What happens when light at a specific wavelength is absorbed by an atom?
An electron jumps to a higher energy level
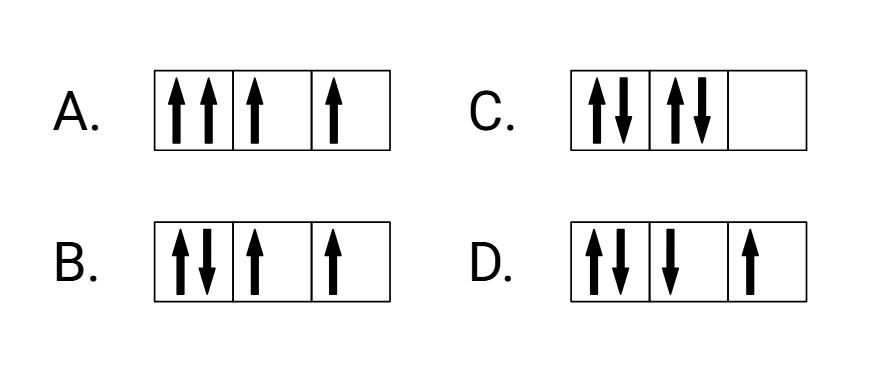
Which of the following box configurations is the correct way to place 4 electrons in a p subshell?
What is B?
The direction on the periodic table that indicates increasing atomic size.
What is down and to the left?
Describe Lattice Energy
What is the energy required to break apart an ionic compound into gaseous ions?
This type of bonding involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
What is ionic bonding?
As frequency of light increases, what happens to the energy and wavelength?
What is energy increases and wavelength decreases?
What is the noble gas configuration of Hg? How many inner, outer, and valence electrons does Hg have?
[Xe] 6s2 4f14 5d10
78 inner electrons
2 outer electrons
2 valence electrons
How do the sizes of anions and cations compare to that of the neutral atom?
Anions are larger and cations are smaller than the neutral atom.
The direction on the periodic table that indicates increasing (more negative) electron affinity.
What is up and to the right?
Estimate the molar absorptivity (units of 1/(M*cm)) of the substance (path length is 1 cm)
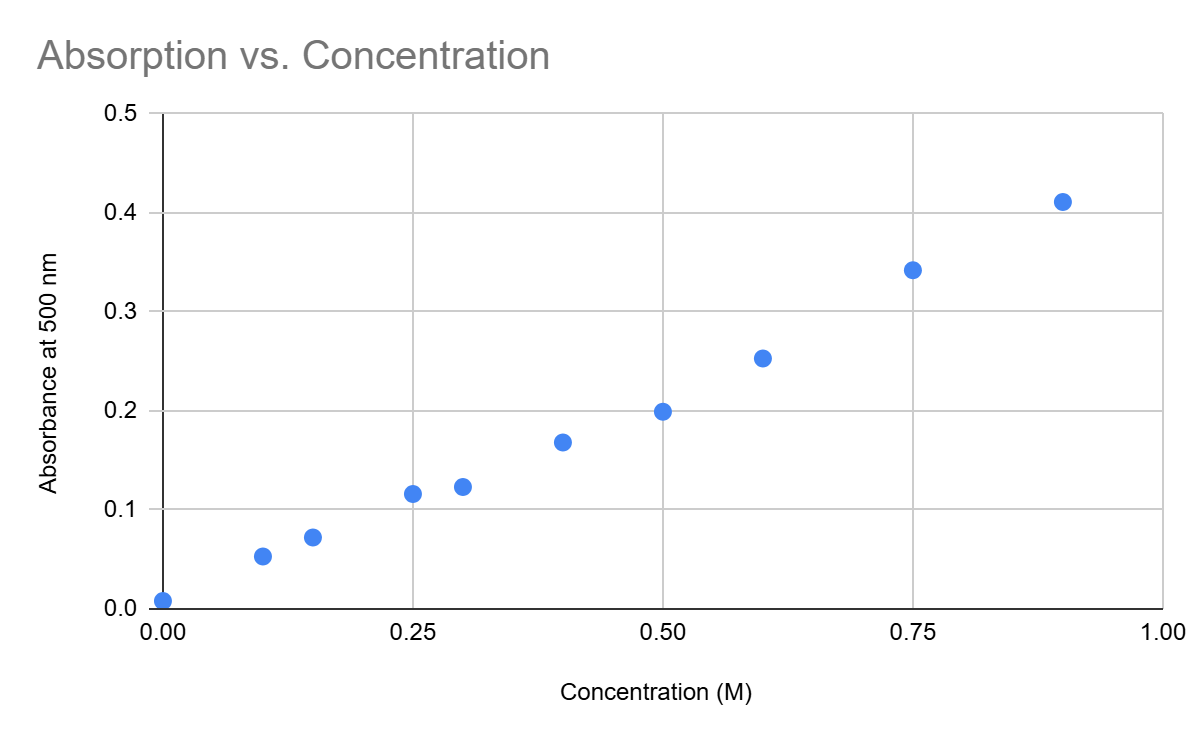
What is approximately 0.47 1/(M * cm)
An X-ray has a frequency of 1018 Hz and a radio wave has a frequency of 106 Hz. Compare the wavelength of the two waves.
X-ray: 3 * 10-10 m
Radio: 300 m
The possible values of l and ml when n = 3.
What are l = 0, 1, 2 and ml = -2, -1, 0, 1, 2?
Which of the following atoms is the largest?
P, Br, Cl, O, As
What is As?
Given these ionization energies, identify the atoms:
Atom 1: IE1 = 899.5, IE2 = 1757.1, IE3 = 14848.7, IE4 = 21006.6
Atom2: IE1 = 495.8, IE2 = 4562, IE3 = 6910.3, IE4 = 9543
a. Ca, Li
b. Be, Na
c. O, S
d. Rb, K
What are Be and Na?
Describe the properties of metals.
What are shiny, malleable, ductile, good conductors, reducing agents, and form basic oxides?
Why can hydrogen only emit 4 wavelengths of visible light?
Quantization of energy and energy levels only allow for specific energy changes.
A given atom has 20 electrons. How many electrons have n = 2, l = 1, and ml = -1?
What are 2 electrons?
Which of these ions is not in the isoelectronic set?
B+, Li-, Be, C2+, N3-
What is N3-?
Order these salts by increasing lattice energy:
NaCl, MgO, KI, LiF
What is KI < NaCl < LiF < MgO?
Which of these electron configurations is the most paramagnetic?
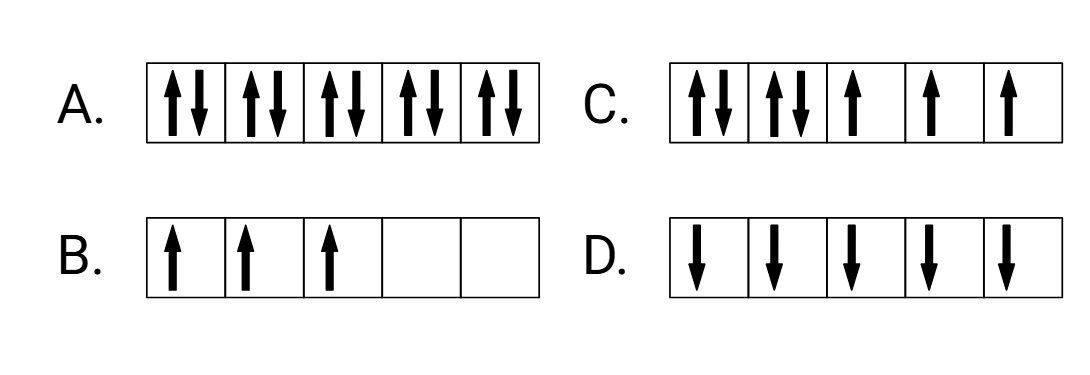
What is D?
Visible light has a range of wavelengths from 400. nm to 700. nm. What is the range of energy for visible light?
Energy ranges from 2.84 * 10-19 J to 4.97 * 10-19 J
The electron configuration of Sn and Sn4+.
Sn: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p2
Sn4+: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 4d10
Order these sets of atoms and ions from smallest to largest:
K+, S2-, Cl-, Ar
Sr2+, Sr+, Sr
What are
K+ < Ar < Cl- < S2-
and
Sr2+ < Sr+ < Sr
Write the chemical reaction associated with the 3rd ionization energy of Oxygen.
What is O2+ --> O3+ + e-?
The electron configuration of Ag
What is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s1 4d10?