Circulation
Increased Pulmonary Flow
Decreased Pulmonary Flow
Obstructed Systemic Flow
Interventions/assessments
100
Murmur intensity is based on this scale.
What are Grades I through VI?
100
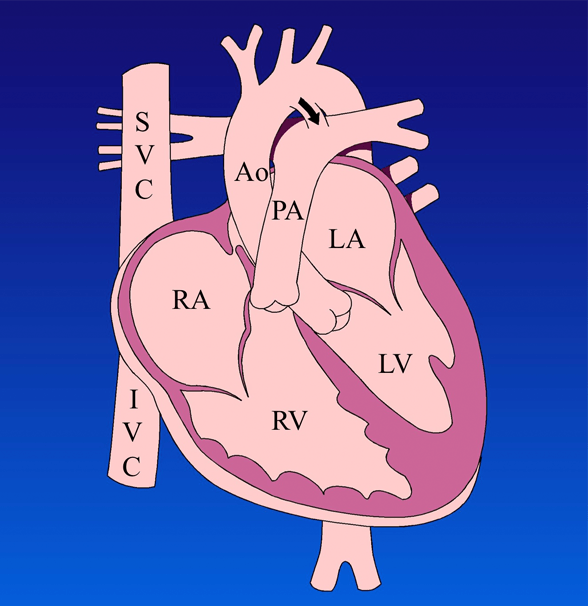
What is a Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)?
100
This defect causes right ventricular hypertrophy and requires balloon dilation of the valve during cardiac catheterization to correct.
What is Pulmonic Stenosis?
100
This defect can cause higher pressures and bounding pulses in the arms.
What is Coarctation of the Aorta?
100
This severe form of pulmonic stenosis presents with severe cyanosis at birth.
Pulmonary Atresia
200
Stroke volume is limited in the infant due to poor muscle compliance. This results in cardiac output being regulated by one factor.
What is the heart rate?
200
This is the most common anomaly causing increased pulmonary blood flow.
What is a Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)?
200
This may be noted due to the overproduction of red blood cells by the bone marrow as a response to hypoxemia.
What is polycythemia?
200
Poor color, delayed cap refill, diminished pulses, and decreased urine output is reflective of this in a child with a defect causing decreased obstructive systemic blood flow.
What is Decreased Cardiac Output?
200
Necrotizing enterocolitis may be found in an infant suffering from decreased blood supply to the GI tract, such as is found with this category of CHDs.
What is obstructed systemic flow?
300
Bradycardia and potential cardiac arrest can sometimes be avoided by appropriately managing this.
What is hypoxia?
300
IV Indomethacin or IV Ibuprofen can be used for this purpose.
To facilitate closure of the Patent Ductus Arteriosus.
300
These four defects are present with Tetralogy of fallot.
What are Pulmonic Stenosis, VSD, Overriding Aorta, and RV hypertrophy?
300
Systemic blood flow in a child born with Hypoplastic Left Heart initially depends on administering this medication to ensure patency of the ductus arteriosus.
What is Prostaglandin E1?
300
Calming measures, Blow-by oxygen, knee-chest position, and IV Morphine.
What can be done to relieve a hypercyanotic spell or "tet spell".
400
This type of murmur causes a palpable thrill.
What is a Grade IV murmur?
400
Oxygenated blood flows from the Left Atrium to the Right Atrium when this defect is present.
What is an Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)?
400
Cyanosis at birth does not improve with oxygen administration when this defect is present.
What is Transposition of the Great Arteries?
400
You win
400
CHF and Pulmonary Edema can result from this category of congenital heart defects.
What are defects that cause obstructive systemic flow?
500
Respiratory distress syndrome or hypoxemia in the premature infant often results in this congenital cardiac defect.
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
500
This defect can easily lead to congestive heart failure as a result of blood shunting from the high pressure left ventricle to the right ventricle.
What is a VSD?
500
Children with TOF may assume a squatting position during a "tet spell" in order to decrease this.
What is systemic venous return (SVR) to the heart?
500
No, you win
500
This is a significant warning sign in infants and children that cardiac arrest is imminent.
What is bradycardia?