Describe this neurosurgical procedure.
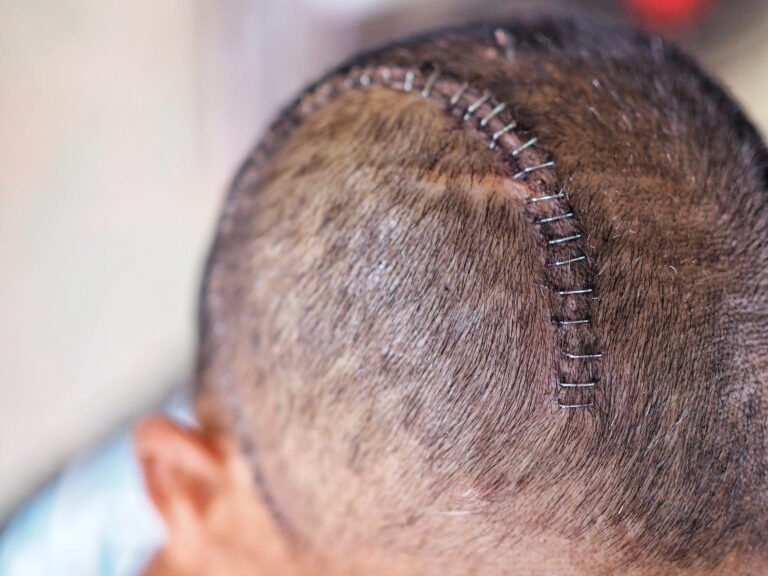
What is a craniotomy.
•Surgeon removes a piece of bone from the skull to access underlying brain tissue
•Space occupying lesions that is causing elevated ICP is then removed (e.g., resect tumour, evacuate bood)
•Piece of bone is returned to the skull in its original position
•It is important to monitor for potential post-operative complications
Common indications for a craniotomy
What are:
•Trauma
E.g., SDH, brain contusions, skull fractures
•Tumour
E.g., Meningioma, glioma, metastases
•Vascular
E.g., ICH, aneurysms, AVMs
•Infection
E.g., abscess, subdural empyema
•Miscellaneous
E.g., epilepsy, deep brain stimulation
Common indications for VP shunt placement
hydrocephalus
brain tumours
This
•Occurs when bacteria invades the meninges and the subarachnoid space
•The immune system eventually reacts to the invaders and the immune cells gather to defend the body
•This results in the inflammation of the meninges
What is meningitis
What are the 5 crucial moments of hand hygiene?
What are:
Describe this neurosurgical procedure
What is a craniectomy
•A neurosurgical procedure that involves removing a portion of the skull, where the patient’s scalp is closed without re-implantation of the bone
•This results in a cranial defect
•The bone flap can be preserved by temporary placement in a subcutaneous pocket and cryopreservation
•If the bone flap is discarded, it can be replaced with a custom-made implant
•A craniectomy increases buffer capacity of the cranium
•It allows outward herniation of brain tissue, which
üPrevents compression of brain stem structures
üRe-establishes brain perfusion
•ICP is reduced by 15-85% depending on size of bone removed
For craniectomies, this can occur with the bone flap
what is...
- discarded (patients will sometimes require a cranioplasty, whereby a custom-made bone flap will be placed)
- preserved by temporary placement in a subcutaneous pocket
- cryopreservation
Describe CSF production and flow
What is...
•The majority of CSF is made in the choroid plexus
•Approximately 500 mL of CSF is produced daily OR approximately 20 mL/h
•CSF flows from the lateral ventricles into the third and fourth ventricles then into the subarachnoid space
•CSF is reabsorbed by the arachnoid villi, which line the subarachnoid space
Signs and symptoms of this complications include
•Fever
•Swollen or painful incision
•Drainage (exudate) from incision
•Dehiscence of incision
•Ulceration of surgical site
•Headache
•Changes in neuro status
What is surgical site infection
This technique is intended to minimize contamination from pathogens. It strives to minimize the interaction of the patient with any organisms that can cause infection.
What is aseptic technique
Describe this neurosurgical procedure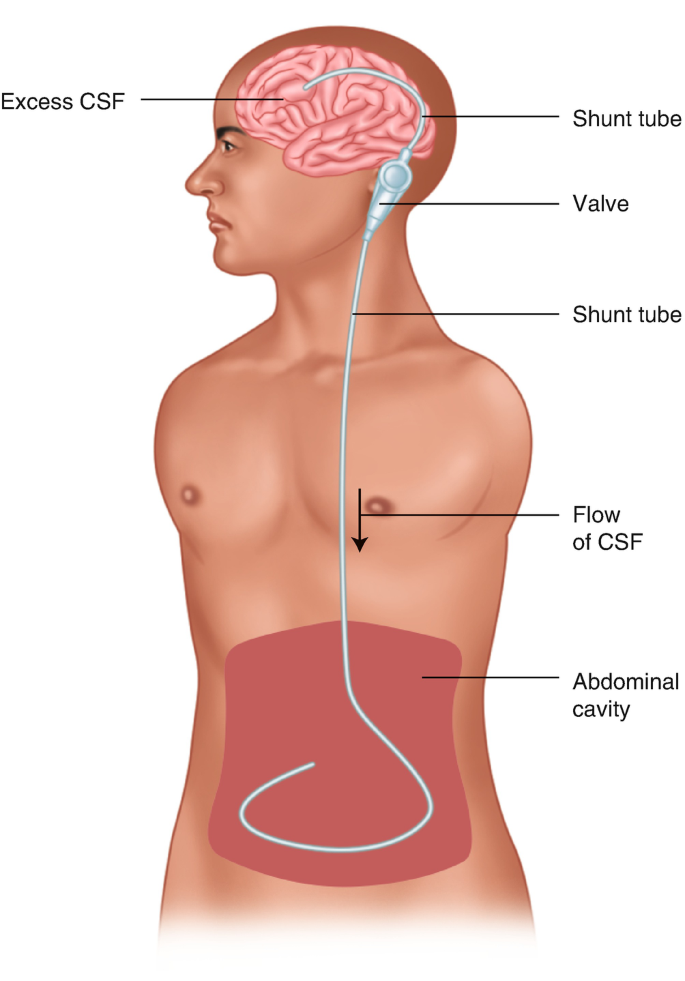
What is a ventriculostomy placement
•Cerebral shunt drains CSF when there is an obstruction in the normal outflow or there is decreased absorption of CSF
•It functions as a low-resistance mechanism and is engineered to control ICP over a range of postural positions and pressures
•The shunt system is comprised of a ventricular catheter (proximal shunt), valve and a peritoneal catheter (distal shunt)
•The valves have either fixed or programmable (adjustable) pressure settings
•Indication: hydrocephalus, tumours
Name this complication and which neurosurgical procedure it can be associated to?

What is Trephine Syndrome aka sinking skin flap syndrome.
This is caused by changes in pressure gradient of ICP and atmospheric pressure
These patients benefit from having the bone flap replaced sooner rather than later
Where are:
the skull
abdomen
This complication
•can be caused by an opening in the dura to the subarachnoid space. This can happen anytime post-op.
•This places patients at risk for wound breakdown, infection (especially meningitis)

What is a CSF leak
Standard duration that craniotomy staples are left in place
What is 10 to 14 days
The first surgical dressing removal is completed by the neurosurgeon
Orders must be provided to nurses regarding wound care
For craniotomies, when surgical incision is dry and intact, it can be left open to air
An order should be provided by the neurosurgeon indicating when staples can be removed
Showering with shampoo and hair products should be avoided in the acute phases
These are 4 types of VP shunt malfunctions
What are
- CSF overdrainage – slit ventricle syndrome
- CSF underdrainage – signs of hydrocephalus
- Shunt obstruction – signs of increased ICP
- Shunt infection
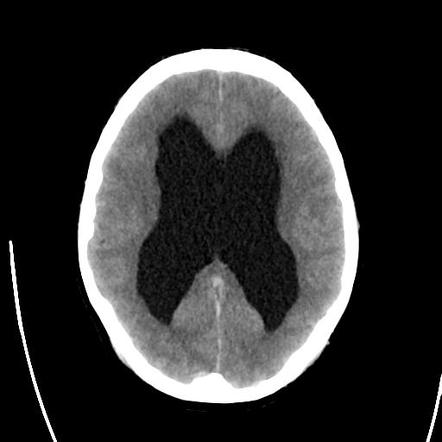
•An active distension of the ventricular system resulting in adequate passage of CSF from its point of production within the cerebral ventricle to its point of absorption into the systemic circulation
2 types include:
•Communication (absorption)
•Non-communication (flow)
What is hydrocephalus
Compare your neurosurgical emergency solutions - Mannitol vs. Hypertonic saline
Hypertonic saline (e.g., 3%) is a volume expander and is more like to cause rise in BP.
If cerebral swelling/ edema and elevated ICP go untreated, this fatal complication may arise.
Signs and symptoms may include:
•Vomiting
•Headache
•Restless, irritability
•Confusion
•Double vision
•Decreased LOC
•Coma
•Temperature changes
**Cushing's triad is your ominous warning sign
What is herniation
This medication is given following craniotomy, craniectomy to reduce cerebral inflammation
What is corticosteroids