What bactria most commonly causes Hordeolum and blepharitis- infectious type?
staphylococcus aureus
between dacryocystitis, dacryoadenitis, and dacryostenosis which one is an infection, inflammation, or narrowing of a duct?
Dacryocystitis - infection of lacrimal SAC due to obstruction
Dacryoadenitis - inflammation of lacrimal GLAND
Dacryostenosis - narrowing or obstruction of nasolacrimal DUCT
Viral Conjunctivitis is usually caused by Adenovirus. What are some clinical representations
*Ipsilateral enlarged and tender pre-auricular LAC, sequentially bilateral, gritty sensation or pertussis, erythema, copious watery discharge +/- mucous, follicular, pt may have fever, malaise, pharyngitis
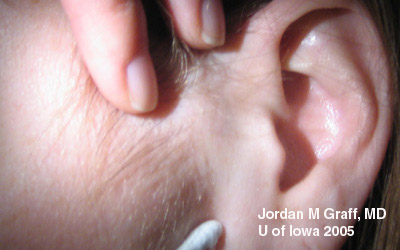
What is the treatment for Gonococcal conjunctivitis
*500 mg or 1gram of ceftriaxone IM, eye irrigation with saline, topical erythromycin and bacitracin, and *refer bc it is a ophthalmologic emergency as it could lead it corneal perforation
in infectious keratitis - viral, what will be visible with fluorescein and wood lamp
dendritic branching
What is the difference between an external and internal hordeolum? what glands are affected ?
internal- inflammation or abscess or meibomian glans
external - abscess of the gland of Zeis (lash follicle) or Moll (sebaceous gland). AKA stye
what type of imaging is ordered for postseptal (orbital) cellulitis
emergent CT with contract of head and orbit
What are some clinical presentations of bacterial conjunctivitis
*mucopurulent discharge (stuck in the AM, occurs all day, yellow, white or green, conjunctival erythema, sequentially bilateral, vision is intact, mild discomfort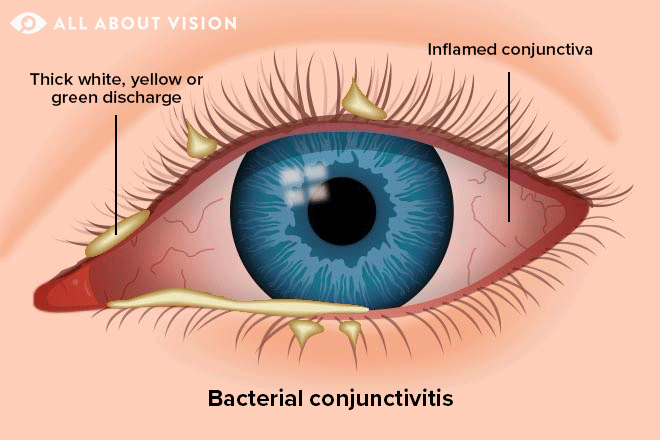
what is the treatment for chlamydial keratoconjunctivits - trachoma vs inclusion
trachoma - 1 gram Azithromycin PO
inclusion - doxycycline 100 mg PO BID x 7 days or Azithromycin 1 gram PO
Risk factors for infectious keratitis - bacterial
*contact lenses, corneal trauma from refractive surgery, Dry eyes (Bell Palsy), topical CS, immunosuppression
Both hordeolum and blepharitis (anterior infectious type) affect the eyelid margin by the same bacteria. However they have different clinical manifestations. What are their treatments ?
hordeolum - warm compress, hygiene, and if painful antibiotic ointment (bacitracin or erythromycin)
blepharitis anterior infectious type - warm compress, hygiene, lid scrub, massage with baby shampoo, antibiotic ointment (bacitracin or erythromycin)
describe the eye involvement in preseptal (periorbital) cellulitis vs postseptal (orbital) cellullitis
preseptal - no eye involvement. normal vision acuity and PERRLA
postseptal - eye involvement. abnormal visual acuity and PERRLA, pain with extra ocular movement, +/- proptosis
What are some clinical presentations of allergic conjunctivitis
*bilateral pruritus, *stringy discharge, teary, redness, hyperemia, chemosis (swelling if conjunctiva), photophobia, visual loss.
Clinical presentation of pinguecula vs pterygium ?
Pinguecula- *yellowish nodule in palpebral fissure, often bilateral, more common medially
Pterygium- *fleshy, triangular growing tissue of the conjunctiva onto the cornea. irritation, erythema, foreign body sensation, often bilateral, most common medially
What are some clinical presentations of infections keratitis - bacterial
*corneal defect readily visible with pen light (round white spot with underlying opacity, +/- hypopyon) *ciliary injections (limbal flush), FB sensation, conjunctiva erythema, difficult keeping eye open, pain, vision changes, photophobia
what are the clinical presentations of Blepharitis anterior vs posterior ?
Anterior infectious - burning, red-rimmed eyelid margin, yellow crusting clinging to lashes, irritation, tear film may be greasy
Anterior Seborrheic - Pruritus (itchy), white dry scales, red-rimmed eyelid margin, irritation
Posterior - eyelid must be flipped to assess. Hyperemic with telangiectasis (increase blood flow and increase redness in area)
treatment for dacryocystitis vs dacroadenitis
dacryocystitis - warm compress and oral/ systematic antibiotics
dacroadenitis - warm compress and first gen cephalosporin
What is the treatment for allergic dry eyes? mild to moderate sx vs severe
Mild to mod: topical mast cell stabilizers= *olopatadine (prophylaxis) , topical and/or systemic antihistamines= loratadine 10mg PO QD
Severe: refer for topical CS
clinical manifestation between chlamydia keratoconunctivitis trachoma vs inclusion
trachoma - bilateral follicular conjunctivitis, epithelia keratitis, corneal vascularization, scarring of the tarsal conjunctiva leading to entropion and trichiasis
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1202088-clinical?form=fpf#b4
inclusion- acute redness, painful, discharge, irritation, preauricular LAD
what is the treatment for infectious keratitis - herpes zoster ophthalmicus ?
high dose of oral anti-viral within 72 hours of sx and refer
when do you refer out for hordeolum vs chalazion
hordeolum - after 48 hrs of minimal progress for incision
chalazion - if CS is needed or if incision and curettage is needed
what can cause keratoconjunctivits sicca?
meds: antihistamins, anticholinergics, psychotropics or a systemic disease: sjorgen syndrome
Describe the following differences between acute viral, acute bacterial, and acute allergic conjunctivitis .
Bilateral vs unilateral
Discharge
conjunctival appearance
associated findings
1. Viral and bacterial can be unilateral or bilateral. Allergic is bilateral.
2. Viral is watery/mucoid, bacterial is purulent, allergic is watery
3. all 3 have diffuse injection, viral and allergic is follicular, bacterial is non-follicular
4. viral- prodrome, bacterial- unremitting discharge, allergic- pruritus and hx of atopy
what are the clinical presentations of cataracts
*glare in bright life or when driving at night, gradual progressive blurry vision, change of focus (development of near-sightedness, monocular double vision), impairs ADLs