Pap smear
secondary prevention
Designation as to the nature of cause of a health problem
diagnosis
the study of the body's response to dysfunction or disease
Pathophysiology
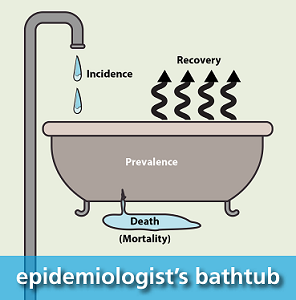
epidemiology bathtub
Type of study where a group of people born about the same time are followed over several years, such as the Framingham Study
Longitudinal or cohort study
immunizations
primary prevention
The extent to which an observation when repeated gives the same result
reliability
An interrru0ption, cessation, or disorder of a body system or organ structure
Disease
the number of new cases arising in a population at risk during a specified time
Incidence
simultaneous collection of information necessary for classification of exposure and outcome status.
Cross sectional study
use of beta adrenergic drugs after a heart attack
tertiary prevention
The extent to which a measurement tool measures what it is intended to measure
validity
the cause of disease
Etiology
a measure of existing disease in a population at a given point in time
Prevalence
What makes up the epidemiological triangle?
Host, environment, and agent
educating on use of wearing a helmet while riding a bike
primary prevention
determining the likelihood or how well the test or observation identifies people with or without a disease
sensitivity and specificity
the existence of two or more chronic diseases
co-morbidities
death rate in a population from a particular disease
mortality rate
the conscientious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients
Evidence based practice
taking tuberculosis drugs after having a positive ppd
tertiary prevention
the extent to which an observation or test result is able to predict the presence of a given disease or condition
Predictive value
How the disease process evolves
pathogenesis
the effects of an illness has on a person's life. Concerned with the long term consequences and effects of the disease on quality of life
Morbidity
These guidelines are systematically developed to inform practitioners in caring for patients with a particular disease. Often have algorithms
Clinical practice guidelines