This assessment depends on the child's cognitive, emotional and physical development, managed by atraumatic, non-pharmacological and pharmacological interventions.
What is pain assessment or pain management
*Remember pain assessment tools and principles of pain management*
Establishing a therapeutic relationship is the foundation, in addition to early discharge planning, establishment of early intervention services and complementary therapies. The nurse recognizes the importance of these nursing interventions in the care of this category of children.
What is the care of the child with special needs?
These are priority nursing interventions in a pediatric emergency.
What are: Assess airway, breathing & circulation, then perform a rapid head-to-toe assessment?
*Remember the order in which you do these depends on the scenario*
The term used to describe end of life care.
What is hospice care?
Asking a child to return to his or her room prior to taking a blood pressure, then escorting the child back to the playroom is an example of this principle.
What is principle of atraumatic care?
*Remember application of this principle*
Monitor the child’s behavior, assist in using stress management techniques, and implement appropriate memory retraining techniques, such as keeping a calendar, writing list, memory cue games, and mnemonic devices to encourage the expression of feelings of frustration or helplessness. These are all useful in evaluating the outcomes of this condition.
What is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)?
Changes in altitude, dehydration, fever, and infection are risk factors for this condition.
What are risk factors for sickle-cell crisis?
A infant weighing 3.2 kg at birth, should weigh this much in lbs at 6 months of age, if the infant has followed the usual pattern of growth.
What is 14 lbs?
Placing mobiles, medications and cleaning products out of reach to prevent injury and maintain safety are priority interventions for this age group.
What are priority nursing interventions for a mobile infant or toddler?
These nursing care interventions are included in the nursing management of a dying child.
What are:
Caring for the family as a unit, managing pain and discomfort, providing nutrition, providing emotional support to child and family and assisting the family through the grief process?
This is the order in which assessment (including vital signs) should be performed for infants/children.
What is least invasive to most invasive /head to toe?
Example: Respiratory rate, heart rate, weight/height/length, and axillary temperature?
These are two ways to evaluate the outcomes for a child with burns.
What are weight gain, normal peripheral pulses, balanced intake and output, increased albumin, child participation in dressing changes, and verbalized controlled pain?
An abnormal glascow scale, changes in vital signs, increased pain, restlessness and posturing. The nurse recognizes these symptoms as important in the diagnosis and treatment of a disorder of this body system.
What is neurologic injury/disorder?
In this age group, milestones include walking with legs planted widely apart and toes pointed forward. Swaying from side to side, falling often, using their senses to explore the world around them, a vocabulary of 50 words are all motor, communication, and sensory development for this age group.
What is a toddler (specifically what is expected for a 24 months old)?
The nurse is caring for a child with a fractured arm. The nurse would prioritize these two interventions.
What are peripheral vascular checks and pain management?
This is the goal of nursing care of a child with chronic illness.
What is:
Assist family in shaping the course of the illness while maintaining quality of life for the child and family.
Clustering care to prevent exertion or energy expenditure is an important aspect of care for pediatric patients with these two body systems disorders.
What is care of the child with a respiratory or cardiovascular disorder?
Treatment of this condition stops when the epiphyseal plates close.
What is the evaluation of outcomes for a child with growth hormone deficiency?
As indications of body functioning, these measurements of the body's fundamental physiological functions provide essential information about basic body functioning. These signs are crucial indicators of a child's overall health status and help healthcare professionals assess and monitor various physiological processes.
What are pediatric vital signs?
*Review vital signs so you can recognize when there is something not right*

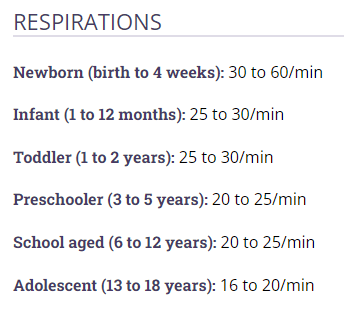
A 1 year old presents with fussiness, HR 120, RR 48, T 101.2,SPO2 of 91% on room air, accessory muscle use and nasal flaring. The nurse identifies these findings as consistent with this nursing problem.
What is acute respiratory distress?
For this subset of children, nursing care includes developing a therapeutic relationship, promoting growth and development, providing care coordination, screening and provision of nutritional needs, providing education and support for the child and family and assisting in the transition to adulthood.
What is the nursing care of a child with special or chronic needs?
In this type of care, the principles/goals are:
Alleviating physical, psychological, emotional, and spiritual suffering, medication management, respecting children’s goals, preferences, and choices, comprehensive caring, using the strengths of interdisciplinary resources, acknowledging and addressing caregivers’ concerns, and building systems and mechanisms of support.
What are the principles of palliative care?
These atraumatic interventions should be included in the plan of care for a child expected to undergo IV therapy.
(Name three interventions)
What are :
-assess site
-consider long term IV for antibiotic therapy courses over 10 days
-Consider removing and restarting an IV for a child with pain at the IV site
*Remember that applying warm compresses or EMLA cream may alleviate the IV site pain but won't fix the situation (phlebitis etc)*
After environmental modifications are made, a child will remain free from harm. This is a positive evaluation of outcomes for which 3 categories of disabilities?
What are intellectual, physical, or behavioral disabilities?
These are signs of dehydration in pediatric patient (name three)
What are:
- few or no tears when crying (late)
- dry mouth (moderate)
- eyes that look sunken (late)
- anterior fontanelle is sunken.
- peeing less or fewer wet diapers than usual (less than 1 ml/kg/hr) (late)
- crankiness (mild)
- weight loss
- no urine output(late)
- elevated heart rate (moderate)
- low blood pressure (late)
- capillary refill is greater than 2 seconds (late sign if greater than 4 seconds)
- skin tenting (late)
*Remember your nursing care for dehydration and how to know your interventions worked*
This age group views dying as temporary because of magical thinking.
What are preschool children?
Preventing spinal injury is the priority intervention for a child involved in this.
What is the priority intervention for a child involved in a motor vehicle accident?
These interventions should be included in the teaching plan of a child with an acute gastrointestinal disorder.
What are:
Inform day care or school of infections
Utilize oral rehydration therapy
Avoid fruit juices, sodas, caffeine
Teach prevention through immunization
Provide skin care to prevent skin breakdown
Perform proper hand hygiene
Prevention with proper vaccination *i.e rotavirus vaccine
This type of care involves the promotion of good communication with the health-care team, management of pain and discomfort, creating a peaceful and comfortable environment, assisting the child to die with dignity, ceasing unnecessary treatments, and allowing the family to express their end-of-life care wishes
What is caring for the a child during the dying process?
Hydration status, PT/PTT, INR levels, AST/ALT levels, response to vitamin K administration, recovery from liver biopsy, seizure activity, and understanding the need to avoid administration of aspirin (including over-the-counter products) when a viral infection is suspected are all included in the evaluation of outcomes for this condition.
What is the evaluation of child with Reye Syndrome?
This scale is used to assess the level of consciousness of children. It comprises of three tests: eye, verbal and motor responses. The three values separately as well as their sum are considered.
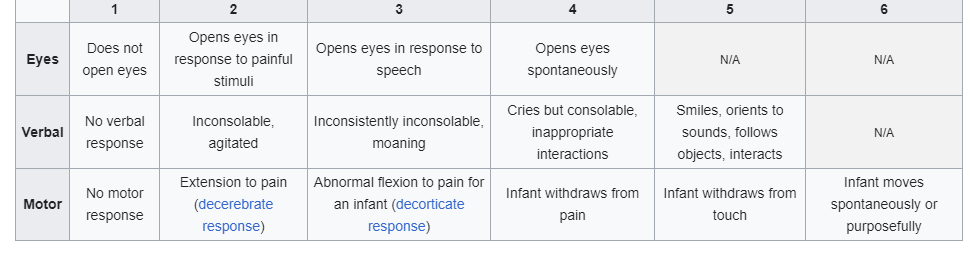
Any combined score of less than eight represents a significant risk of mortality. A score of 12 or below indicates a severe head injury. A score of less than 8 indicates that intubation and ventilation may be necessary. A score of 6 or below indicates that intracranial pressure monitoring may be necessary.
What is the pediatric glascow scale?
*
These are two common pediatric renal disorders listed in your ATI book. The first condition is caused by a recent strep infection, and the other can be genetic.
What are nephrotic syndrome and acute glomerulonephritis?
*recognize risk factors, signs and symptoms and what to do about what you find*
These frameworks are utilized when prioritizing care (name three).
What are :
1. Urgent vs non-urgent
2. Acute vs chronic
3. Stable vs unstable
4. Safety vs risk reduction
*Remember that a patient with an acute need is given priority as they may pose a threat*.
*An unstable patient is priority because they have needs that pose a threat to the client’s survival. *
*Safety/risk reduction assigns priority to the situation with the greatest safety risk and the greatest risk to physical or psychological well-being
Communicable diseases are easily spread through droplet, airborne, or direct contact . These (name three) communicable diseases require more than standard isolation precautions during hospitalization.
What are
Airborne/contact: varicella
Droplet: rubella, fifth disease, pertussis, mumps
*Know which precaution to apply to what scenarios*
Administration of these stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies against specific diseases to decrease or eliminate certain infectious disease in society and prevent infectious diseases and their complications.
What are vaccines?
*Remember what vaccines are given at what age*
When caring for a child with an immunologic disorder, the nurse must employ a plan of action and know if the plan of action (interventions) is effective. These (name two each) interventions are included in caring for a child with an immunologic disorder.
What are:
Administer analgesics and antipruritics as ordered.
Administer immunologic or corticosteroids as ordered.
Apply cool compresses or luke warm water to areas of pruritus.
Provide fluids frequently.
Dress the child in light clothing.
Use diversional activities and distraction.
Monitor skin for color changes, temperature, redness, swelling, warmth, pain or signs of infection, changes in rash lesions, distribution, or size.
Identify allergic/anaphylactic reactions and intervene appropriately
Encourage fluid intake and proper nutrition.
Keep child’s fingernails short.
Encourage child to press on rather than scratch the area of pruritus.
Use topical ointments or creams as ordered.
Educate on prevention of infection.
Encourage appropriate vaccinations