A material through which an electric charge moves with difficulty. Ex. Plastic, rubber, glass, dry wood.
What is an Insulator
What energy transformation occurs in a lightbulb?
What is electrical energy to light and thermal energy?
These three parts are needed in EVERY circuit?
What is a conductor (wire), an energy source (battery), and a recipient (lightbulb).
A circuit that is NOT complete is called a? (the circuit has a gap in it)
What is an open circuit
What is the effect when a light in a parallel circuit is not working?
What is Nothing, all other lights stay on.
A material through which an electric charge can move easily. (ex. Copper, gold, and silver)
What is a conductor
A power saw turns electrical energy into what type of energy?
What is the energy of motion (mechanical)?
The job of this optional part of a circuit makes the circuit go from open to close.
What is a switch.
When there are no gaps or spaces in a circuit it is described as being what kind of circuit?
What is a closed circuit
What happens when flip the switch to turn on a light?
What is the circuit becomes closed and the energy starts flowing (the lights turn on).
An electric charge that flows in a loop is called
What is an Electric Circuit
A TV turns electrical energy into what kind of energy?
What is Light and sound energy
This part of a circuit conducts the current.
What is the wire.
A circuit with one single, sequential path is called what kind of circuit?
What is a series circuit
What happens in a series circuit when one light goes out
What is they all go out
An electric charge can flow in only one circular path in this type of circuit.
What is a series circuit
What energy transformation occurs in an over?
What is electrical to thermal?
This part of the circuit completes the circuit.
What is the switch
A circuit with two or more paths is called what kind of circuit?
What is a parallel circuit
What happens to the lights when the switch is closed and lightbulb c goes out?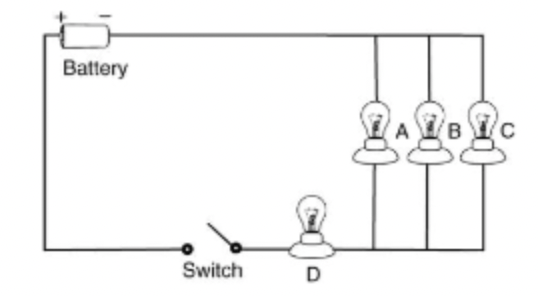
Light bulbs A, B, and D stay on (it is a parallel circuit).
What is the energy source for the street light below?
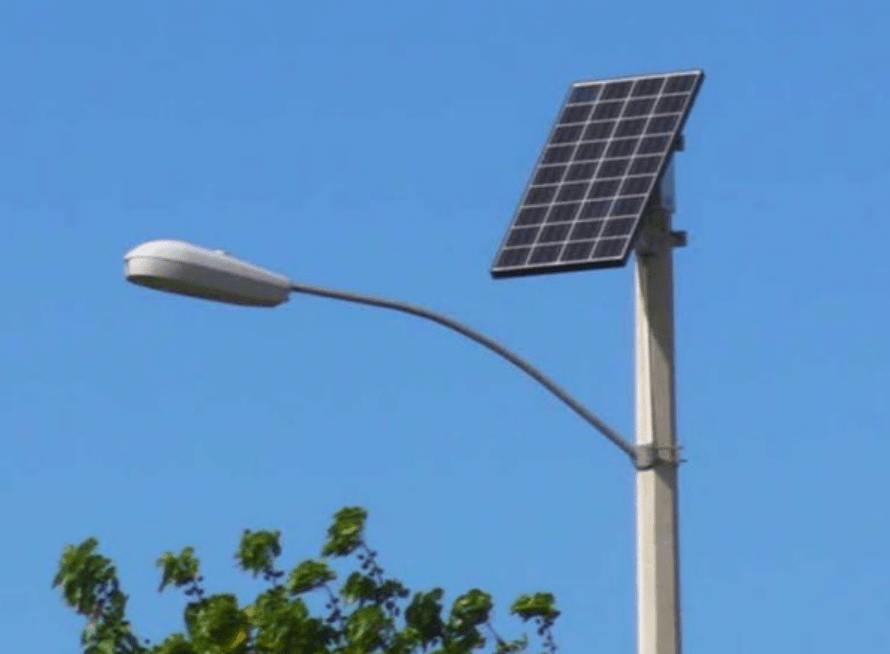

What is the solar panel (taking in the rays of the sun)?
This part of the circuit is responsible for pushing the electric current through the circuit and providing the electric current.
What is the energy source or battery.
What happens in a series circuit when one light in the circuit is missing or broken?
What is none of the other lights will work (when one goes out they all go out).
There is too much energy flowing through a circuit at once. What happens to the wires? (Hint: how does it feel, before the caboom?)
What is they get hot?