What’s the first intervention for life-threatening extremity bleeding in a hostile environment?
Hasty Tourniquet
If a casualty is breathing on their own, what position should they be in?
Position of comfort
When applying a chest seal- do you put it on in the inhale or exhale? Why?
Exhale! Because we want to get as much air out as we can (we don't want to trap air in)
Name 3 things we're checking for in Circulation
Pelvic Fractures, Pulses, Skin color, Cap refills
Why is keeping casualties warm important?
To avoid SHOCK!
You're under fire. Your battle buddy goes down and is not moving. What is your priority under Care Under Fire?
Suppress the threat, return fire
True or False: You can safely place a chest seal over a shirt or uniform if you're in a hurry.
FALSE!
Chest seals must be applied directly to bare skin to work properly.
How long should you hold direct pressure before reassessing a wound?
2-3 minutes!
What are two ways to open the airway?
Head-tilt-chin-lift & Jaw Thrust
What are your landmarks for an NCD? What is the alternate placement?
Between 2 and 3 intercostal space, mid-clavicular. Or 4 and 5 intercostal space anterior axillary line.
Name 5 different locations to check a pulse.
Carotid, radial, brachial, groin, pedal
When dealing with an eye injury, do you cover both eyes or just the injured one? And why?
ONLY the affected one because it prevents further injury and anxiety
A casualty is unconscious but breathing. You’ve already controlled major bleeding. What’s your next intervention?
Insert an NPA and place in the recovery position
Name 5 items that come in an IFAK?
Tourniquets, combat gauze, chest seals, NPA, NCD, TCCC, sharpie, gloves
What is the most common reason tourniquets fail?
Not tightening enough
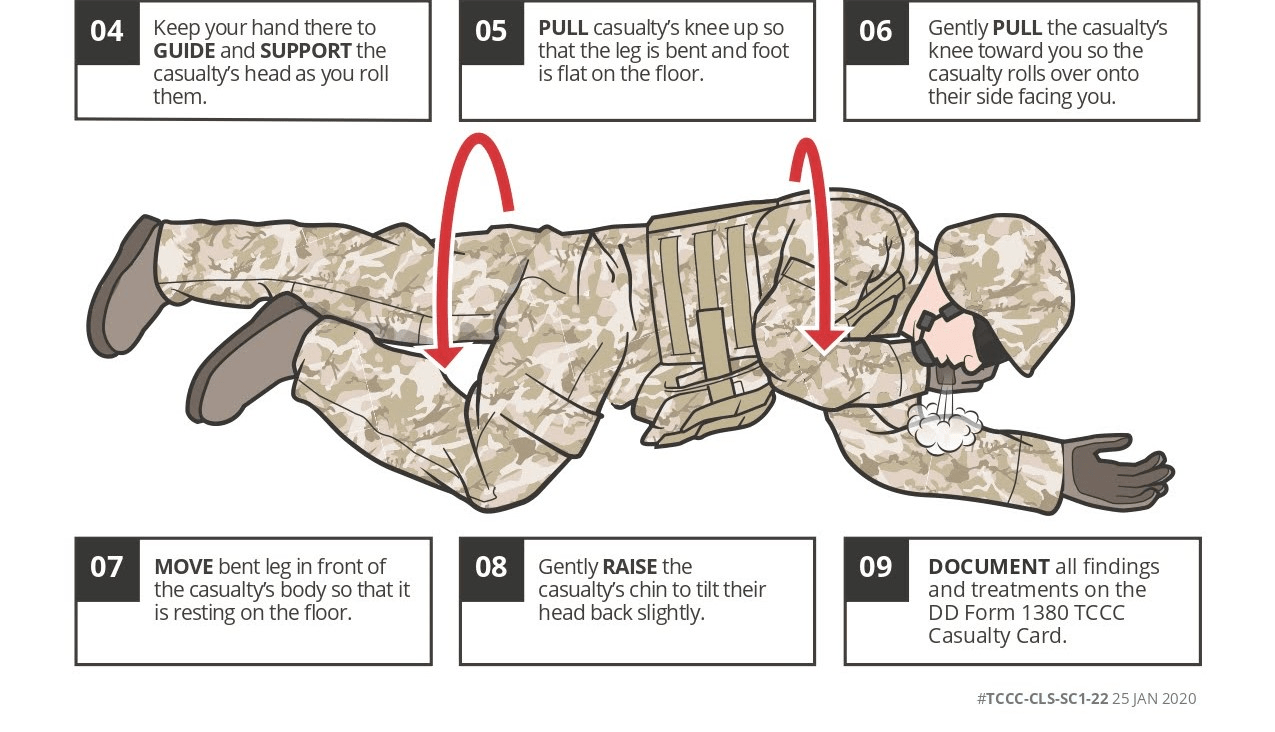
Show me how to put someone in the recovery position.
What are we checking for in Respiration?
Signs of chest injury, quality of breathing, respiratory rate, open chest wounds, equal chest rise and fall
What scale do we use to measure a casualty's level of consciousness? And what does it stand for?
AVPU! Alert, verbal, pain, unresponsive
List two actions to prevent field hypothermia.
Remove wet clothing, wrap casualty in insulating materials, keep off ground.
You approach a casualty who is alert but has bright red blood spraying from their arm. What’s your immediate action?
Apply a tourniquet high and tight.
If a casualty starts singing while you're packing their wound, what should you do?
Keep packing—they're conscious, but that doesn't mean bleeding has stopped
What are the three parts of a rapid blood sweep?
Neck, armpits, groin
When using a BVM, how often are we giving a breath?
Every 5-6 seconds
Name 3 signs and symptoms of a Tension Pneumothroax.
Difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, rapid pulse, distended jugular veins, absent rise and fall of the chest, bluish skin, chest pain, tracheal deviation
What is the name or abbreviation of where the Pelvic Binder goes?
Greater Trochanter!!
What are signs of an eye injury? Name 3.
Vision loss, impalement, pain, blood, bruising, lacerations
You sealed a chest wound, but the casualty’s breathing gets worse, and their trachea starts to shift. What do you suspect and what should you do?
Tension pneumothorax → perform needle decompression.
Your casualty has severe facial trauma. When assessing a casualty's airway, another CLS stud tells you to put an NPA in. What do you do?
NO! NPA's and facial trauma are NOT friends.
What key signs indicate that a tourniquet has been applied effectively?
The bleeding stops completely and no distal pulse can be felt below the tourniquet.
What does NPA stand for? How do we measure and insert an NPA?
Nasopharyngeal Airway. Measure from tip of the nose to the ear lobe, lube it up, head-tilt-chin-life, piggy nose, insert bevel end to septum and insert at 90 degrees.
What is a tension pneumothorax?
A tension pneumothorax is when air gets trapped inside the chest and it can’t get out. This builds pressure inside the chest cavity, which pushes onto other organs.
What do we do with tourniquets during Circulation? Then demonstrate one.
Tourniquet replacement & tourniquet conversion
List 5 signs and symptoms of a head injury.
Headache, pupil responses, vomiting, nausea, blurry vision, seizures, loss of consciousness, restlessness, confusion, slurred speech
After treating a casualty for massive bleeding, they become confused, pale, and their radial pulse is absent. What does this mean, and what is your priority?
They are in shock → cover them to prevent hypothermia and prepare for rapid evacuation
What medications come in a Combat Pill Pack? What are they used for?
Meloxicam- Anti-Inflammatory
Moxifloxacin- Antibiotic
Acetaminophen- Pain