What travels along the neurons?
electrical impulses
Glucagon is secreted by the?
Pancreas
What is homeostasis?
The maintenance of a constant internal environment.
What is a reflex arc?
the pathway through the body that brings out a reflex action
What is a drug?
A drug is any substance taken into the body that modifies or affects chemical reactions in the body.
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of?
Brain and spinal chord
Whats a hormone?
Explain the concept of homeostatic control by negative feedback with reference to a set point.
Homeostasis controls internal conditions within set limits. Homeostasis is controlled by a mechanism called negative feedback. Any change to the conditions in the system causes a response that reverses the change, so that conditions return to normal levels.
What is the order/pathway of the reflex arc
receptor -> sensory neurone -> relay neurone -> motor neurone -> effector
What do antibiotics not affect?
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of?
the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord
What is the role of Glucagon?
Glucagon is a hormone secreted by the pancreas when blood glucose levels are too low. Its main role is to increase blood glucose levels by stimulating the liver to break down stored glycogen into glucose and release it into the bloodstream
Describe the control of blood glucose concentration by the liver and the roles of insulin and glucagon.
The liver regulates blood glucose levels with the help of insulin and glucagon, hormones secreted by the pancreas. When blood glucose is high (after eating), the pancreas releases insulin, prompting the liver to convert excess glucose into glycogen for storage. When blood glucose is low (during fasting/exercise), the pancreas secretes glucagon, triggering the liver to break down glycogen into glucose. This feedback system ensures blood sugar remains stable, preventing extreme fluctuations.
What is the function of each neurone in the reflex arc, compare them.
The sensory neuron detects the stimulus, the relay processes the information, and the motor neuron triggers a response in the effector
What are pathogens?
A disease-causing agent such as a virus or a bacterium.
What is a stimulus? What is a nervous system ?Give one example of an external and an internal stimuli
A stimulus is a change in the environment that can be detected by an organism. Some stimuli are external, such as noises and smells. Some stimuli are internal, such as changes in body temperature and carbon dioxide levels in the blood. The nervous system is an organ system that allows humans and other animals to detect stimuli and respond to them.
identify in the following diagram the specific enocrime glands and the hormones they secrete

c - adrenal glands and adrenaline
d - pancreas and insulin
e - ovaries and estrogen
f - testes and testosterone
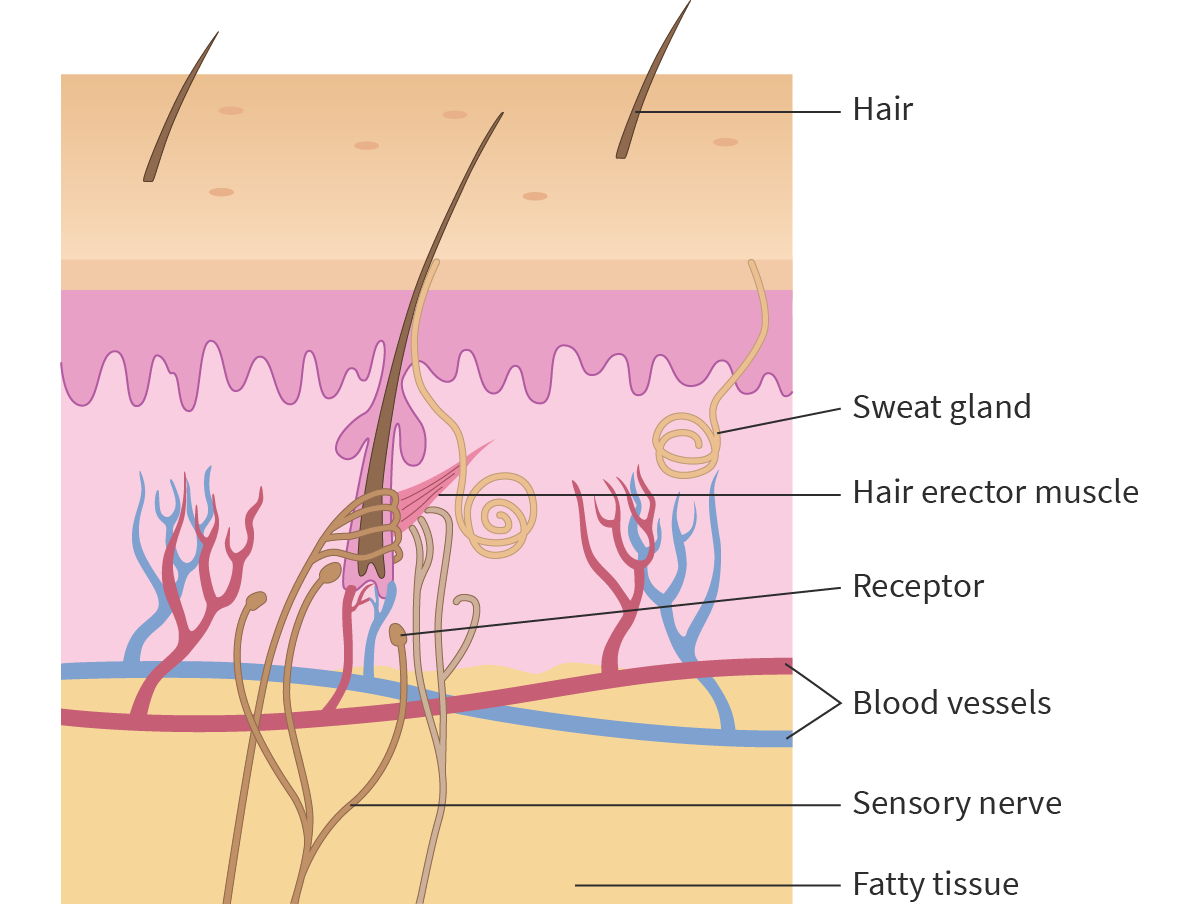
Identify in diagrams and images of the skin:
hairs, hair erector muscles, sweat glands, receptors, sensory neurones, blood vessels and fatty tissue
Describe the pathway of a reflex arc when a person touches a hot object
When you touch a flame, skin receptors send signals to a sensory neurone, which transmits them to a relay neurone in the spinal cord. The spinal cord sends signals to motor neurones, which activate the biceps muscle to move the hand away, preventing damage.
Describe the use of antibiotics for the treatment of bacterial infections. [also give the different ways (2) in which different antibiotics affect different bacteria]
Antibiotics are a category of medical drugs that kill bacteria or stop them from reproducing. They can protect us from many harmful bacterial infections.
Different antibiotics affect different bacteria in different ways. They may:
- cause the bacterial
cell membrane to break, killing the bacterial cell
- prevent bacteria from making new cell walls, so the bacteria cannot reproduce or grow.
Describe sense organs
A sense organ consists of a group of receptor cells that respond to a specific stimulus.
Describe adrenaline's role and its effects.
Adrenaline is the hormone secreted in ‘fight or flight’ situations, such as when you feel fearful, angry or excited. It has many target organs and produces wide-ranging effects in the body.
Its effects are:
(a). increased breathing rate
(b). increased heart rate
(c). increased pupil diameter
Describe the maintenance of a constant internal body temperature in mammals in terms of:
(a). insulation, sweating, shivering, the role of the brain
(b). vasodilation and vasoconstriction of arterioles supplying skin surface capillaries
The body maintains a constant temperature of around 37°C through thermoregulation, controlled by the hypothalamus. Fat under the skin acts as an insulator, reducing heat loss in cold environments. When too hot, the body sweats, and vasodilation increases blood flow to the skin, allowing more heat to escape. When too cold, shivering generates heat through respiration, and vasoconstriction reduces blood flow to the skin to conserve heat. The hypothalamus monitors body temperature through blood and skin receptors, activating these mechanisms to prevent dangerous fluctuations that could be life-threatening.
What is a reflex 𝒂𝒄𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏
means of automatically and rapidly integrating and coordinating stimuli with the responses of effectors (muscles and glands).
How can using the antibiotics only when essential can limit the development of resistant bacteria such as MRSA?
By only using antibiotics when essential, it limits the exposure of bacteria to antibiotics and reduces the likelihood of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria such as MRSA developing. This is because bacteria that are not exposed to antibiotics are less likely to develop resistance mechanisms as they are not essential for their survival.