Function of the circulatory system?
delivery of oxygen, nutrients, hormones, cells of the immune system and other substances to body tissues, and removal of waste products of cellular metabolism.
Blood vessel are composed of three layers:
Inside to outside
- tunica intima
- tunica media
- tunica externa
s: increase heart rate and conduction through the nodes.
P: slows heart rate and prolongs intranodal conduction
BOTH: vasodilation of the coronary vessels
What is cardiac output and its normal range?
- amount of blood in L moved by the heart in 1 minute.
- normal is 4-8L/min
True of False:
The lymphatic system is made up of a two way network of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes.
False
- the lymphatic system is a ONE WAY network
What ensures constant coronary blood flow, maintains blood flow at a nearly constant rate between MAP of 60- 140 mmHg and enables organs to regulate blood flow by altering resistance.
Autoregulation
Gold standard for evaluation of structures of the heart. uses ultrasounds to view the structures and to help identify abnormal anatomy
ECHO
What are the three layers of the heart wall from inside the heart to outside?
- Endocardium, myocardium and then pericardium
pulmonary arteries and pulmonary veins
pulmonary arteries are the vessels that carry the blood to the lungs from the heart.
pulmonary veins are the vessels that carry the blood from the lungs to the L atrium.
What is the difference between automaticity and rhythmicity?
automaticity - property of generation spontaneous depolarization to threshold
Rhythmicity - regular generation of an action potential by the heart's conduction system
- SA - 60-100 bpm
- AV- 40-60 bpm
A ________ in cardiac output indicated heart failure; while a _________ in cardiac output signifies decrease systemic vascular resistance (common in sepsis)
decrease; increase
What adrenergic receptor is mainly in the conduction system in the heart (SA and AV nodes)
Beta 1
What is coronary perfusion pressure?
the difference between pressure in the aorta and pressure in the coronary vessels
Elicits signs and symptoms of heart disease and coronary artery disease
Exercise and stress testing
follow the path of a RBC through the heart and all chambers/ valves starting in the R atria.
R atria -> tricuspid valve -> R ventricle-> pulmonic valve-> pulmonary arteries -> lungs-> pulmonary veins-> L atria-> mitral valve -> L ventricle -> aortic semilunar valve -> aorta-> body
What vessels make up the R coronary arteries?
Conus, marginal branch, posterior descending branch
Frank- Starling Law
How does HR vary naturally with respiration
Inspiration - rate increase
expiration - rate decreases
What is the function of the lymphatic system?
it is important in fluid balance, immune function and transport of lipids, hormones and cytokines.
Coronary Blood flow is _______ proportional to the vascular resistance of the coronary bed.
inversely
Dye is injected, used to assess the lower extremity for the presence of thrombi in the large veins of the leg.
venography and arteriography
What is LaPlace's Law?
States that wall tension is related directly to the product of the intraventricular pressure and internal radius and inversely related to the wall thickness
- greater the wall thickness the less the wall tension
superior and inferior vena cava
Both the superior and inferior vena cava delivers blood from the body to the R atrium.
What parts of the brain take part in cardiovascular control?
medulla - regulates HR and BP
pons
hypothalamus - HR changes in temperature
cerebral cortex - HR in emotional states
thalamus
What is the equation for cardiac output
CO = HR x SV
Found in the heart and vascular smooth muscle
Beta 2
Nitric oxide, adrenomedullin (ADM), the endothelins and prostacyclin are all what type of mediators?
vasodilating
evaluation of electrical conduction with the heart, provides information about the nature and causes of dysrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardias and heart block.
Electrophysiologic (EP) studies
What occurs with turbulent flow and what type of noise is heard on auscultation?
- murmurs are heard
Coronary arteries
These vessel supply the heart with necessary oxygen and nutrients.
mediated by stretch receptors in the aortic arch and carotid arteries sense changes in blood pressure
Baroreceptors reflex
- BP drops, baroreceptors increase heart rate
- BP increases, baroreceptors decrease HR
What factors affect cardiac output?
Preload - volume inside the ventricles at the end of diastole
afterload - resistance to ejection of blood from the L ventricle
myocardial contractility
Heart Rate
Found in systemic and coronary arteries, causes smooth muscle contraction and vasoconstriction
Alpha 1
Coronary blood flow is _____ proportional to the perfusion pressure
directly
invasive procedure that provides a means to visualize the chambers of the heart continuously
cardiac cath and angiography
What type of flow is described as concentric layers of molecules move "straight ahead", each layer flows at a different velocity. Why aren't all the arrows the same?

Laminar flow
- the vessel walls are preventing the blood from moving as fast because of the cohesive attraction. This causes the center of the lumen to have the highest blood velocity.
What vessels make up the left coronary arteries?
Changes in heart rate that occurs after IV injections of blood or other fluids
- mediated by atrial volume receptors that innervate the vagus nerve
Brainbridge reflex
What type of agents affect contractility and include hormones, neurotransmitters or medications
inotropic agents
What are characteristics of the lymphatic system?
- contains a series of valves
- flow of excess interstitial fluid (lymph) goes towards the heart
angiotensin II, vasopressin (aka antidiuretic hormone), epinephrine, and norepinephrine have what effect on vascular smooth muscle?
They are all vasoconstrictors
radio-pharmaceuticals are used to map the coronary arteries and myocardium
Technetium scanning
What is Poiseulle's law?
Resistance is DIRECTLY related to tube length and fluid viscosity
Resistance is INVERSELY related to the radius of the tube
What is the order of vessels starting from arteries to larger veins
heart ->Arteries (aorta)-> arterioles-> capillaries-> venules -> larger veins (inferior vena cava)-> heart
What happens in the phases of the cardiac cycle?
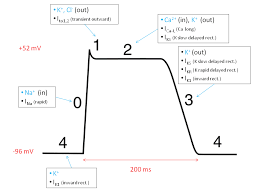
0- depolarization
1- early repolarization - calcium slowly enters
2- plateau, continuation of repolarization with slow entry of calcium and sodium into the cell
3- potassium begins to move out of the cell
4- return to resting membrane potential
What hormones can have an effect on stroke volume and thus on blood pressure?
aldosterone, vasopressin and natruietic hormones
located in the sympathetic ganglia and nerve terminals, inhibits the release of more norepinephrine, promotes vasodilation
alpha 2
Which safety mechanism prevent overstimulation and opposes Beta 1 and 2
Beta 3
A test that examines the waveform obtained noninvasely by placing a transducer on the skin over the carotid artery while the individual's head is turned slightly away
- provided information on the elasticity/stiffness of the arterial wall
Arterial pressure pulse wave form analysis
