Which statement is true according to the law of conservation of energy?
a. energy can be created
b. energy can be destroyed
c. energy can change forms
c. energy can change forms
Energy CANNOT be created or destroyed; energy CAN change forms (ex. electrical to heat)
What type of energy transformation takes place in hydroelectric power plants?
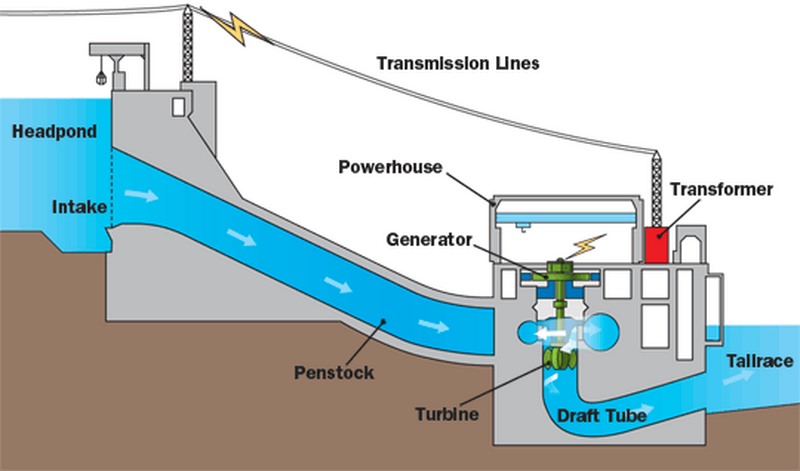
mechanical energy (of the moving water which moves a turbine) transforms into electrical energy.
Brianna is working to design a soccer ball that conserves all of its kinetic and potential energy. She drops the ball to the ground from a height of 2 meters. If it really works, how high should the ball bounce?
EXACTLY 2 meters. (We are assuming no air friction or resistance. Yeah, that's a big assumption.)
What word do we use to describe the amount of energy output we get in relation to the amount of energy input that goes in to a system?
Efficiency
Efficiency= Work Output/Work Input x 100
What unit do we use to measure energy?
Joules
What happens to the total energy in a closed (or isolated) system?
The total energy is conserved (meaning it does not change.)
The energy into the system = energy out of the system.
There is chemical energy in the food you eat.
How much of the energy is transformed into heat, other chemical forms in your body, used to help you move, or leftover as waste or fat?
ALL of the chemical energy is transformed.
(Remember energy cannot be created or destroyed.)
You are at a science museum and see a pendulum in the center of the foyer. The weight of the pendulum is hanging from the middle of the ceiling by a rope. It is a children's museum so you assume you are allowed to touch the weight. While your dad is not watching you lift the weight to your height of 1.6 meters. If the kinetic and potential energy of the pendulum weight is completely conserved, what should its height be when it swings back to you?
The weight will return to the same height it was released which was 1.6 meters.
At the bottom of a half pipe, the kinetic energy of the skater is 45 J. What is the mechanical energy? (Assume no energy is "lost" to heat or sound)
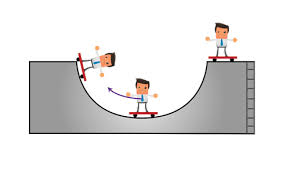
At the bottom, the PE would be zero and the KE would be at it maximum (45 J).
ME= PE + KE
ME= 0+45
ME= 45 J
Which takes more thermal energy to heat:
sand or water? (remember sea breeze & land breeze)
It takes more thermal energy to heat water. That is why though the sun's radiant energy hits each at the same time, the water takes longer than the sand to heat up.
What does the term “conservation” mean in regards to energy?
Energy is not created or destroyed, the same amount is always present in some form.
Luke pushes a Red Bull derby car, giving it kinetic energy. When this happens, what happens to the amount of energy in Luke's arm?

Luke's arm lost energy.
A car is in motion when the driver applies the brakes, causing the car to stop. What happened to the kinetic energy of the moving car?
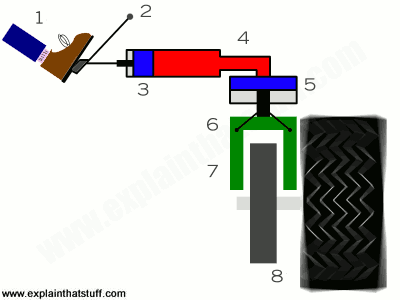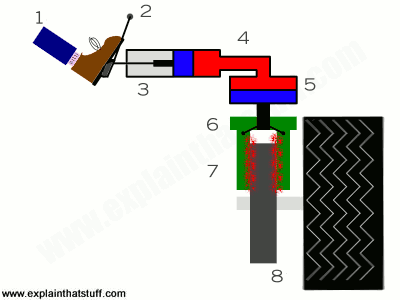
The kinetic energy was transferred to another form such as heat (when the brake pad touches the brake disc, friction between the two generates heat)
What is the potential energy of a 10 gram ball that is held 2 meters above the ground?
A. 20 Joules
B. 196 Joules
C. 19.6 Joules
D. 200 Joules
B. 196 Joules
PE= mgh (10)(9.8)(2)
A can of soda with at room temperature (23 C) is placed in a refrigerator with a lower temperature. Which direction will heat energy flow?
The heat energy will flow from the soda to the refrigerator air. (warmer to cooler)
A parked car begins to move when the driver presses the accelerator. How is energy conserved in this situation?
The energy of the car's fuel (potential chemical energy) is changed or transferred to kinetic energy (mechanical energy).
At what point or points is the kinetic energy equal to zero?
N and L
A student is holding a pumpkin at a height of 2 meters. The pumpkin has 50 joules of potential energy and 0 joules of kinetic energy.
The pumpkin is released from that height. How much potential and kinetic energy does the pumpkin have right before it hits the ground?
The pumpkin will have 50 joules of kinetic energy and 0 joules of potential energy.
What is the kinetic energy of a 30 gram ball that is rolling at a speed of 2 meters per second?
A. 120 J
B. 60 J
C. 30 J
KE= .5mv2
KE = (.5)(30)(22)
KE = 60J
A. 60J
A ball is thrown up into the air. When it gets to the very top, what kind of energy does it have? BE VERY SPECIFIC!
gravitational potential energy
When Alex kicked a soccer ball, the ball gained energy and Alex lost energy. The amount of energy the soccer ball gained is _____________ the amount of energy that Alex lost.

equal to
Emma is heating three pots of water on the stove. Each pot is the same size, material, and is set to the same heating level. Each pot has a different amount of water. Which pan of water will take the least energy to bring to a boil?
The pot with the smallest amount of water will take the least amount of energy to boil.
Ms. Norris lifts up her coffee cup and places it on the front demonstration table. The cup gained gravitational potential energy. Where did this energy come from?
The energy the cup now has (gravitational potential energy) came from the work Ms. Norris put into the cup lifting it onto the table.
An object is 5 meters off the ground and has a potential energy of 200 Joules. What is the mass of the object? :) Round to the nearest whole number.
m = 4 kg
PE= mgh
200J = m(9.8)(5)
200J=49m
m= 4 kg
What term refers to a group of objects that transfer energy only to each other and not to the environment around them?
A closed system