An 18 y/o patient presents to the ER with a clouded sensorium, agitation, hyperactivity, mild paranoia, pressured speech and euphoric though labile mood. Physical exam notable for HTN, tachycardia and vertical nystagmus. What substance did he likely ingest?
PCP
This is the most common psychiatric presentation following a stroke
Depression
This is the metabolic abnormality commonly found with anorexia nervosa, purging subtype.
Hypokalemia**
Can also occur in bulimia
Purging --> loss of HCl
Volume loss/dehydration --> contraction metabolic alkalosis
--> hypokalemia
This is the most common solid tumor of the CNS in children
Neuroblastoma

Treatment of acetaminophen overdose
N-acetylcysteine **
23 y/o patient presents to the ER after a party. Found to have dehydration, dilated pupils, HTN, and elevated CPK. What substance did he likely ingest?
MDMA *
(could also be cocaine, other stimulants & amphetamines)
Electrolyte finding in MDMA use?
EEG findings in delirium
Diffuse slowing of background rhythm

What mood stabilizer should be held before ECT, as it associated with prolonged seizures?
Lithium
This is the anti-epileptic of choice for treatment of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy.
Valproic Acid
- sudden jerks of enitre body that occur early in the morning or with sleep deprivation
- first presents as brief episodes of involuntary muscle twitching
- What is the buzzword for EKG finding?

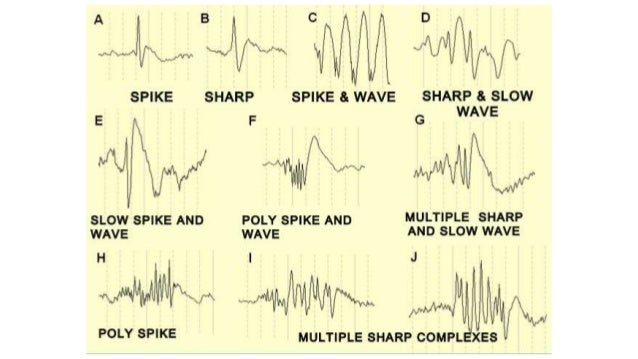
40 y/o pt presents with delirium, tremor, diaphoresis, rigidity, hyperpyrexia, and myoclonus in making the transition from the use of clomipramine to phenelzine. Pt is most likely experiencing?
Serotonin syndrome
When switching from SSRI --> MAOI, wait 2 weeks, or 5 weeks if with fluoxetine

Tx?
A heroin dependent female discovers she is pregnant and wants to detox. What is the recommended treatment plan?
Methadone maintenance until delivery then detox *
Methadone is gold standard answer for boards, however in clinical practice can use buprenorphine.
Risk of neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS)
A 67-year-old patient was started on fluoxetine and a week later presents to the ER with mild confusion, lethargy, and polydipsia. What electrolyte abnormality is likely?
Hyponatremia
A 40 y/o M developed gradually progressive dementia and abnormal involuntary movements. Older brother and father have similar illness. DNA analysis will likely show?
Excess CAG triplets (Huntington’s disease)


Maternal SSRI use during pregnancy is associated with this syndrome in the baby.
Neonatal adaptation syndrome
Presents in about 30% of patients
Generally presents within a few hours following birth and may include a combination of respiratory distress, feeding difficulty, jitteriness, irritability, temperature instability, sleep problems, tremors, shivering, restlessness, jaundice, rigidity, and hypoglycaemia.
Tx: supportive
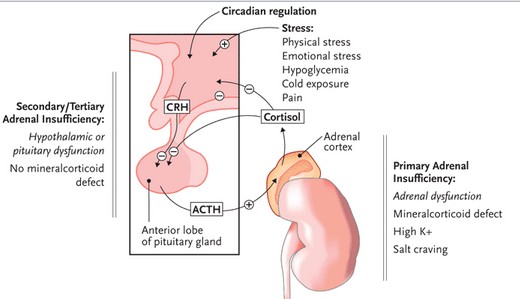
35 y/o pt presents to the ER with severe depression and episodes of anxiety for 9 months that have become so bad he can no longer leave the house, has severe weight loss, hyperpigmentation of exposed skin, and cold tolerance. What is the diagnosis?
Addison’s disease (adrenal cortex insufficiency)
low aldosterone --> hypotension, high K+, low Na+
low cortisol --> hypotension
primary insufficiency --> ^ ACTH from ant pit --> MSH --> ^ hyperpigmentation (distinguish from secondary)
Alcohol use is associated with what changes in sleep?
Decreased sleep latency, decreased REM

A 79-year-old patient presents with personality changes, cognitive difficulties, affective lability, and olfactory and gustatory hallucinations. MRI reveals hyperintensities in the temporal lobes. What is the diagnosis?

HSV encephalitis
Treatment?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for treatment of depression targets this brain region.
Prefrontal Cortex
A child with ADHD presents with poor control of symptoms on methylphenidate. Next step in management:
dextroamphetamine
both classes increase NE and DA
If one class doesn't work, switch to the other

A 40 year old with AIDS presents with symptoms of progressive hemiparesis and a R homonymous visual field deficit. There are patchy white matter lesions on MRI and LP is normal. What is the diagnosis?
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy *
Bonus question: what virus causes this?
- Typically presents with subacute neurologic deficits, including altered mental status, visual symptoms such as hemianopia and diplopia, hemiparesis or monoparesis, and appendicular or gait ataxia. Seizures occur in up to 18 percent of patients.
- Clinical suspicion for PML should be heightened if neuroimaging reveals discrete unilateral or bilateral foci of demyelination in the white matter that do not conform to vascular territories and exhibit neither mass effect nor contrast enhancement


This is the molecular mechanism of ketamine
NMDA receptor antagonist
Schizophrenia also has downregulation of NMDA receptors, leading to similar psychotic symptoms. Same with Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis.

This is the most common manifestation of acute neurosyphilis.
Stroke
Bonus points: What is the FIRST manifestation of neurosyphilis?
What other symptoms may be present?
C/L is consulted on a 28y/o with emotional lability and impulsivity. LFT’s are elevated. A close relative had similar sx and died at 30y/o from hepatic failure. Which blood level would be diagnostic?
Ceruloplasmin (Wilson’s disease) *
Treatment?
What is the most common biological cause of prenatal neurotoxicity linked to the development of intellectual disability (mental retardation)?
Alcohol exposure
A patient with schizophrenia presents to the ER after a recent medication adjustment with fever, diaphoresis, stiffness, tachycardia, confusion. Name the diagnosis, most typical lab finding, and treatment.
Dx: Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
Presentation:
Fever
Encephalopathy
Vital sign instability
Enzymes elevated
Rigidity
Labs: elevated creatine kinase
Tx: (controversial)
- dantrolene (skeletal muscle relaxant) along with hydration and cooling
- bzd
- bromocriptine (DA agonist)
