fluorine requires one. Sharing a pair of electrons between one N atom and one F atom will result in an octet of electrons for fluorine but not for nitrogen. We, therefore, need to figure out a way to get two more electrons for the N atom.
Therefore: Nitrogen must share a pair of electrons with three fluorine atoms to complete its octet. Thus, the binary compound these two elements form must be NF3
Which of these compounds is an exception to the octet rule: carbon dioxide, water, ammonia, phosphorus trifluoride, or arsenic pentafluoride?
What is AsF5 is an exception to the octet rule?
Explanation: exceptions to the octet rule are of three main types: 1. Molecules and polyatomic ions containing an odd number of electrons 2. Molecules and polyatomic ions in which an atom has fewer than an octet of valence electrons 3. Molecules and polyatomic ions in which an atom has more than an octet of valence electrons.
Predict whether these molecules are polar or nonpolar: (a) SO2, (b) SF6
What is polar, and nonpolar?
Explain: Because oxygen is more electronegative than sulfur, SO2 has polar bonds. For each of these, the VSEPR model predicts a bent molecular geometry. Because the molecule is bent, the bond dipoles do not cancel, and the molecule is polar
(b) Fluorine is more electronegative than sulfur, so the bond dipoles point toward fluorine. For clarity, only one S¬F dipole is shown. The six S¬F bonds are arranged octahedrally around the central sulfur. Because the octahedral molecular geometry is symmetrical, the bond dipoles cancel, and the molecule is nonpolar.
Phosgene, a substance used in poisonous gas warfare during World War I, is so named because it was first prepared by the action of sunlight on a mixture of carbon monoxide and chlorine gases. Phosgene has the following elemental composition: 12.14% C, 16.17% O, and 71.69% Cl by mass. Its molar mass is 98.9 g/mol. Draw three Lewis structures for the molecule that satisfy the octet rule for each atom. (The Cl and O atoms bond to C.) Using formal charges, determine which Lewis structure is the dominant one.
What is  & the first is the most dominant?
& the first is the most dominant?
Explanation: The first structure is expected to be the dominant one because it has the lowest formal charges on each atom.
Assuming 100g of the substance: The ratio of the number of moles of each element indicates that there is one C and one O for each two Cl in the empirical formula, COCl2. The molar mass of the empirical formula is 98.91 g/mol, the same as the molar mass of the molecule. Thus, COCl2 is the molecular formula
True or False:
1.) Oxygen has larger first ionization energy (IE) than fluorine.
2.) The second IE of an atom > the first IE.
3.) The third IE is the NRG needed to ionize three e- from a neutral atom.
What is False, True, False.
Explanation: First IE strips away an electron from a neutral to become a cation whereas in the second IE an electron is stripped away from the cation to become more positive releasing another electron. The cation will hold electrons more tightly resulting in higher IE. IE is a sequential process so the last statement is false.
For the molecule with the chemical formula C2H3N, where the N is connected to only one other atom. How many double bonds are there in the correct Lewis structure?
What is zero?
*HONC rule allows you to determine how many bonds you expect. For hydrogen it's 1, O is 2, N is 3, & C is 4.

True or false: (a) The C¬C bonds in benzene are all the same length and correspond to typical single C¬C bond lengths. (b) The C¬C bond in acetylene, HCCH, is longer than the average C¬C bond length in benzene.
What is false and false?
Explanation: C-C bonds in benzene are between the length of a single and a double bond, so they are not as long as a single bond. The length of the bond in acetylene (a triple bond) is smaller.
Predict the H-C-H and C-C-C bond angles in propyne:
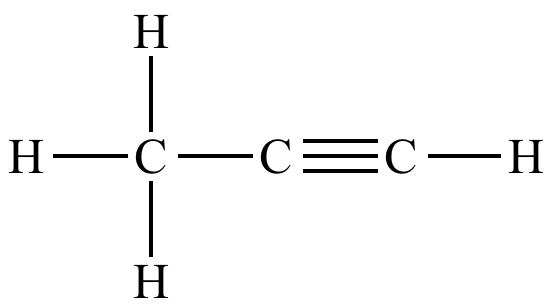
What are 109.5° and 180°?
Ammonium chloride, NH4Cl, is a very soluble salt in water, is there an N—Cl bond in solid ammonium chloride? (b) If you dissolve 14 g of ammonium chloride in 500.0 mL of water, what is the molar concentration of the solution? (c) How many grams of silver nitrate do you need to add to the solution in part (b) to precipitate all of the chlorides as silver chloride?
What is no N-Cl bond, 0.52M, 44.5g AgNO3?
Explanation: There are 2 types of bonds in ammonium chloride. One is covalent between N and H, The other is an ionic bond between NH4+ & Cl-. convert grams to moles, know that concentration is moles/liter or molarity. (c) Rxn between ammonium chloride and silver nitrate is represented by the balanced equation: AgNO3(aq) + NH4Cl(aq) -----> AgCl (s) + NH4NO3(aq). Find moles of NH4Cl present in soln (14g / 53.5g/mol = 0.2617 moles) and then multiply this by the molar mass of silver nitrate = 44.5g.