This is the end product, made up of amino acids, is the end product of the central dogma.

What are proteins.
(polypeptide chains a partial credit answer)
This is the definition of a mutation.
What is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a genome of an organism or extra chromosomes.
Genes are made up of DNA found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. All genes are located in THESE tightly coiled structures of DNA wrapped around histones.
What is a chromosome
Skin tone, eye color, height.
Any set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism.
Traits or physical features also expectable answer.
In a Eukaryotic cell, DNA is always found here.
What is the nucleus!
This first step of protein synthesis occurs in the nucleus.

What is Transcription.
This type of mutation involves a change in nucleotide bases that has no impact on the final amino acid chain. It is neither harmful or beneficial.
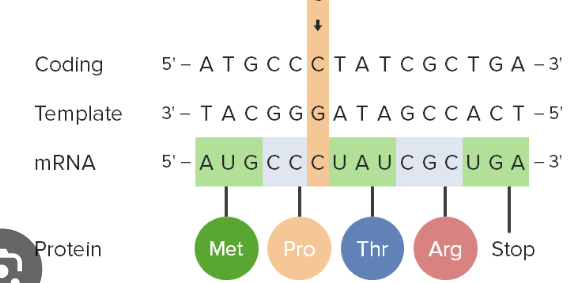
What is a silent mutation.
This is the term for a variation in the genes for a trait.
What is an allele.
Cells that are diploid and not involved in reproduction are called this.
What is a Somatic Cell.
This number of nucleotide bases are found in a CODON.
What is three.
This second step of protein synthesis happens in ribosomes found in the cytoplasm of the cell.
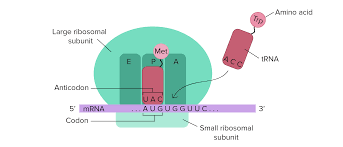
What is Translation.
This the type of gene that Sickle Cell impacts.
What is hemoglobin.
Genes are passed down from biological parents to offspring. Because of this each gamete cell only has this many unpaired chromosomes.
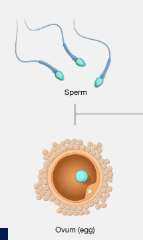
What is 23 or half!
Blue eyes is a recessive trait. When two parents have blue eyes this/ these eye color(s) their offspring will have (unless there are mutations).
Any why!
Since blue eyes are recessive it means that both parents are homozygous for blue (both have blue alleles).

The following nucleotide sequence of DNA would code for what sequence of mRNA:
A T T C G G T G A
DNA: A T T C G G T G A
mRNA: U A A G C C A C U
This strand of nucleotides travels out of the nucleus and into the ribosomes for tranlsation.
What is mRNA.
This type of mutation results in a premature stop codon resulting in a shorter, incomplete protein.

What is a nonsense mutation.
A person will have this gene combination does a person need to have protection against malaria.
What is heterozygous for sickle cell disease - one normal hemoglobin and one sickle cell gene.

This is the phenotype of being homozygous for the sickle trait.
What is sickle cell disease.
The following two mRNA codons translate to these two amino acids:
AUG CAU 
What are:
MET (start codon and first amino acid)
HIS
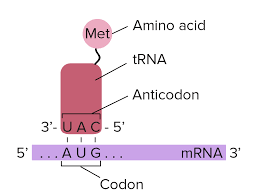
This is the location and role of tRNA in the central dogma.
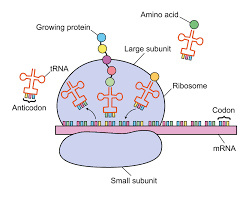
tRNA located in the cytoplasm enters the ribosome and the anticodon of tRNA pairs with the corresponding codon of the mRNA. The tRNA carries an amino acid that matches with the codon.
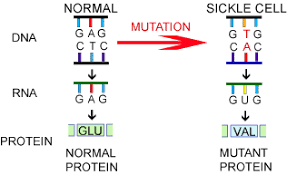
Sickle cell disease, is this type of mutation to the hemoglobin gene that results from the amino acid VAL being translated instead of GLU. This change in amino acids causes the abnormal "sickle" hemoglobin shape.
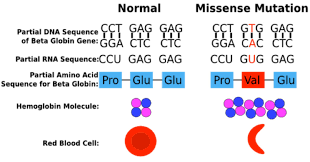
What is missense mutation.
This is a 3-5 sentence explanation of how genes, alleles and chromosomes related!
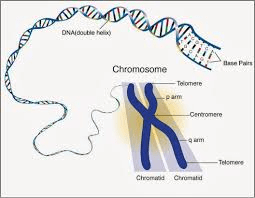
What is.....
Chromosomes are made up of DNA wound around histones and located in the nucleus. Humans have 46 chromosomes arranged in 23 pairs. Genes are segments of DNA that code for proteins that control specific traits (such as eye color) and alleles are the different variations of that particular gene (blue vs. brown eyes).
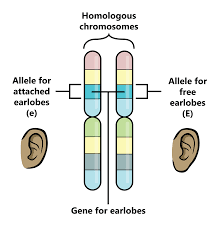
This is the phenotype AND outcome of that phenotype for someone with the genotype for sickle cell disease.
What are "sickle" or "moon" shaped red blood cells that make it more difficult to carry oxygen around the body.
This is how many nucleotide bases it would take to code the following polypeptide chain of amino acids (hint there is also a stop codon involved)
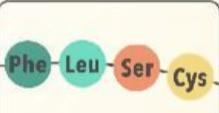
What is 15.
1 amino acid = 1 codon = 3 nucleotide bases
4 amino acids x 3 bases = 12 bases
A stop codon tells tells translation to stop because this chain is done. So we would add one more codon that does not get translated into an amino acid 'bead.
4 amino acids + a 1 stop codon = 5
5 x 3 = 15
Example:
Phe is coded by codons UUU or UUC