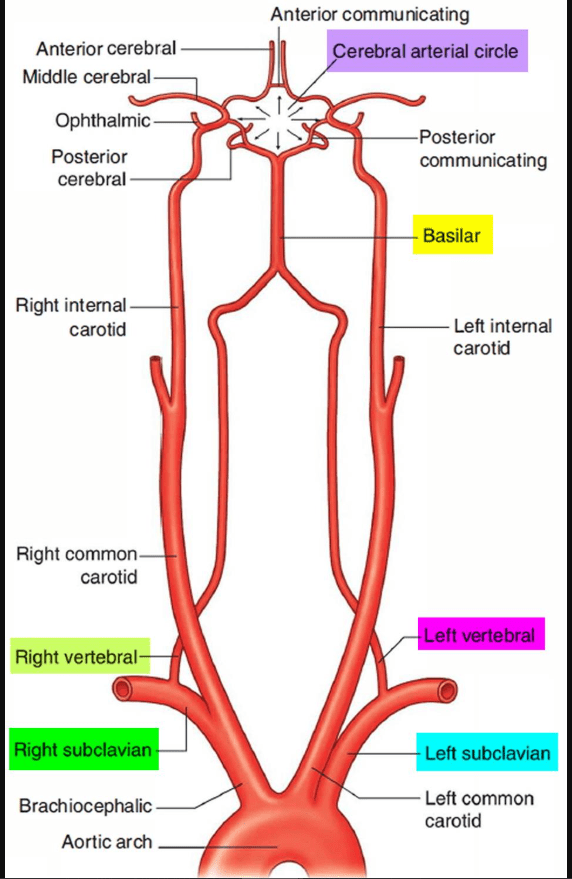
What is #2
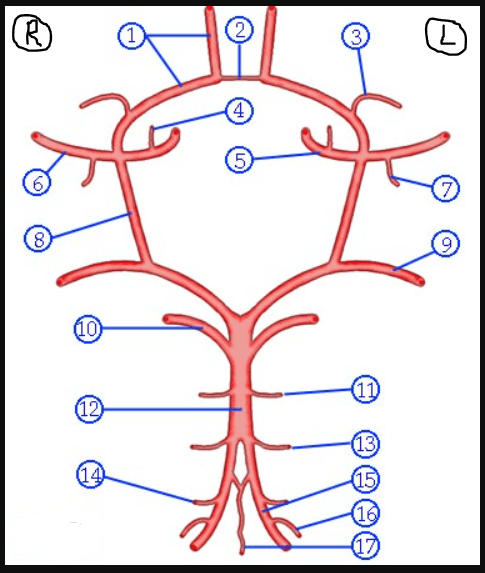
Anterior Communicating Artery (ACoA)
What is #1
Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA)

What is #12
Basilar Artery

What is #9
Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA)

What is #8
Posterior Communicating Artery (PCoA)

What are the AKAs for the Circle of Willis?
Cerebral Arterial Circle
Willis' Circle
Loop of Willis
Willis Polygon
Who is the Circle of Willis named after and what year was it first described?
Physician Thomas Willis
He first described it in 1664
Where is the circle of Willis Located?
At the base of the brain
What is the primary function of the Circle of Willis?
To ensure a constant blood supply to the brain
What is the clinical significance of the Circle of Willis?
It can protect the brain from ischemia (lack of blood flow) and stroke in cases of vascular damage or obstruction due to collateral circulation.
i.e.
It allows blood to flow through alternative routes if one of the main arteries is blocked or narrowed.
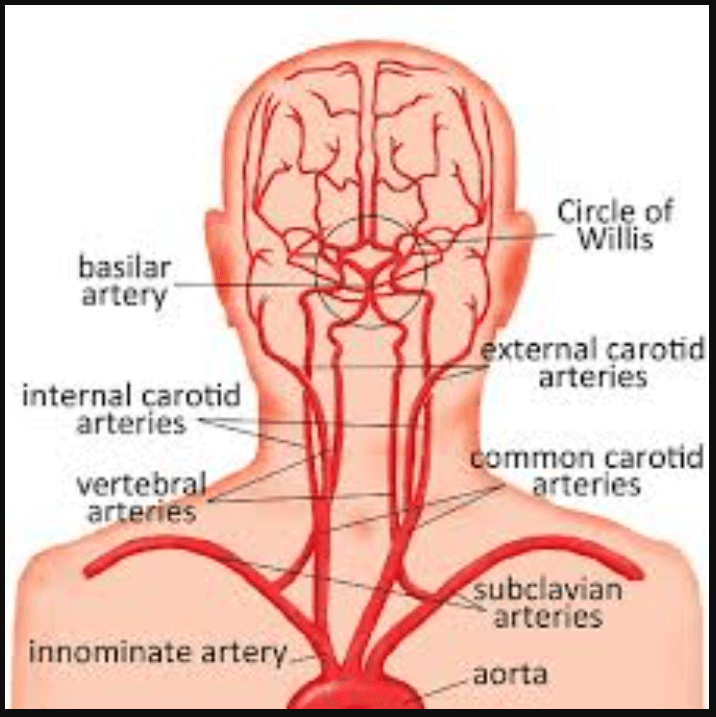
What arteries come together to form the Circle of Willis?
The carotid arteries and vertebral arteries
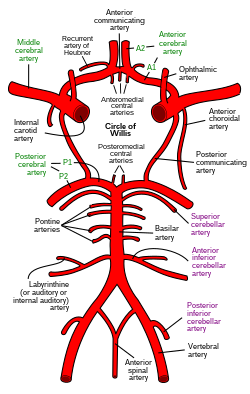
Anterior Circulation is formed by the________.
ACAs, ACoA, and the middle cerebral arteries (MCAs) (which are branches of the ICAs).

Posterior Circulation is formed by the _______.
PCAs, which arise from the basilar artery formed by the vertebral arteries.

The Left and Right ICA arise from the _______.
Left and Right common carotid arteries
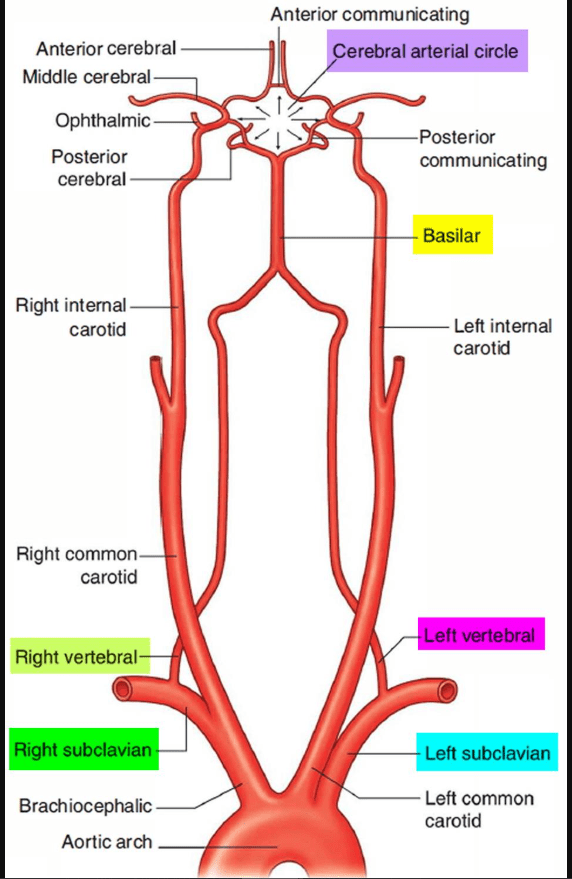
The vertebral arteries arise from ______.
The subclavian arteries
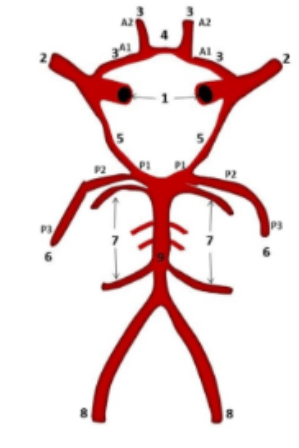
What is Subclavian Steal Syndrome?
Blood is "stolen" from the vertebral artery on the affected side to preserve blood flow to the upper limb.
Subclavian Steal Syndrome results from a proximal or distal stenosis?
Results from a proximal stenosis (narrowing) of the subclavian artery, one of arteries originating off of the aortic arch.
Does the Subclavian Steal Syndrome have the potential to affect blood flow in the Circle of Willis?
Yes.
This reversed flow, or "steal," means that blood is diverted from the brain's posterior circulation (vertebrobasilar system) to the arm, potentially reducing blood flow to the brainstem and cerebellum, which are supplied by the vertebrobasilar system. The Circle of Willis and its function can be compromised by the reduced blood flow in the vertebrobasilar system.
What is #1
ICA
What is #8
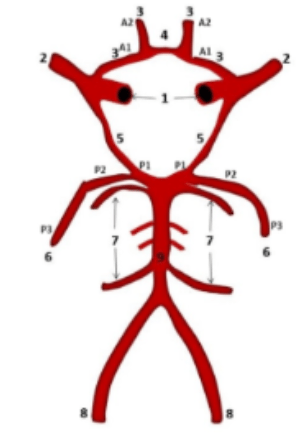
Vertebral Arteries
How many segments does the MCA have
There are 4 MCA Segments:
M1 Segment:
This is the initial segment of the MCA, extending from the internal carotid artery (ICA) to the point where the MCA bifurcates or trifurcates.
M2 Segment:
This segment runs from the MCA bifurcation to the circular sulcus of the insula (also known as the insular sulcus).
M3 Segment:
This segment stretches from the circular sulcus to the superficial aspect of the Sylvian fissure.
M4 Segment:
This segment is composed of the cortical branches that arise from the M3 segment and supply the cerebral cortex.
How many segments does the ACA have?
There are 5 ACA Segments:
A1 (Horizontal / Pre-communicating Segment):
Originates from the internal carotid artery (ICA) bifurcation.
Extends medially to the anterior communicating artery (ACoA).
Supplies the anterior hypothalamus, septum pellucidum, fornix, and anterior striatum.
Medial lenticulostriate arteries arise from this segment.
A2 (Vertical / Infra-callosal Segment):
Courses around the rostrum of the corpus callosum, from the ACoA to the genu of the corpus callosum.
Supplies the medial frontal lobe and the anterior part of the corpus callosum.
A3 (Pre-callosal Segment):
Curves around the genu of the corpus callosum.
Supplies the anterior part of the corpus callosum and the cingulate gyrus.
A4 (Supra-callosal Segment):
Runs above the body of the corpus callosum.
Supplies the superior part of the corpus callosum and the parietal lobe.
A5 (Post-callosal Segment):
Runs above the body of the corpus callosum and posterior to the coronal suture.
Supplies the posterior part of the corpus callosum and the parietal lobe.
How many segments does the PCA have?
The PCA has 4 segments:
P1 Segment:
The P1 segment is the part of the PCA proximal to the posterior communicating artery (PCoA).
P2 Segment:
The P2 segment is the part of the PCA distal to the PCoA.
P2A (anterior): This sub-segment courses through the crural cistern.
P2P (posterior or ambient): This sub-segment courses through the ambient cistern.
P3 Segment:
The P3 segment of the PCA refers to the part of the artery that runs through the quadrigeminal cistern.
P4 Segment:
The P4 segment corresponds to the parts (cortical branches) of the PCA that run along or inside both the parieto-occipital sulcus and the distal part of the calcarine fissure.
What is #2
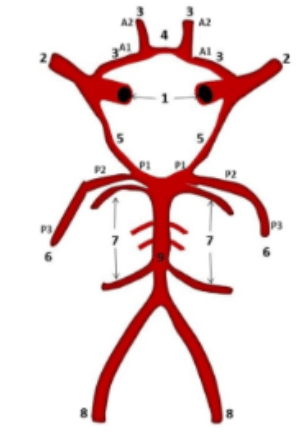
MCA
What is #7
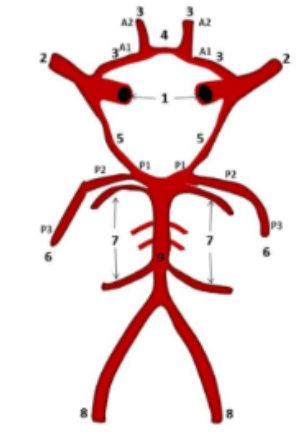
Cerebellar Arteries