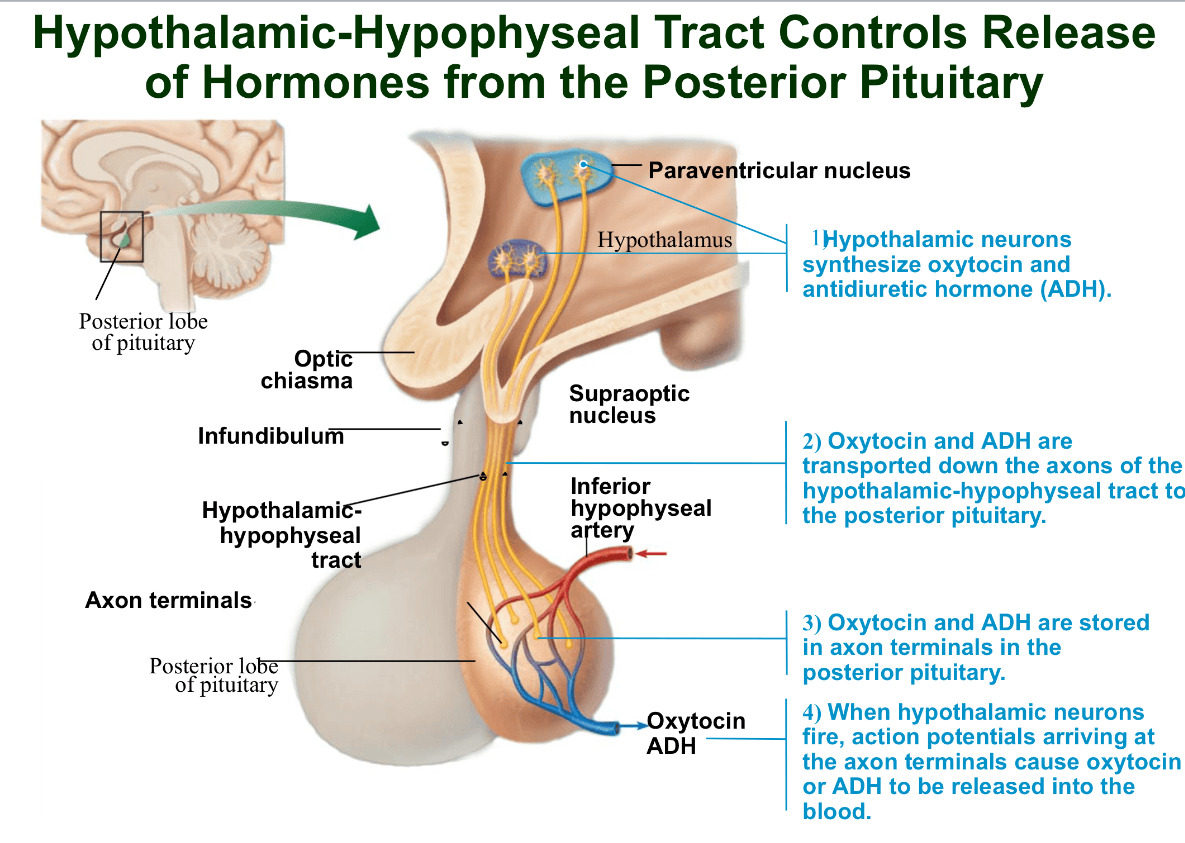
Explain the hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract
Neurons that run through the infundibulum and connect the hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary.
Originates in 2 hypothalamic nuclei(remember nuclei are a collection of neurons that make up grey matter in the CNS)
paraventricular nucleus: produced oxytocin
supraoptic nucleus: produced ADH
both ADH and oxytocin are stored in the axon terminal of the post pituitary until an action potential triggers its release into the bloodstream
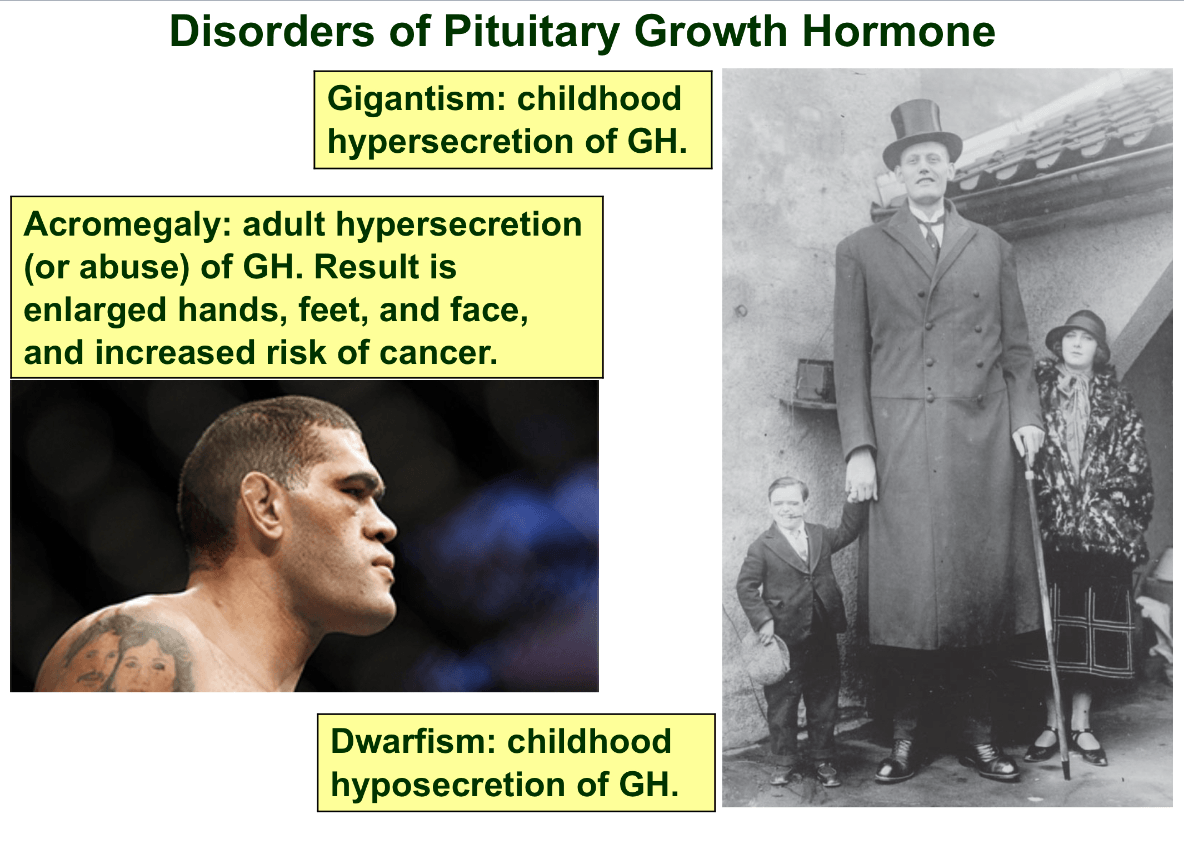
Explain the differences between gigantism, acromegaly and dwarfism
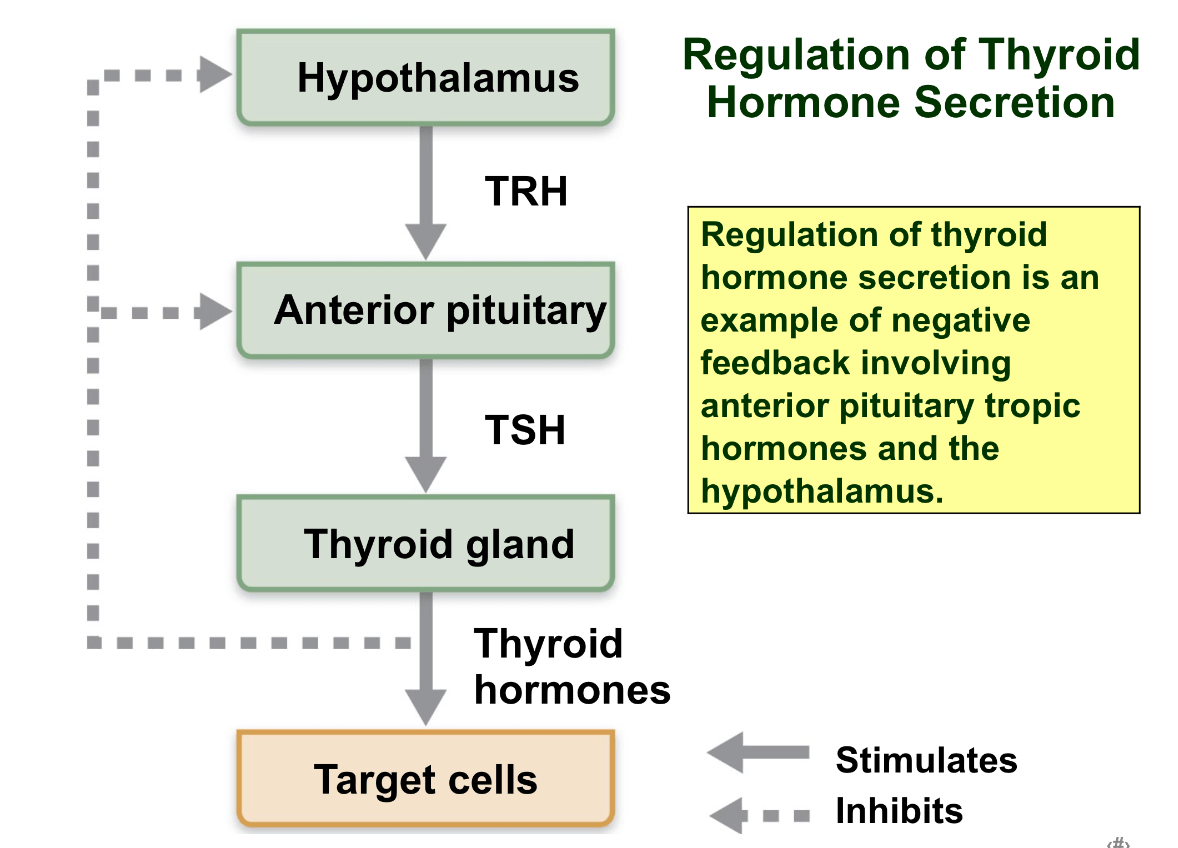
What does the thyroid hormone effect?
Increasing BMR and body heat production, regulating tissue growth and development(esp in the skeletal, nervous and reproductive systems), increasing number of adrenergic receptors in blood vessels which helps maintain blood pressure and enhance sympathetic nervous system.
This patient has developed a large lump on his throat as seen below. What is the cause of this lump?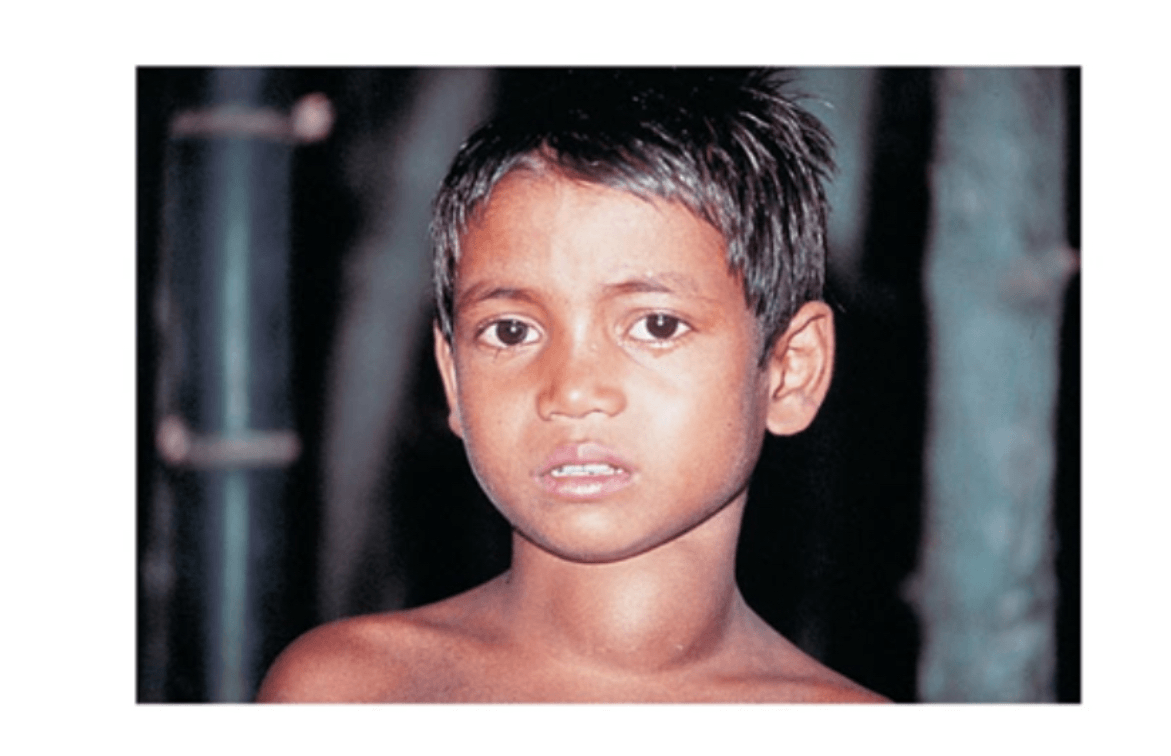
This is a goiter(enlarged thyroid) caused by a lack of iodine. Remember that iodine plus thyroglobulin forms a long term storage form of TH. However, a lack of iodine does not allow TH to be formed properly. TH works as a negative feedback mechanism when it binds to receptors in the ant pituitary to prevent more TSH from being made. If there's no TH because there is no iodine, then TH cannot act in the negative feedback loop, causing excess TSH being released from the anterior pituitary.
Also known as vasopressin, this hormone inhibits urine formation by causing kidney tubules to reabsorb more water thus promoting water balance and hydration. This hormone is also stimulated by low BP and pain.
ADH(antidiuretic hormone)
Explain the layers of the adrenal glands from superficial to deep
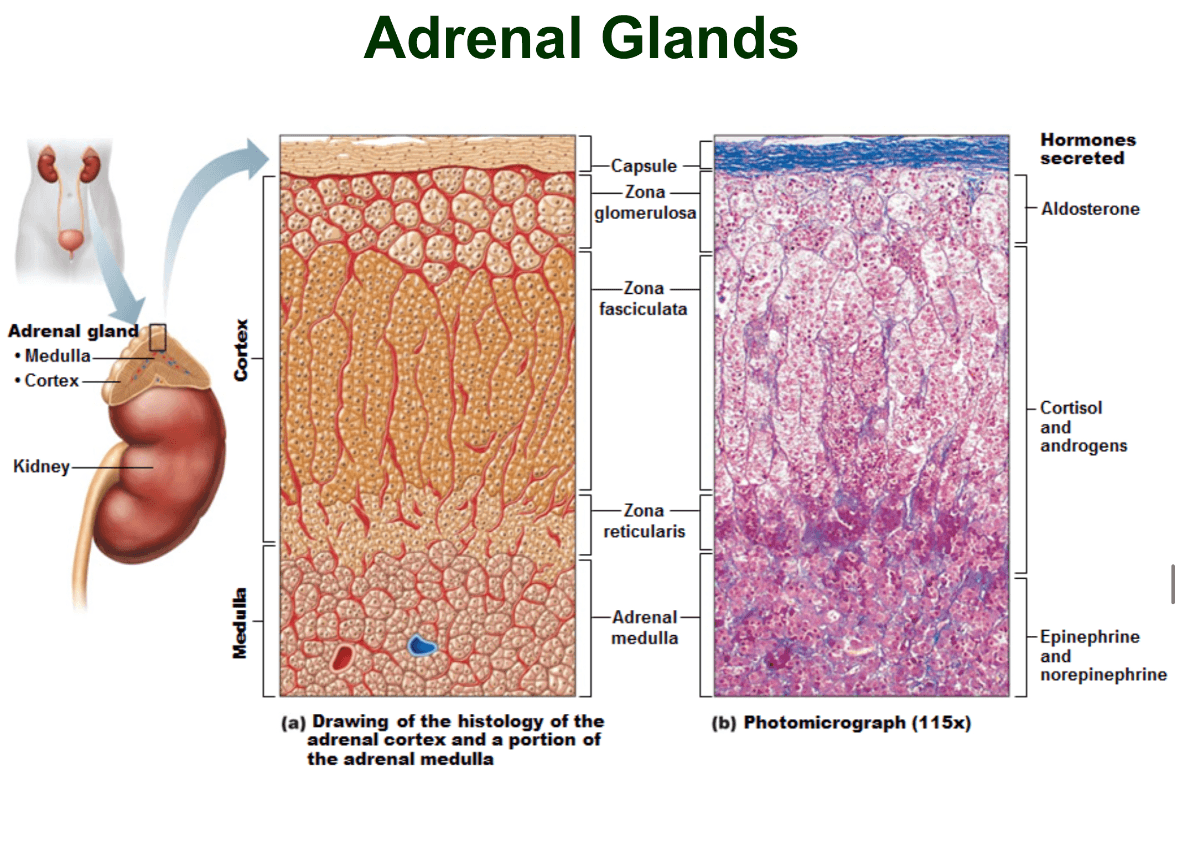
Produced by zona reticularis, effects promote muscle mass, bone density, secondary sexual characteristics and sex drive. Mostly androgens but provide primary source of estrogen for post menopausal women. Hypersecretion can cause masculinization and increased body hair
Gonadocorticoids from the zona reticularis
the adrenal cortex produced low levels of sex hormones(estrogen and testosterone) in both males and females
This substance acts as a diuretic by inhibiting ADH secretion which leads to increased urinated and dehydration
Alcohol
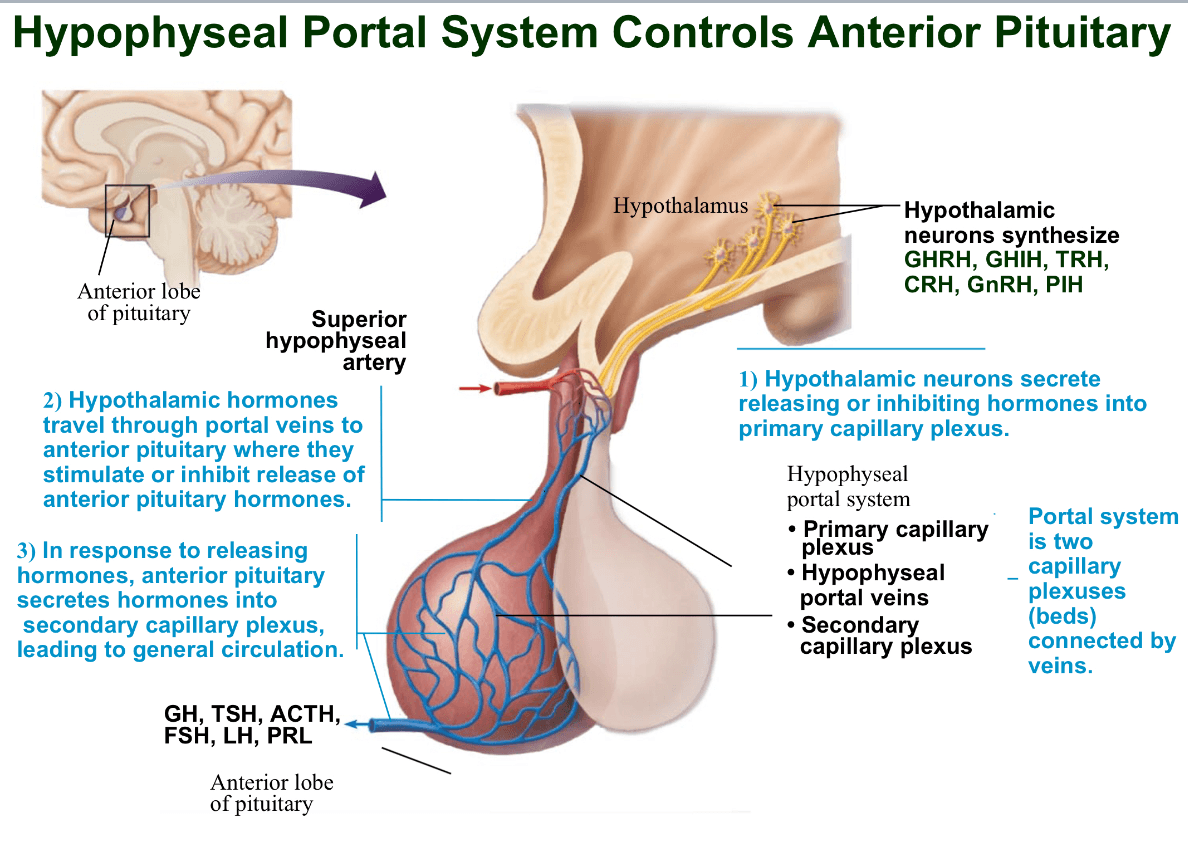
What is the hypophyseal portal system
a vascular connection between the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary. hypophyseal portal veins connected a primary capillary plexus in the infundibulum to a secondary capillary plexus in the anterior pituitary
releasing and inhibiting hormones from the ventral hypothalamus travel through this system and into the anterior pituitary
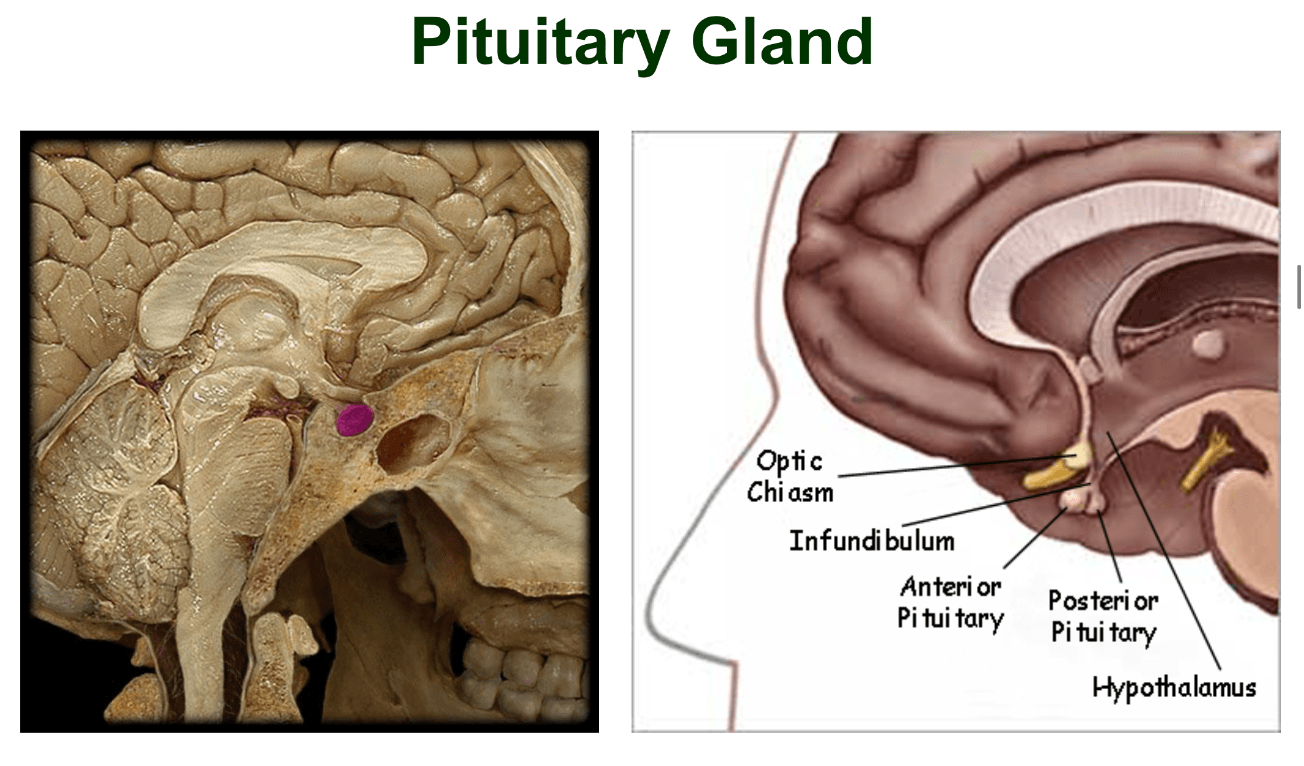
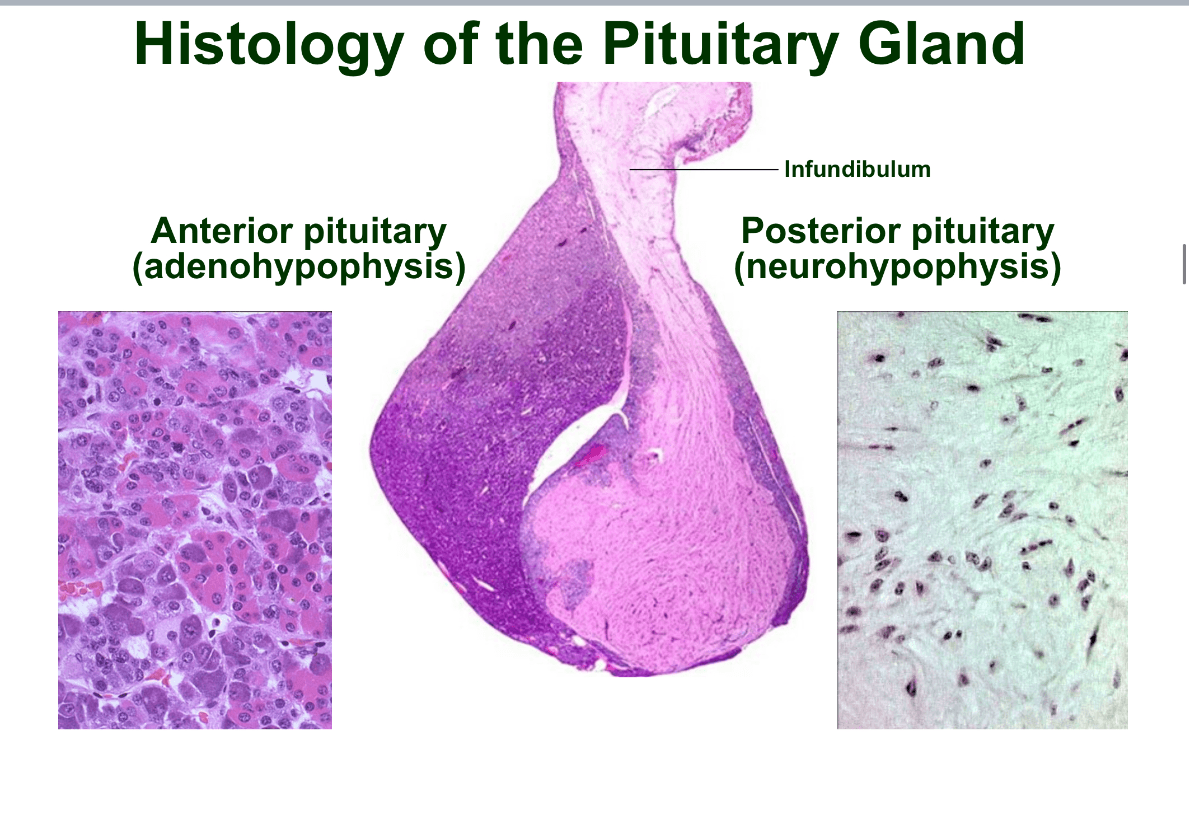
This gland is located in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone. It is the master endocrine gland because it influences other endocrine organs. It is also controlled by the hypothalamus and connected to it by the infundibulum. What is the gland?
Pituitary gland
consists of 2 lobes:
1. posterior pituitary plus the infundibulum is the neurohypophysis(neural tissue that arises from the hypothalamus during development, storage for 2 neurohormones produced by the hypothalamus.)
2. anterior pituitary aka the adenohypophysis(glandular tissue that produces and secretes numerous hormones)
This tropic hormone stimulates milk production in the breasts. What is it inhibited by? What stimulates its release
Prolactin
Inhibited by prolactin inhibiting hormone from the hypothalamus
Elevated estrogen levels as well as infant suckling after birth stimulates prolactin release
Adrenocorticotropic hormone or corticotropin is a tropic hormone released by the anterior pituitary that stimulates the adrenal cortex to release corticosteroids including glucocorticoids that help to resist body stressors.
ACTH is controlled by corticotropin releasing hormone(CRH) from the hypothalamus with levels peaking early in the morning
Rising blood levels of glucocorticoids feedback and inhibit ACTH secretion(negative feedback)
stressors including fever and hypoglycemia trigger CRH release and therefore increased ACTH secretion.
Explain the renin angiotensin aldosterone mechanism
A view of pancreatic tissue
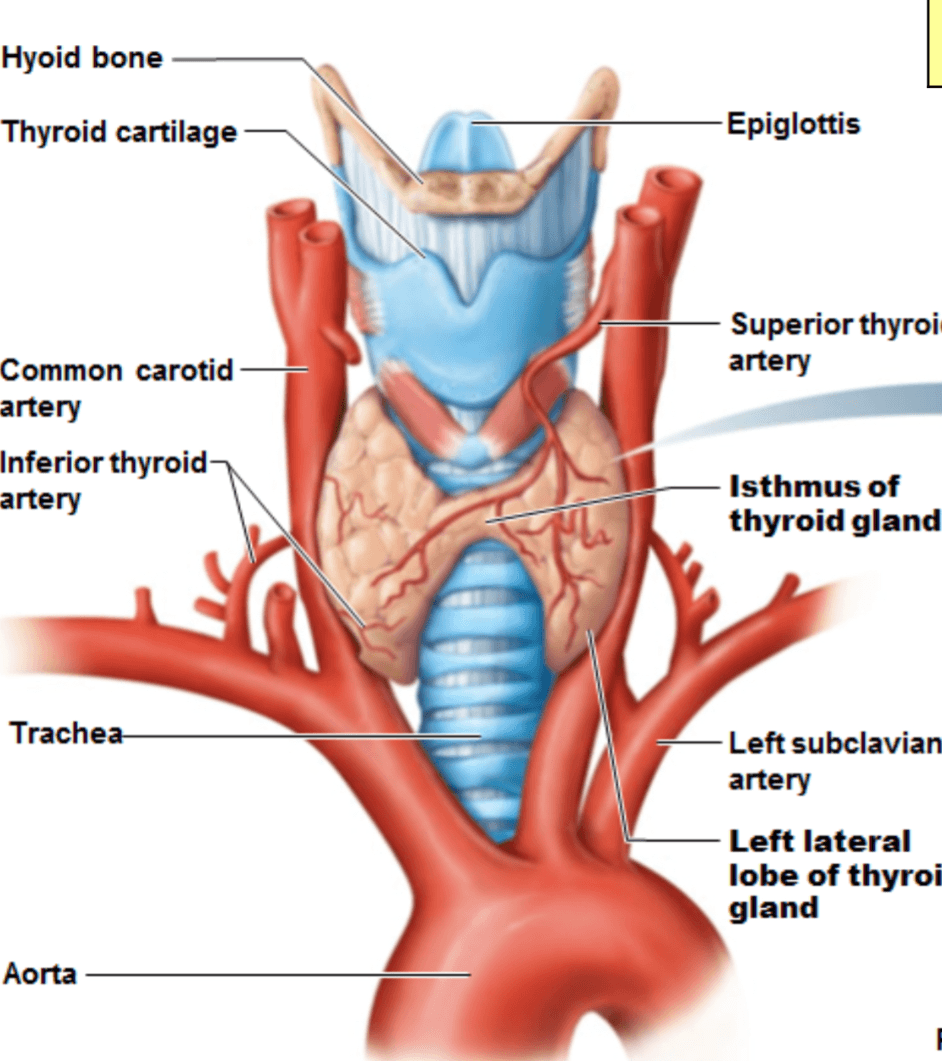
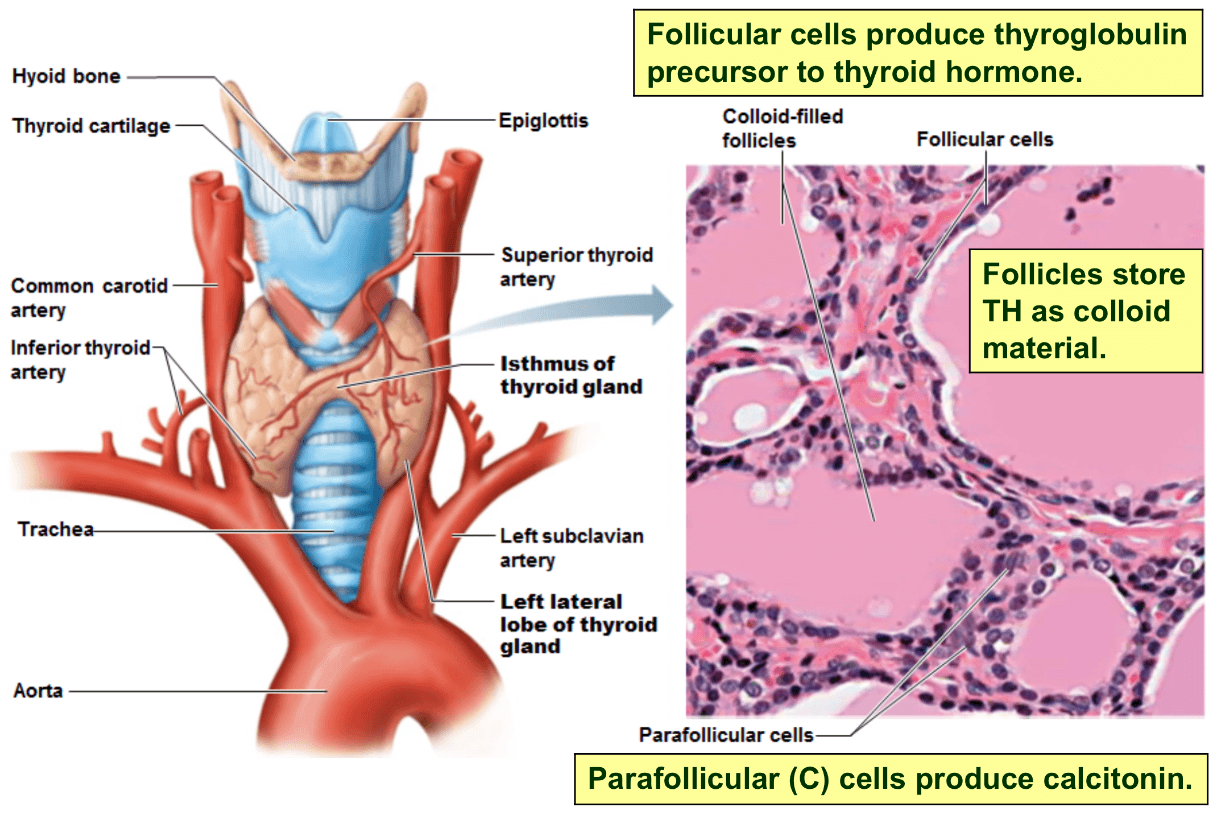
This is the largest pure endocrine gland in the body, located on the trachea inferior to the larynx. Consists of two lateral lobes connected by a median mass called the isthmus.
Thyroid gland
What are follicular cells, colloid and parafollicular cells? Where are they found?
Follicular cells-line extracellular spaces called follicles, they produce thyroglobin(precursor to thyroid hormone)
Colloid-lies within follicles, made of thyroglobin and iodine, which is the long term storage form of thyroid hormone
parafollicular cells or C cells-produce calcitonin and are found between follicles, not along their edges
Jackie is experiencing low metabolic rate, lethargy, edema, chills, constipation and mental sluggishness. What is she suffering from?
Myxedema(hypothyroid disorder)
Explain Graves' disease and the symptoms
Graves' is an autoimmune hyperthyroid condition
LATS or long acting thyroid stimulators are antibodies that act like TSH. They bind to TSH receptors on the thyroid, causing the thyroid to release an excess of T3/T4.
Symptoms include: elevated metabolic rate, sweating, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, weight loss and protruding eyeballs
An ADH deficiency syndrome that includes symptoms of intense thirst and excessive urination
Diabetes insipidus
Elevates blood volume and blood pressure by stimulating sodium reabsorption and water retention by kidneys
also causes elimination of potassium triggered by high blood potassium.
Low blood volume and low BP trigger what mechanism?
Aldosterone
low blood volume and low BP trigger the renin angiotensin aldosterone mechanism
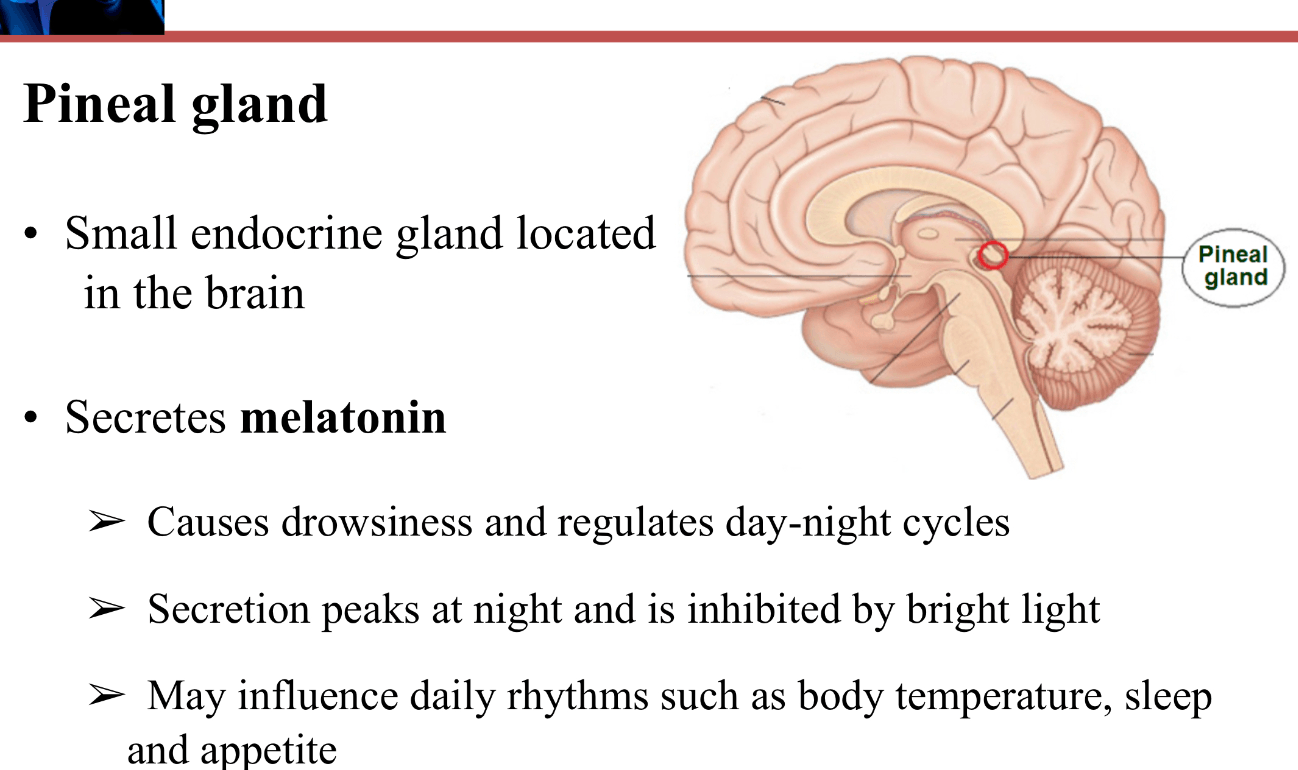
Pineal gland which secretes melatonin
Explain the histology of the pituitary gland
the anterior pituitary is darker than the posterior
These tropic hormones regulate the gonads(ovaries and testes). What controls the release of these tropic hormones
-This hormone stimulates production of gametes
-This hormone promotes production of gonadal hormones
-In females, these tropic hormones control the ovarian cycle
Gonadotropins(follicle stimulating hormone aka FSH and luteinizing hormone aka LH)
-FSH stimulates production of gametes(sperm and eggs)
-LH promotes production of gonadal hormones
Gonadotropin releasing hormone(GnRH) from the hypothalamus stimulates gonadotropin release after puberty
elevated gonadal hormone levels inhibit FSH and LH release(neg feeback)
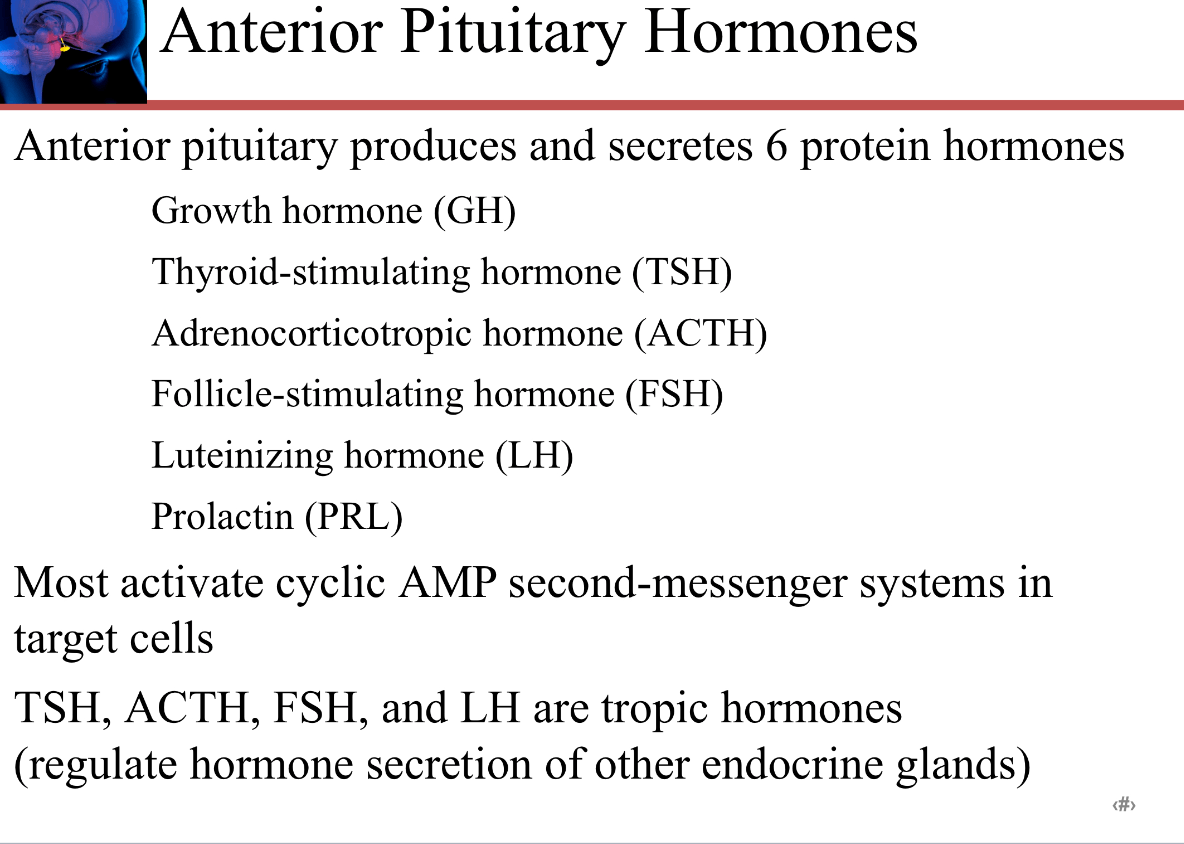
Name the 6 protein hormones that are produced and secreted by the anterior pituitary. Which of them are tropic hormones
This tropic hormone stimulates the development and activity of the thyroid gland. What is it and what is it controlled by?
Thyroid stimulating hormone(thyrotopin)
TSH is controlled by thyroid releasing hormone(TRH) from the hypothalamus
Infant Jack experiences mental retardation, short stature, thick tongue and neck. What is Jack's diagnosis and what is it caused by?
Cretinism
Caused by severe hypothyroidism in infants
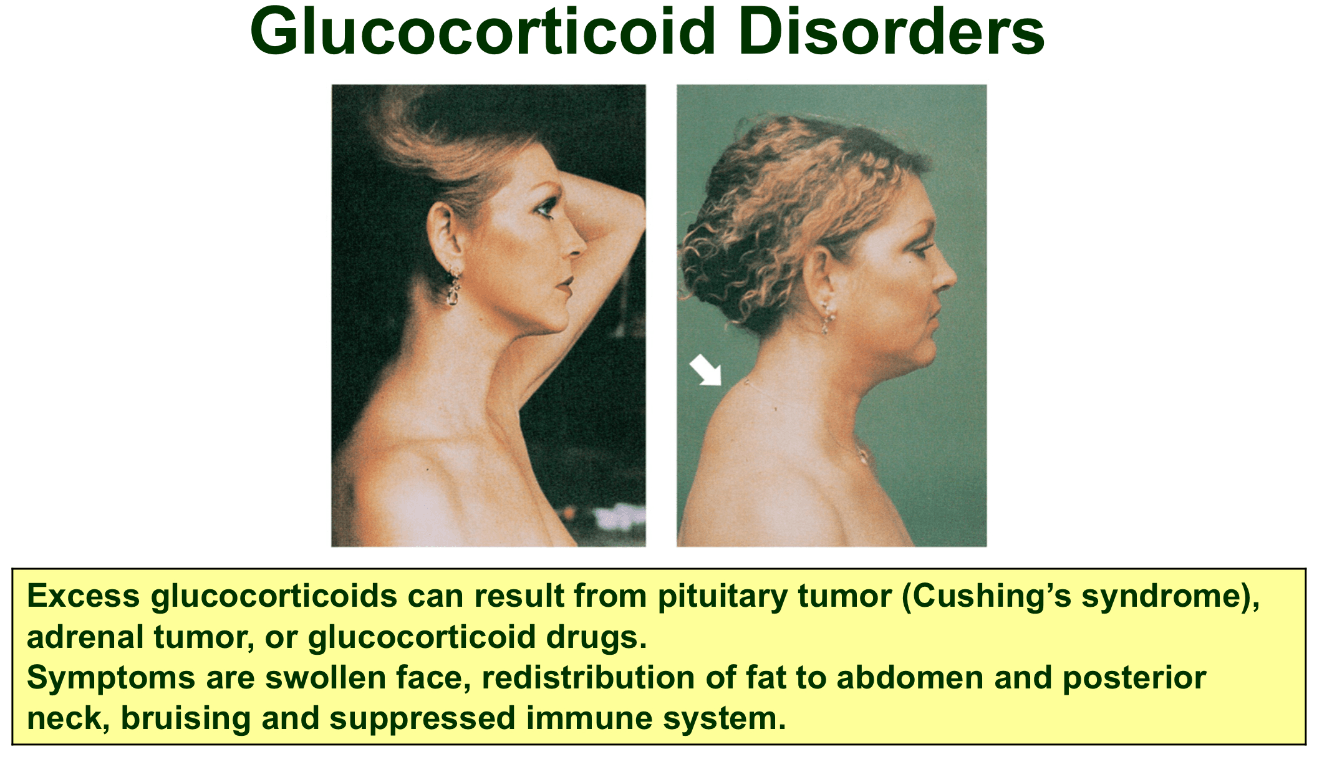
Symptoms include swollen face, redistribution of fat to abdomen and posterior neck, bruising and suppressed immune system. What is the disorder and what is it caused by?
An autoimmune disorder that destroys beta cells of the pancreas resulting in severe insulin deficiency. About 10% of diabetes cases
Type 1 diabetes
Formerly insulin dependent or juvenile diabetes
What is the hormone and where is it released from? Homeostasis of this hormone and its effects are controlled by what?
Growth hormone-from the anterior pituitary
Homeostasis of GH and its effects are controlled by growth hormone releasing hormone(GHRH) and growth hormone inhibiting hormone(GHIH) from the hypothalamus
Explain how ADH is impacted by osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus
Osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus monitor solute and water concentration in the blood. Water follows high solute concentration. So elevated solute concentration would trigger the excitatory impulses in the hypothalamus that stimulate post pituitary to release ADH(since water follows high solute concentration, if a lot of solute is leaving say during urination, water is going to want to move with it. ADH is stimulated to prevent that from happening)
A disorder that results from thyroid defects, inadequate TRH or TSH release or lack of dietary iodine
Hypothyroid disorders
The major metabolic hormone of the body, affecting nearly all cells. This hormone is lipid soluble so it binds to intracellular receptors and directly activates genes. How is this hormone transported into the blood stream and what is it controlled by?
Thyroid hormone: made of 2 amino hormones(thyroxine T4 and triiodothyronine T3)
TH release from the follicles is controlled by thyroid stimulating hormone(TSH)
Since it is not water soluble, TH is transported in the blood by thyroxine binding globulins(TBG)
A short peptide chain of 9 amino acids that is a strong stimulant of uterine contraction during childbirth, stimulates milk ejection during lactation and acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain where it influences social behavior, bonding and affection
Oxytocin
stored in the posterior pituitary until neuronal control causes the post pituitary to release it
This gland synthesizes corticosteroids from cholesterol. What are the layers of this gland from superficial to deep
Adrenal cortex of the adrenal gland
Zona glomerulosa procudes mineralcorticoids
zona fasciculata produces glucocorticoids
zona reticularis produces gonadocorticoids(sex hormones)
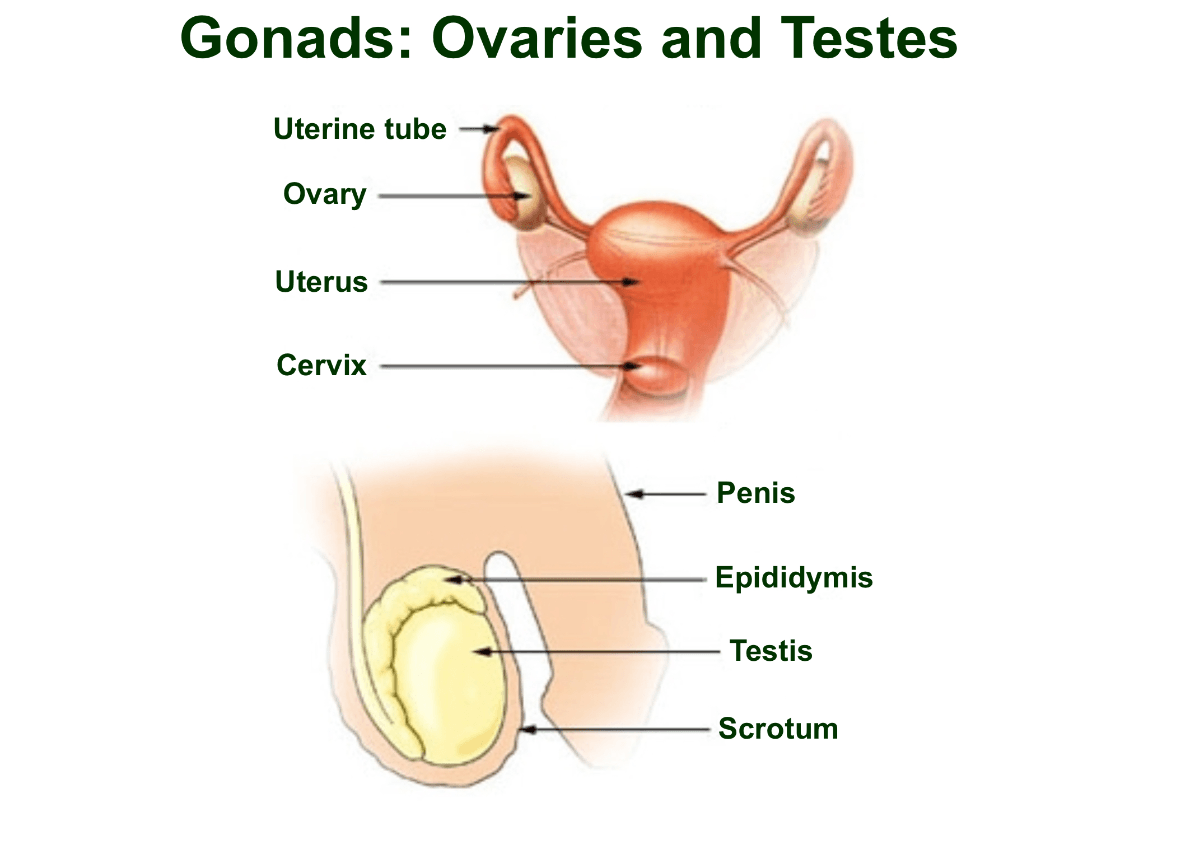
Paired male gonads with both endocrine and exocrine functions. What is it and what makes it have endocrine and exocrine functions?

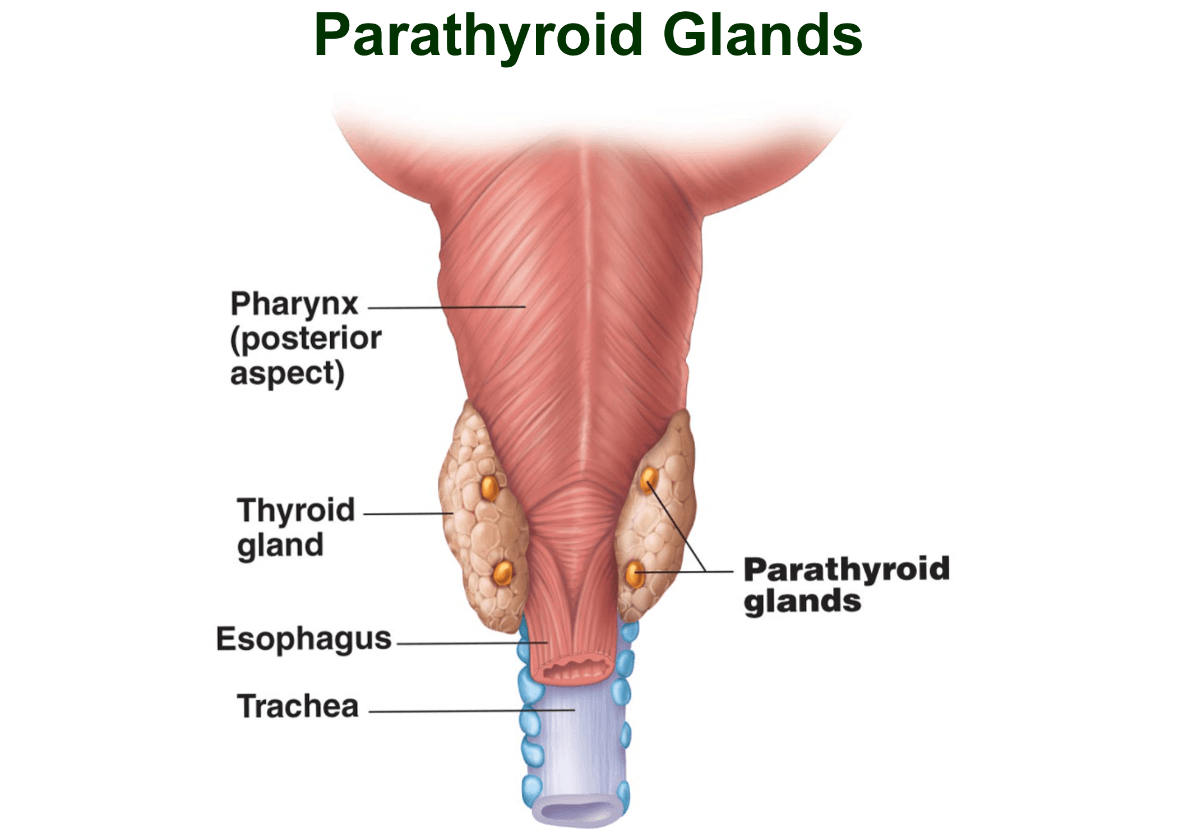
What is the parathyroid gland, what does it secrete?
Parathyroid glands are small tiny glands on the posterior thyroid
secretes parathyroid hormone, in response to low blood calcium levels
stimulates osteoclasts to digest bone matrix, releasing calcium to blood, increases calcium reabsorption by kidney tubules(to reduce the loss of calcium in urine), increases vitamin D activation which functions to increase calcium absorption in the small intestine
increased blood calcium inhibits PTH release
What is the primary mineralcorticoid? What is its function and where is it produced
Aldosterone, produced from the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex
regulates electrolyte concentration in ECF esp sodium and potassium and determines fluid volume of ECF because water following sodium
sodium is the most abundant cation in ECF, changes in sodium cause changes in blood volume and pressure
A deficiency of both glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. Symptoms include weight loss, low blood glucose and sodium, dehydration and low blood pressure
Addison's disease
Produced by parafollicular C cells of the thyroid. What is the hormone and what is it secreted in response to?
Calcitonin
Produced in response to elevated blood calcium levels
-stimulates calcium uptake into bone, inhibits osteoclast activity which leaves calcium in bone matrix
antagonistic to PTH
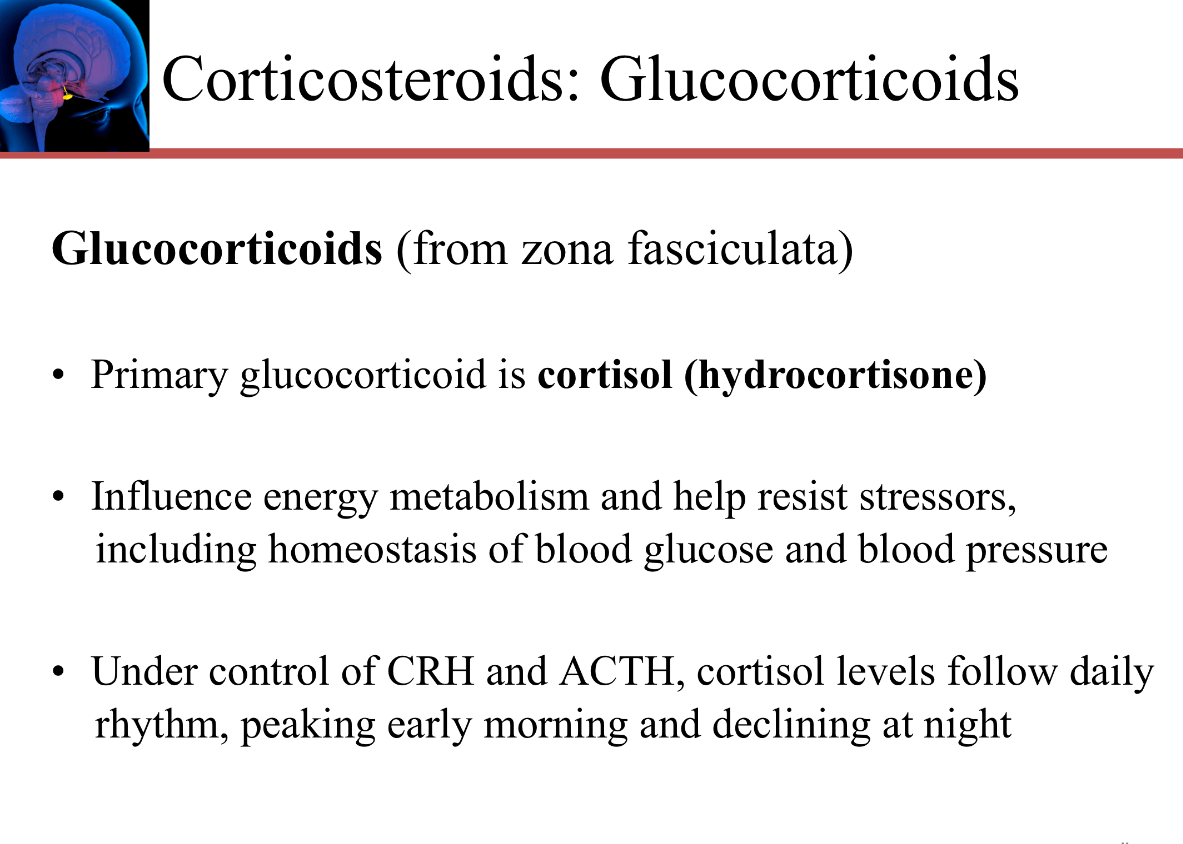
What is the primary glucocorticoid? What is its impact on the body?
Paired female gonads with both endocrine and exocrine functions. What are they and what makes them have endocrine and exocrine functions?

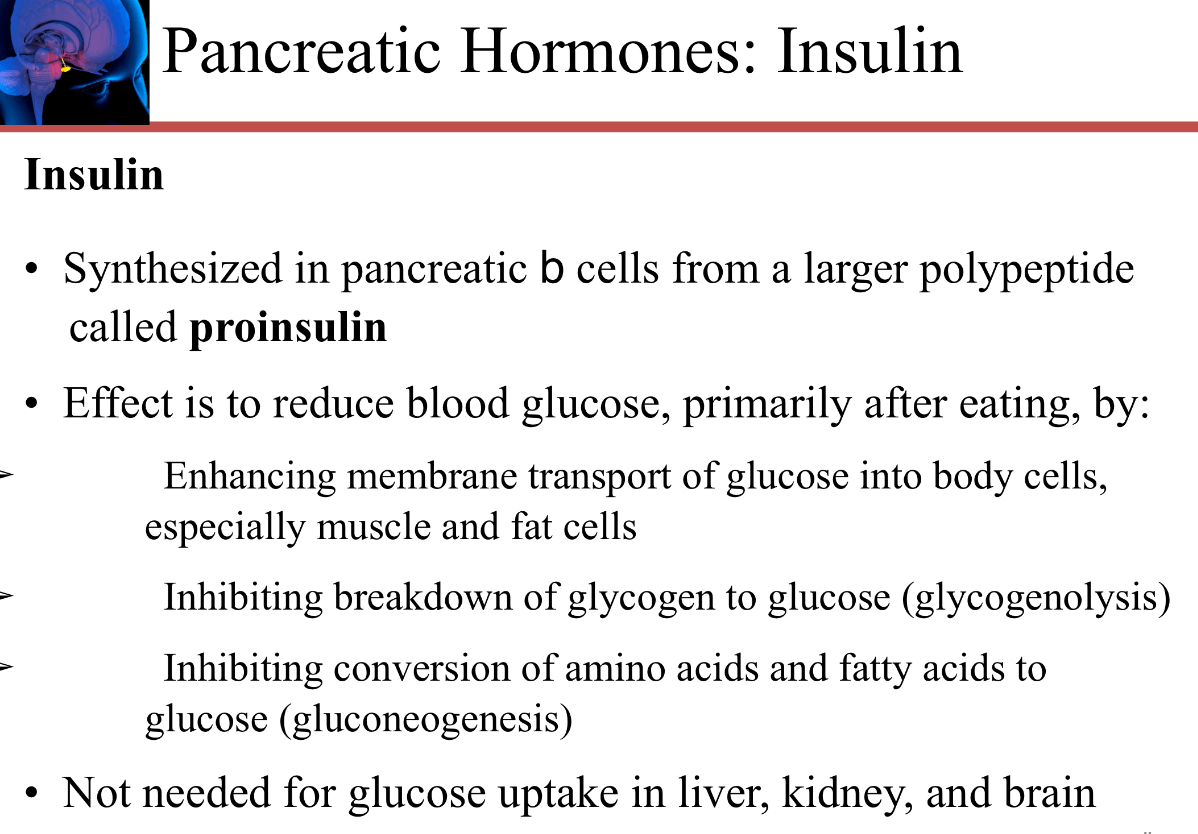
Explain the impact that insulin has on the body

What does the adrenal medulla release? What are its effects?
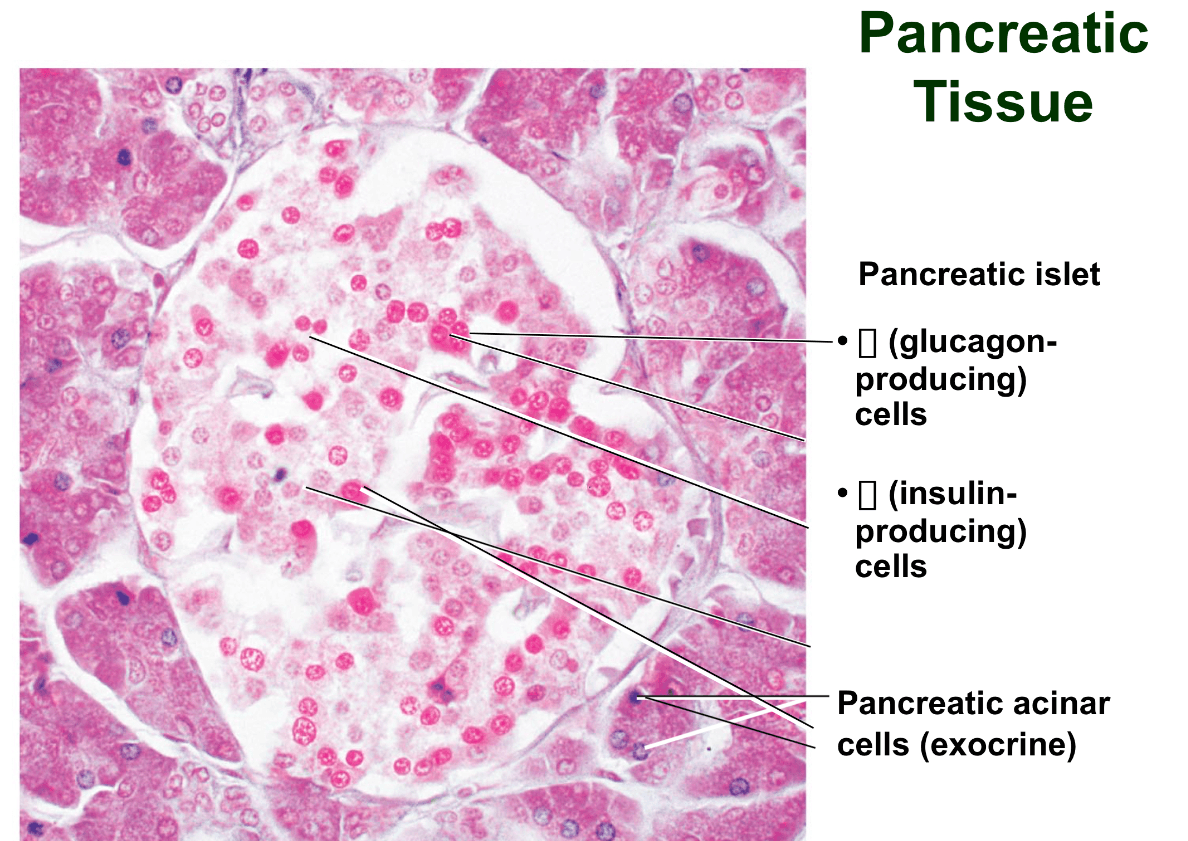
The endocrine and exocrine gland that is located partly behind the stomach. What is the gland and what makes it endocrine and exocrine?

Explain how multiple factors trigger insulin release
Hyposecretion or hypoactivity of insulin.
Body cells fail to uptake glocose after eating
results in high blood glucose
body responds to this with fight or flight response and stress hormones, causing blood glucose to rise even more
Diabetes mellitus
Insulin resistance or lack of sensitivity to insulin. Associated with obesity, excess sugar consumption and lack of exercise. Can be managed by diet and exercise. 90% of diabetes cases
Type 2 diabetes
formerly non insulin dependent or adult onset diabetes
Explain how glucagon impacts blood sugar

Results from excess insulin secretion or overdose. Causes low blood sugar, triggers release of hyperglycemic hormones resulting in anxiety, tremors, weakness and possible loss of consciousness
Hyperinsulinism