The measures of center
mean and median
A false treatment that when given, sometimes to a control group, compare the effects of an actual treatment
placebo
Observes individuals and measures variables of interest but does not attempt to influence the responses
observational study
You need this in place in order to generalize results to a population
random sampling
Bias introduced to a sample when individuals can choose on their own whether to participate in the sample
voluntary response
The measures of variability
range, interquartile range (IQR), standard deviation
The group of subjects who do not receive a treatment AND the reason that one is needed in an experiment
control group
so that a group of untreated subjects exists to compare to
Deliberately imposes some treatment on individuals to measure their response.
experiment
This needs to be in place in order to conclude causation in an experiment
Random Assignment
A sampling scheme that biases the sample in a way that gives part of the population less representation then it has in the population
undercoverage
To randomly assign 25 people out of 50 to a treatment... complete the last step. Be specific!
- Assign each person a number from 1-50
- Randomly generate 25 numbers between 1 and 50, ignoring any repeats
- ??
The 25 people whose numbers were selected will receive the treatment, the remaining 25 will be in the control group
In a study, when the researchers know who is getting a treatment, but subjects do not
single blind
A medical team examines the records of 5 large hospitals and compares the survival times of those cancer patients who had surgery versus those who had chemotherapy.
Observational Study
I randomly sample seniors from WMHS about their favorite sport. Can I generalize the results to the entire school?
No, because it was not a random sample of the entire school... only from seniors.
(You could generalize the results to all seniors.)
Bias introduced when a large fraction of those randomly sampled fails to respond, and those who do respond are likely to not represent the population.
nonresponse
The IQR in the boxplot below
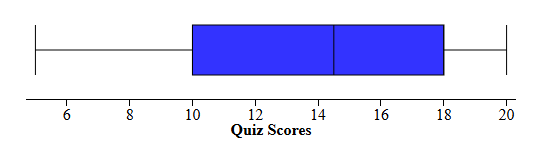
8
The value that the experimenters record as data to see any difference between a control group and a treatment group
response variable
In gym class, the effect of exercise on blood pressure is studied by requiring that half of the students walk a mile each day while the other students run a mile each day,
Experiment
In an experiment to see if a SAT prep class affects SAT grades, I let students choose if they wanted to be in the class or not. I saw that the SAT prep class got higher scores overall. Can I conclude that the prep class causes higher scores
No, because the treatments were not randomly assigned
Anything in a survey design that influences responses falls into this category of bias
response
The mean SAT score for students graduating high school in the year 2024 was 505. The standard deviation for these same scores was 125.
Interpret the standard deviation. THIS MUST BE PERFECTLY CORRECT
the SAT scores for HS graduates in 2024 typically differed from the mean of 505 by 125
What the results of a study are off from the truth this is often because of some type of
Bias or confounding variable
The relationship between weights of bears and their lengths is studied by measuring bears that have been anesthetized
Observational Study
What conclusion can I make from the following Experiment?
50 NBA players are chosen randomly to be in this study. 25 are randomly assigned to wear Jordans in their next game and 25 are randomly assigned to wear LeBrons. The player wearing Jordans overall scored higher than the LeBron group.
Among all NBA players, wearing Jordans causes players to get more points than LeBrons
This is the reason that convenience sampling produces bias
the sample will not accurately represent the population