We must screen for VBI in cervical cases, especially when presented with reports of dizziness; VBI is closely related to the Circle of Willis, please draw an illustration of this point (aka fully detailed Circle of Willis with inclusion of vertebral arteries)
not labelled: superior cerebellar artery (just inf to posterior cerebral artery)
What are the 3 tests that assess for the presence of displaced otoconia in the semicircular canals?
Dix-Hallpike (posterior)
Cervical Extension Test (anterior)
Supine Roll Test (horizontal)
What are the cluster (3) for Canadian C-Spine Imaging Rules?
Risk Factor Identified (no to all = r/o x-ray)
- age >/= 65 years old
- neuro S+S or midline tenderness
- unwillingness/inability to to perform upright AROM
Dangerous MOI
- fall from >/= 5 stairs
- axial trauma
- collision at > 100 km/hr (62 mph) or with rollover/ejection/pushed into oncoming traffic/hit by bus or truck
- motorized recreational vehicle/bicycle
AROM < 45 degrees
What factors do we have a moderate-high confidence of no effect on prognosis of WAD?
Alignment
Direction of Impact
Position at Time of Impact
Awareness of Impending Collision
Headrest Use
When having you patient perform JPE testing, what is the distance from the center (in cm or degrees) that would be considered significant?
7 cm or 4.5 degrees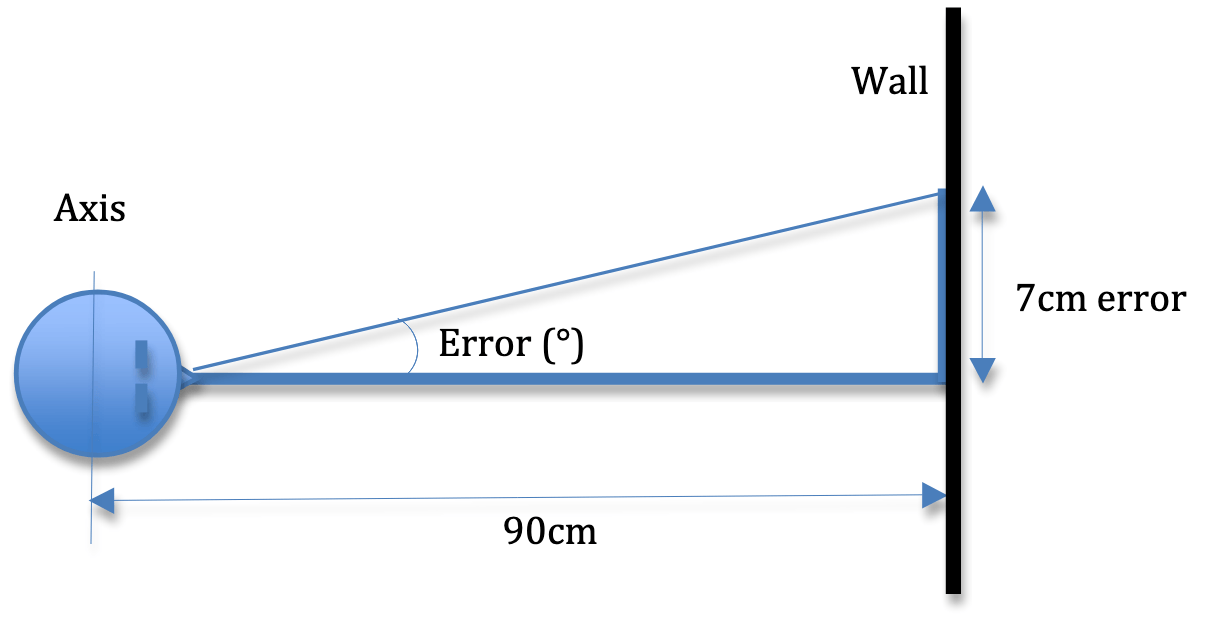
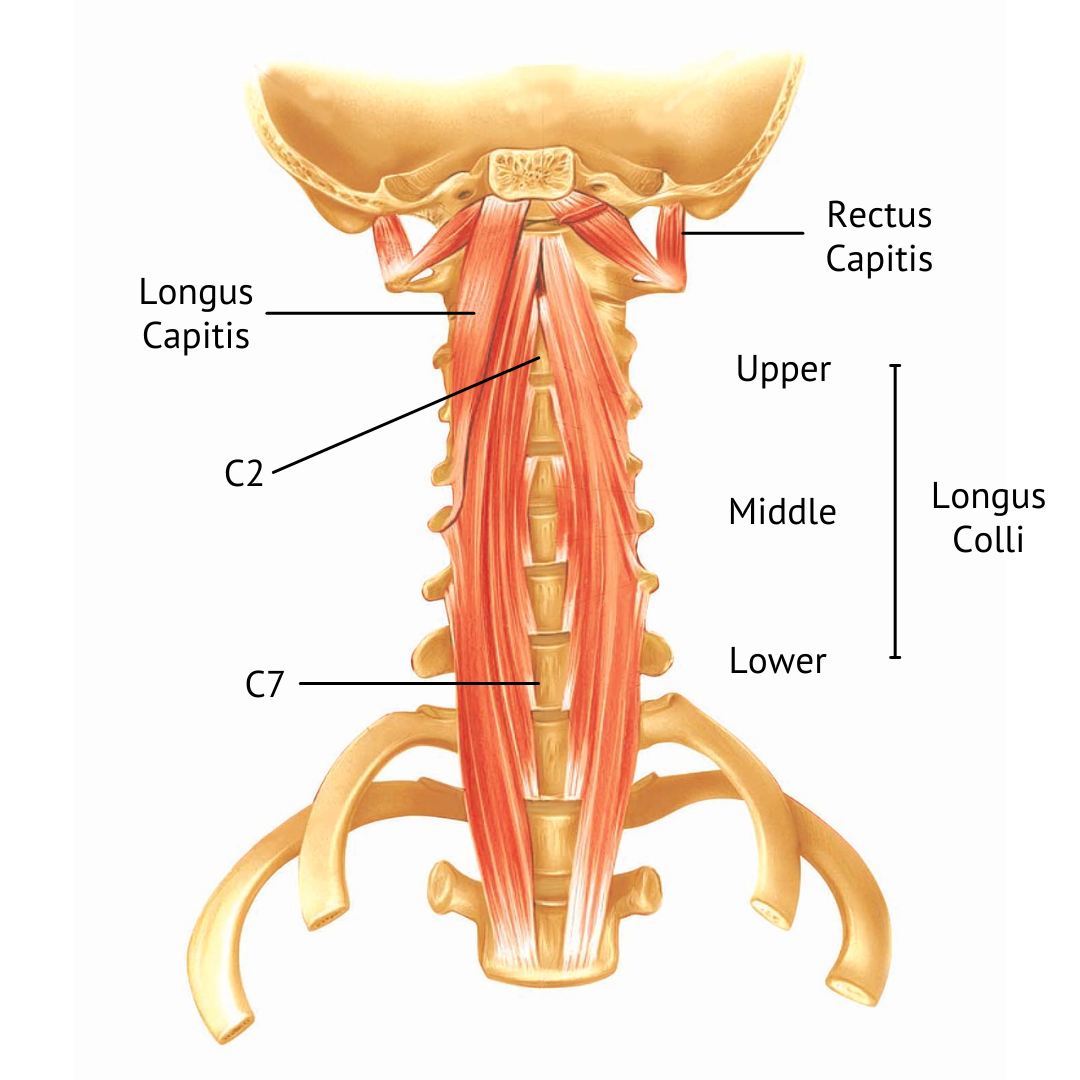
When we refer to the "deep neck flexors" to which 4 muscles are we referring?
"Prevertebral" Muscles:
1. Rectus Capitis Anterior (short)
2. Rectus Capitis Lateralis (short)
3. Longus Capitis
4. Longus Colli
Your patient presents to the clinic with dizziness when she looks over her left shoulder, you decide to perform the Swivel Stool test and find the following:
Eyes Closed turn to the left = Dizzy
Eyes Open with Body Swivel to Right = Dizzy
Eyes Open with Head Turn to Left = Dizzy
What system is affected?
Mechanoreceptors of the Neck
What are the 5 D's and 3 N's associated with Vertebrobasilar Artery Insufficiency?
Dizziness
Dysarthria
Diplopia
Dysphagia
Drop Attacks
Ataxia
Nystagmus
Nausea
Numbness
Briefly what are the QTF Classifications for WAD?
(Hint: starts at 0 and goes to 4)
0: no symptoms of neck pain, no physical signs
1: pain/stiffness/tenderness, no physical signs
2: decreased ROM, point tenderness, neck symptoms
3: (see above), decreased/absent DTR, muscle weakness, sensory deficits
4: neck symptoms, fracture/dislocation
Spend time on notes to differentiate A, B, C WAD2 Classifications
With each of the following impairments that may be seen in different categories of concussions, list 1 appropriate intervention:
- Cervical MSK- Vestibulo-Ocular
- Autonomic Dysfunction/Extertional Intolerance
- Motor Function
Cervical MSK:
- manual therapy to address restrictions in joint mobility + muscle length
- therapeutic exercise for DNF endurance and periscap strength
- postural education
- joint proprioception
Vestibulo-Ocular:
- referral if more oculomotor + not responding to interventions
- convergence insufficiency intervention
- canal repositioning maneuvers (CRM) for BPPV- gaze stability retraining
-habituation for motion sensitivityAutonomic Dysfunction/Exertional Intolerance:
- aerobic exercise protocol (based on Buffalo Concussion Test) -- start at 20 mins/day at 80-90% HR thresholdMotor Function:
- postural control retraining- dual tasking practice
- sensory re-organization
- sports specific tasks
- work specific tasks
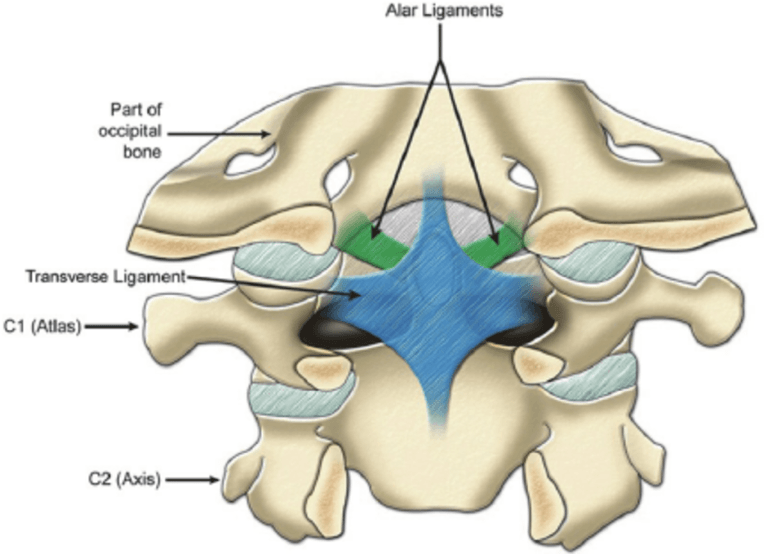
We are familiar with the Alar and Cruciate (Transverse) Ligaments, name the other important ligaments that are prominent in the cervical spine.
Ligamentum Nuchae
Ligamentum Flavum: helps check flexion
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament (ALL): helps check extension, thin in C Spine
Posterior Longitudinal Ligament (PLL): helps check flexion, wide in C Spine
Interspinous Ligaments: helps check flexion

What are the 7 components of an oculomotor exam?
Alignment
Spontaneous Nystagmus
Gaze Evoked Nystagmus
Extra-Ocular Movements
Saccades
Pursuit
Vergence/Accommodation
A patient with what previous medical history is at increased risk of developing cerebral artery dysfunction?
Past history of CVA
Arteritis
Atherosclerosis
Pre-Disposed to Strokes (high stroke risk factors)What two risk factors have the greatest prognostic value for persistent problems following a whiplash incident?
High Pain Intensity
High Self Report Disability
Side Note:
other risk factors incl...
- high post traumatic stress
- strong catastrophic beliefs
- cold hypersensitivity
What tests and measures are appropriate for the Motor Function category of the APTA's Concussion CPG?
CTSIB
DGI
FGA
HiMAT
TUG Cog
In Vladimir Janda's Upper Crossed Syndrome, which muscles are inhibited and facilitated?
Inhibited: neck flexors, rhomboids, serratus anterior, lower traps
Facilitated: pectoralis, SCM, upper traps, levator scap
What are appropriate interventions for cervical spine with clinical instability? (Name at least 1)
Coordination Exercises
Strengthening Exercises
Endurance Exercises
Stretching Exercises
Mobilization/Manipulation Above + Below Hypermobility (not as effective as exercise)
Ergonomic Corrections
What are the SIX red flags related to the Cervical Spine?
Cervical Fracture (see Canadian C Spine Rules)
Upper Cervical Instability
Cervical Artery Dysfunction (5 D's and 3 N's, stroke risk, CN)
Neoplastic Conditions (age > 50, cx hx, thoracic sx, unexplained weight loss, constant/night pain)
Systemic Inflammatory/Infectious Disease (abnormal vitals, fatigue, fever)
Cervical Myelopathy (dexterity loss, sensory disturbance, muscle wasting in hands, pathological reflexes, clumsy gait, incontinence)
What is the appropriate dosing when focusing on DNF training, deep neck extensors, and postural muscles in order to help with motor retraining, postural correction, and pain inhibition?
Frequent and short doses --> 10 repetitions performed 4-5x/day
This Concussion CPG category exam consists of ligamentous testing and VBI followed by JPE and Swivel Stool Testing
Cervical Musculoskeletal Function
What two major arteries pass through the anterolateral neck?
Carotid (common carotid splits into internal and external)
Vertebral
Side Note:
- both susceptible to injury/disruption BUT vertebral > carotid
- contralateral upper cervical ROT will stress vertebrobasilar blood flow
What three examination techniques are unique to the category Neck Pain with Movement Coordination Impairment?
Cranial Cervical Flexion Test (using BP bladder)
Neck Flexor Endurance Test (between 3-8 seconds is the lower end of the cut off threshold)
Joint Position Error (performed 3 ft away from bullseye target)
Side Notes:
Also expect the following
- neck pain at end range/worsens at end range
- myofascial trigger points (MTP)
- pain can be provoked at involved segments
Cervical Myelopathy is considered a red flag finding and requires immediately referral out; it typically presents with weakness below the area of compression, sensory changes in one or both hands, abnormal reflexes, clumsy gait, and extra-segmental distribution of signs/symptoms; what is the Cervical Myelopathy Test Cluster to rule out myelopathy?
Age > 45 years old
Hoffman's Reflex
Babinski Reflex
Inverted Supinator Reflex
Gait Deviation
If 4/5 are (-) the probability for myelopathy are low
Individuals with WAD 1 (neck symptoms of pain, stiffness, tenderness with no physical signs of injury) have been observed to recover in what amount of time?
(Typically) Recovered in 6 months
Additional Notes:
- WAD 2 has mod-severe range of symptoms and typically takes > 6 months to recover
This Concussion CPG Category exam consists of head thrust, DVA, Dix-Hallpike or Roll Test, and an Oculomotor exam
Vestibulo-Ocular Impairments
 Name the structure the uppermost line points to
Name the structure the uppermost line points to
Dens/Odontoid Process: occupies the area where C1 body would be, it is held in place there by the transverse ligament
Across the craniocervical region, what is the total expected flexion, extension, axial rotation, and lateral flexion?
Flexion: 40 degrees (textbook); 45-50 degrees (PPT slides)
Extension: 50 degrees (textbook); 85 degrees (PPT slides)
Axial Rotation: 49-51 degrees (textbook); 90 degrees (PPT slides)
Lateral Flexion: 22 degrees (textbook); 40 degrees (PPT slides)
What symptoms might you look for in a patient with neck pain secondary to a systemic disease, such as infectious meningitis?
Fever
Severe and unrelenting HA
Confusion
Photophobia
Vomiting
Stiff Neck
Side Notes:
- no trauma
- worsening
- young age
- community living
- immunocompromised
What changes might be seen on radiographs in an individual status post whiplash injury?
Curvature Changes of the Spine
- Rear impact: T and L spine curvatures straighten + flexion of upper C spine
- Front impact: extension of upper C spine + hyperflexion at lower C spine
- Side impact: upper and lower C spine lateral bending in opposite direction, more severe vs frontal MVC as more energy is transferred to patient in accident
BONUS: increase atlantodental interval widens -- increase in space between atlas and dens, would indicate compromised transverse ligament and present as positive Sharp Pursor Test
Your patient is demonstrating Autonomic/Exertional Intolerance type Concussion; according the to CPG what tests and measures might have been conducted on this patient to arrive at diagnosis of this category?
Lots of vitals (at rest vs with activity vs orthostatics)
Buffalo Concussion Treadmill test
The C Spine is unique for several reasons, one of which is the way in which nerves roots exit the spinal column; do they exit above or below the vertebrae for which they are named?
Above
(transition occurs after C7)
What type of posture may be observed in an individual with Upper Crossed Syndrome?
Shoulders and Chin Forwards
Increased Kyphosis
Describe the Neoplastic/Cancer Cluster that has a very high sensitivity to RULE OUT cancer
Age < 50
No history of cancer
No weightloss
Improves with conservative care
When does most recovery generally occur in WAD?
First 3 months
What are the 4 domains of concussion identified in the APTA's CPG?
Cervical Musculoskeletal Function
Vestibulo-Oculomotor Function
Autonomic Dysfunction/Exercise Intolerance
Motor Function (incl motor coordination and control, dual tasking)
What are the two primary ligaments of the upper cervical spine? (think C1 & C2)
Cruciform Ligament (aka transverse ligament and its vertical components)
Alar Ligament
What are the neck pain classifications as identified by the 2017 CPG?
Neck Pain with Mobility Deficits
Neck Pain with Movement Coordination ImpairmentsNeck Pain with Headaches
Neck Pain with Radiating Pain
You are working with a 68 year old patient who comes to you with general low C/upper T spine pain that has been steadily worsening since the onset. She states that there was no injury and she's felt it coming on gradually for a while, it keeps her up at night as she absolutely can't get comfortable. As you are palpating her vertebrae, you note that they are extremely prominent and easy to identify; when asked about this presentation she notes that she recently lost some weight and none of her clothes fit. What is the red flag?
You are working with a 68 year old patient who comes to you with general low C/upper T spine pain that has been steadily worsening since the onset. She states that there was no injury and she's felt it coming on gradually for a while, it keeps her up at night as she absolutely can't get comfortable. As you are palpating her vertebrae, you note that they are extremely prominent and easy to identify; when asked about this presentation she notes that she recently lost some weight and none of her clothes fit.
Neoplastic Condition
What symptoms are associated with WAD (name at least 1)
Neck Pain
Headache
Tingling/Numbness/Arm painThoracic and Lumbar spine symptoms
A patient who has suffered a concussion can experience a wide variety of symptoms, name at least 3 applicable symptoms
Headache
Neck Pain
Nausea/Vomiting
Visual Disturbances
Dizziness
Fatigue
Sleep Disturbances (falling asleep, sleeping more/less than usual)
Sensitivity to light (photophobia)/noise (phonophobia)
Irritability
Difficulty Concentrating/Remembering