
What is the diagnosis?
Tumid lupus - presents with indurated, edematous, erythematous, often annular plaques without epidermal involvement, typically on face and trunk
on a spectrum with Jessner's (similar clinical appearance) and reticular erythematous mucinosis (identical histologic appearance)
anti-ssDNA is associated with what disease?
Linear morphea; correlates with disease severity/activity
also associated with risk of developing SLE in DLE patients
Which antimalarial does not have associated retinal toxicity?
Quinacrine

Name three autoantibodies associated with this condition
Neonatal lupus is associated with anti-Ro (SSA), anti-LA (SSB), anti-U1RNP.
What percentage of patients with DLE progress to SLE?
5-20%
5% for patients w/ head-only involvement; 20% for patients with diffuse involvement

What is the diagnosis? Bonus: what autoantibody is most often positive?
Rowell's syndrome - targetoid lesions clinically resembling EM arising in setting of ACLE, SCLE, or DLE
typically Ro/SSA+
What is the most specific autoantibody for Sjogren syndrome?
alpha-fodrin is the most specific
others: anti-Ro (SSA), anti-LA (SSB)
Which antimalarials should not be given together?
hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine - both can lead to retinal toxicity
A woman has a child with neonatal lupus. What is the chance her subsequent child could be similarly affected?
25%
HCQ throughout pregnancy can decrease risk of child with cardiac NLE; prenatal steroids may also decrease risk of developing congenital heart block
Patients with hypertrophic CCLE are at risk for what?
SCC (akin to hypertrophic LP)

This finding is associated with which auto-antibody?
Anti-MDA5 (also known as anti-CADM-14)
Associated with rapidly progressive ILD, skin and oral ulcers, palmar papules
This autoantibody is highly SPECIFIC for SLE and is associated with lupus nephritis.
Anti-dsDNA (double stranded DNA) is highly specific for SLE and is a/w lupus nephritis.
Another highly specific antibody for SLE is anti-Smith (Sm) antibody.
You start a patient on hydroxychloroquine. What is the recommended frequency of ophthalmologic exams?
Baseline, within first year of starting therapy, yearly after 5 years of treatment (should include visual acuity and dilated exam)

What cytokine is upregulated?
Diagnosis: morphea (en coup de sabre variant)
TGF-beta (pro-fibrotic)
others: IL-4, IL-6
What are the 2 HLA subtypes associated with SCLE?
HLA-B8 (strongest association), HLA-DR3
"Beats by Dre"

A patient on hydrochlorothiazide develops this eruption. What autoantibody is likely to be positive? Bonus if you can name another drug culprit!
anti-Ro (SS-A) in 80%; anti-LA (SS-B) also seen
other causes of drug-induced SCLE: terbinafine, griseofulvin, NSAIDs (piroxicam), CCBs, antihistamines, PPIs, docetaxel, ACE inhibitors, TNF alpha inhibitors (MC etanercept)
Which autoantibody is associated with cardiac involvement in dermatomyositis?
anti-SRP (signal recognition particle) -- poor prognosis
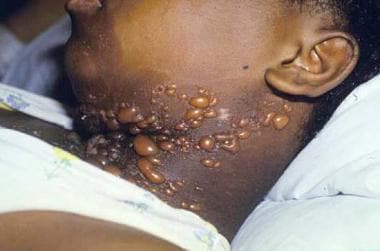
ELISA testing is positive for autoantibodies to collagen VII. What is the treatment of choice?
Dapsone (treatment of choice for bullous lupus)
what autoantibody is associated with juvenile DM with calcinosis?
anti-p140 (NXP2) - also associated with contractures in kids
What is the most common complement deficiency associated with SLE?
C2 (overall low risk of developing SLE, 10-20%, but is much more common)
In contrast, C1q, C1r/s and C4 deficiencies are very rare but have a very high risk of developing autoimmune disease.
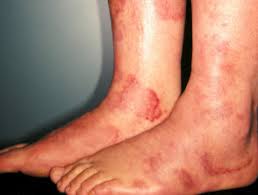
This patient has low CH50. What autoantibody is positive?
C1q - seen in ~100% of patients with hypocomplementemic urticarial vasculitis.
Anti-C1q autoantibodies are also associated with lupus nephritis.
Name 3 aminoacyl tRNA synthetase autoantibodies associated with dermatomyositis.
anti-Jo1, anti-PL7, anti-PL12, EJ/OJ
anti-synthetase syndrome: myositis, mechanic's hands, arthritis, Raynaud's phenomenon, severe ILD.
Name 3 potential skin-related side effects of antimalarials.
yellow pigmentation of skin (quinacrine); drug induced LP; morbilliform hypersensitivity eruption (higher risk in dermatomyositis), psoriasis exacerbation, blue-gray to black hyperpigmentation particularly on shins, nail hyperpigmentation
What are the two variants of juvenile dermatomyositis?
Classic JDM (Brunsting variant) - most common, classic skin and muscle disease, has frequent calcinosis cutis, corticosteroid responsive
Vasculopathic/ulcerative JDM (Banker variant): rare (<10%), rapid onset severe muscle disease, severe vasculitis with cutaneous ulcerations, livedo reticularis, muscle infarction, GI ulceration/perforation; recalcitant to steroid therapy w/ poor prognosis
A positive lupus band from biopsy of sun protected, non-lesional skin is associated with what autoantibody?
anti-dsDNA (a/w severe extracutaneous disease including renal disease)