What phase is a substance in if it has a no definite shape but a definite volume?
Liquid
What is condensation? Make sure to explain change in energy and particle movement.
Change from gas to liquid. Energy decreases and particles move slower.
Define Suspend and give an example.
To float or not dissolve in a liquid.
Algae in a lake.
When a liquid turns into a solid, is energy removed or added?
Removed
True or False?
Pressure causes a change of volume in solids.
False
Draw water as a solid, liquid, and gas. Describe the differences in how particles move.
Gas is spread out and moves the fastest, colliding or moving past each other.
Liquid is packed together rolling and switching places.
Solid is closely packed in, do not move places, but they do vibrate.
What is term for the phase change from liquid to solid.
Stand up with your group mates and demonstrate what that change looks like, each of you being an individual particle.
Freezing
Define Temperature. How do we measure it?
Definition: The average kinetic energy of a substance
Measure temperature using a thermometer.
What happens to volume when you take away thermal energy from a gas?
The molecules slow down, contract, and volume decreases.
What happens to pressure if the temperature of a gas increases? Why?
Pressure increases when temperature increases because the particles gain energy, move faster and collide more, pushing against the enclosure.
Which phase is most abundant in our solar system? Describe its qualities.
the fourth state Plasma, has the most thermal energy and highest temperature. Has charged particles (Ions)
 At what temperature is vaporization happening? What does this tell us about condensation?
At what temperature is vaporization happening? What does this tell us about condensation?
 140°C
140°C
Condensation also happens at 140°C
What term describes why chick-fil-a sauce, hot cocoa, and a milkshake all flow at different speeds. Rank these liquids using this term.
Viscosity
Lowest Viscosity - Hot cocoa
Middle Viscosity - Milkshake
Highest Viscosity - Chick-fil-a sauce

What term describes the phase change from point A to point C? What has to happen to the thermal energy?
Melting
Thermal energy must increase.
Describe what would happen to a container of nitrogen gas if you pump more nitrogen particles into it and increase them temperature. (explain how)
The container will burst because raising temperature causes the particles to move faster and increasing the number of particles causes more colliding, both increasing the energy. This puts more and more pressure on the inside of the container until it can't hold it anymore.
 Which of the two types of solids would butter be and why? Which structure best supports this answer?
Which of the two types of solids would butter be and why? Which structure best supports this answer?
Amorphous
(B)

What is the process of changing from a liquid to a gas? Name the two different types and at least one way they are different.
Vaporization
Evaporation - occurs at the surface, can happen at a range of temperatures
Boiling - occurs through the entire liquid, happens at definite temperature
Explain how water bugs are able to skip across water. Provide another example of this from class.
the close packing of liquid molecules at the surface causes a thin sheet-like covering called surface tension.
Examples: suspending the paper clip, the penny lab
Mr. Hoadley's gecko is sitting on the heating rock, describe the flow of thermal energy. Is this exothermic or endothermic?
Thermal energy flows from hot to cold.
Exothermic.
Mrs. Hagedorn took her Happy Haggy Day balloons home on a cold winter day. She was really upset when they started to deflate. How would you use your big chemistry brain to make her feel better?
The helium gas inside the balloons lost thermal energy, causing the particles to move slower and contract, BUT once the balloons get inside a warm house the gas will gain thermal energy back, moving faster and colliding, inflating the balloons.
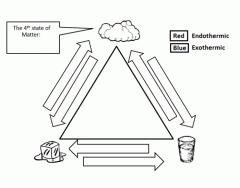 Fill in the phase changes using the key for endothermic vs. exothermic.
Fill in the phase changes using the key for endothermic vs. exothermic.
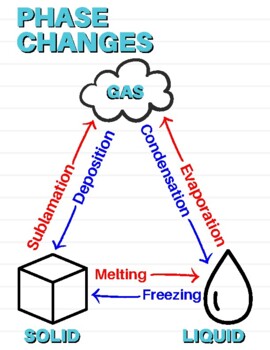
 What are some differences that distinguish point B from point D?
What are some differences that distinguish point B from point D?

Point B is the transition between the solid and liquid phase. Can be melting or freezing. Has less energy.
Point D is the transition between the liquid and gas phase. Can be vaporization or condensation. Has more energy.
Describe what happens in sublimation vs deposition.
Provide an example.
In sublimation a solid gains enough energy to change directly to the gas phase, skipping the liquid phase.
example: dry ice
In deposition a gas loses energy to change directly to the solid phase, skipping the liquid phase.
example: morning frost
Define Potential, Kinetic, and Thermal Energy with an example of each.
Potential Energy - stored energy
example: sitting at the top of a hill on your bike
Kinetic Energy - energy in motion
example: riding down a hill on your bike
Thermal energy - total energy
example: potential energy + kinetic energy
Why it would take Mr. Guenther longer to cook noodles in the mountains than in the teacher's lounge? Explain using details of the relationship between temperature and pressure.
In the mountains pressure decreases. When the pressure on water decreases, the water molecules need less energy to break through the surface, causing the boiling point to decrease and occur at a lower temperature. The noodles must boil for longer.