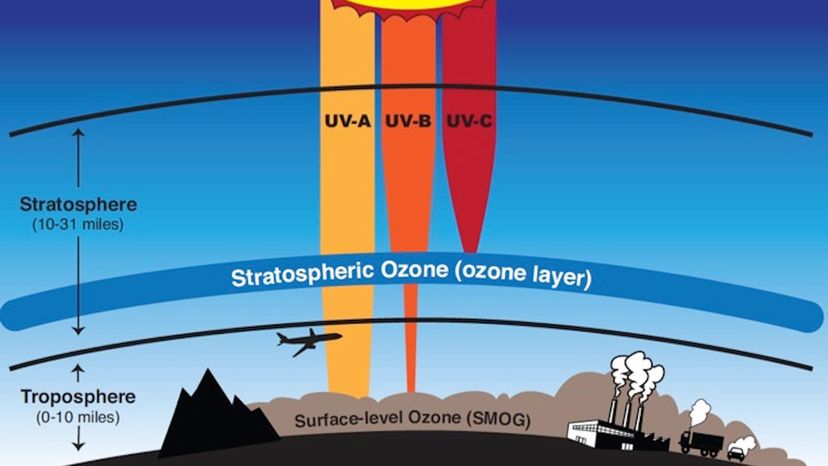
What layer of Earth’s atmosphere contains the ozone layer?
The stratosphere
What planet is known as the “Red Planet”?
Mars

What “R” words describe the three main ways to reduce waste?

True or False: The Earth revolves around the Sun in exactly 365 days.
False: The Earth takes about 365 and one-quarter days to revolve around the sun

What is the closest planet to the sun?
Mercury
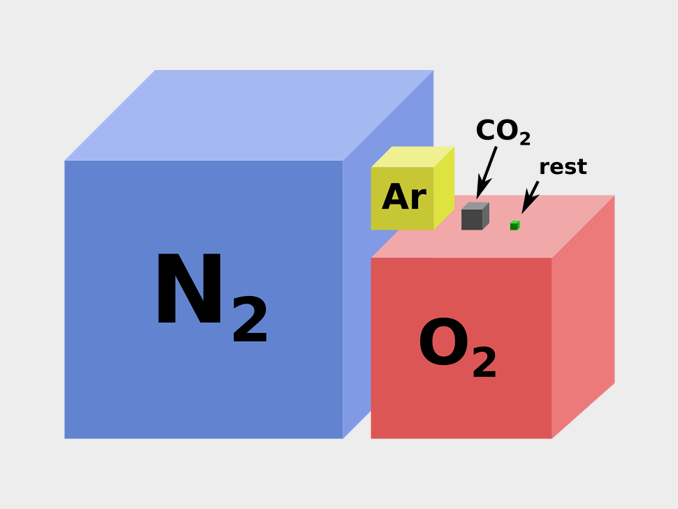
Which gas makes up most of Earth’s atmosphere?
Nitrogen
Which planet has the most moons in our solar system?
The planet with the most moons in our solar system is Saturn with over 80 confirmed moons.
What is deforestation and why is it harmful to the planet?
Deforestation is the cutting down of forests, and it is harmful because it destroys habitats and increases carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Why do we have seasons on Earth?
Earth has seasons because its axis is tilted about 23.5 degrees relative to its orbital plane around the Sun
What are the two main gases that make up the sun?
Hydrogen and Helium
What type of front occurs when a warm air mass meets and rises above a cold air mass?
A warm front

Why does the Moon cause tides on Earth?
The Moon causes tides on Earth because its gravity pulls on the oceans.
What is the main cause of ocean acidification?
Ocean acidification is mainly caused by excess carbon dioxide dissolving into seawater.
What is the difference between renewable and nonrenewable energy? Give one example of each.
Renewable energy can be replaced naturally, such as solar power, while nonrenewable energy cannot be replaced quickly, such as coal.
What is the difference between a meteor, a meteoroid, and a meteorite?
meteoroid: a small rocky or metallic body in space
meteor: the streak of light when a meteoroid enters earth’s atmosphere
meteorite: the remains of a meteoroid that reaches the ground
What is the difference between weather and climate?
Weather is short-term atmospheric conditions; climate is the long-term average pattern of weather
What are the two main differences between terrestrial planets and gas giants?
Terrestrial planets are small, rocky, and dense, while gas giants are large, mostly made of gas, and less dense.
Why is biodiversity important for ecosystems?
Biodiversity is important because it keeps ecosystems stable and able to provide resources.
What causes the Northern Lights (Aurora Borealis)?
The Northern Lights are caused by charged particles from the Sun colliding with Earth’s atmosphere near the poles.
What is the difference between a red giant and a white dwarf in terms of stellar evolution?
a red giant is a late stage in a medium-sized star’s life when it expands and cools after exhausting hydrogen in its core
a white dwarf is the compact, dense remnant left behind after a red giant sheds its outer layers
Explain how the Coriolis effect influences global wind patterns.
The Coriolis effect makes winds curve (right in the Northern Hemisphere, left in the Southern), shaping trade winds and jet streams
Explain why Venus is hotter than Mercury, even though Mercury is closer to the Sun.
Venus is hotter than Mercury because its thick carbon dioxide atmosphere traps heat through the greenhouse effect.
Explain how the burning of fossil fuels leads to both air pollution and global warming.
Burning fossil fuels causes air pollution through smog and acid rain, and global warming by releasing greenhouse gasses.
What do Kepler’s 3 Laws of Planetary Motion describe?
1.Planets move in oval (elliptical) paths around the Sun, not perfect circles.
2. A line connecting a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times.
3. Planets that are farther from the Sun take longer to orbit than those closer in.
Explain why observing distant galaxies also allows us to look back in time.
Because light takes time to travel, the light from distant galaxies we see today left them millions or even billions of years ago. thus, we are observing them as they were in the past, not as they are now.