What does the capital letter (ie K, L, M) mean in an x-ray name?
The energy level that the electron fell TO.
What type of signal does XPS detect?
Photoelectrons (or, electrons)
What type of signal is detected in XES?
As you increase the energy of the incident x-ray beam, how does the absorption coefficient change?
It decreases
What attire should you wear to lab?
Closed toed shoes, safety goggles, long pants
M represents n= ?
3
Describe one piece of information we can determine about a sample from an XPS spectrum.
- Chemical composition
- Oxidation state/chemical environment of types of atoms in the sample
XES is also called...
X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF)
Around approximately what energy would you expect the onset of the K edge to appear for aluminum?
What is one piece of information you can find in the X-ray data booklet?
Binding energies
X-ray emission energies
The greek letter in an X-ray name generally represents...
How many energy levels the electron dropped.
Of the electrons that were ejected from the sample and labeled in the spectrum below, which had the highest kinetic energy when they hit the detector?
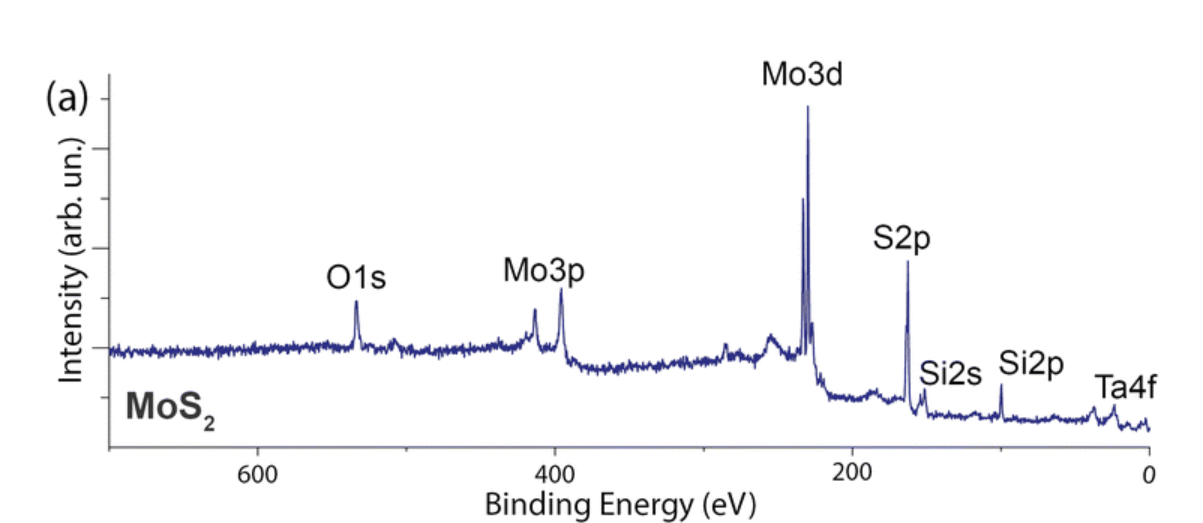
Ta 4f because they had the lowest binding energy.
Why is XES not surface sensitive?
Because this technique measures x-rays that are emitted from the sample, and x-rays have a greater path length in the sample than electrons. So if x-rays are generated deep in the sample, they can still be detected.
What is the highest energy edge to appear in an XAS spectrum (assuming you are using a broad enough energy range to obtain all the edges)?
K-edge
Which two quantum numbers do you add together to get the total angular momentum quantum number?
l and ms
How many sub-levels does the L shell have?
3
Could an Al K-alpha 1 source eject a 2s electron from Rb?
no
Does XES require you to change the energy of the source as the spectrum is collected? Why or why not?
No it does not.
Why does XAS require the use of a monochromator?
You fabricate an organic solar cell, and you put a transparent coating of a few nm on top of it to protect the polymer. Which spectroscopic technique would be best to characterize the chemical composition of the coating - XPS, XES, or XAS?
XPS because it is surface sensitive
An L-alpha 1 X-ray is emitted when an electron drops FROM the 3d 5/2 level TO which level?
Hint - use your x-ray data booklet
2 p 3/2
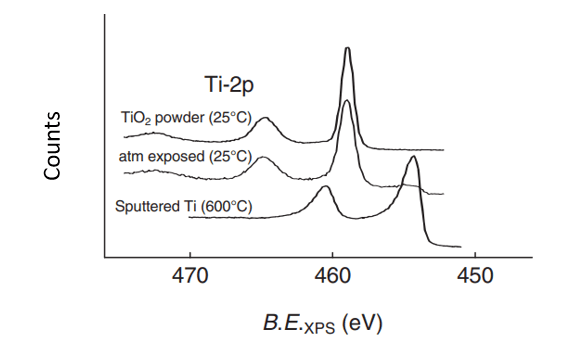
Why are the 2p peaks for the oxidized titanium shifted to higher energies?
Because the Ti has fewer electrons, so the ones that are left get less shielded from the nucleus, and it takes more energy to eject them.
What is the energy of the Cu K-alpha 1 characteristic x-ray and HOW did you calculate it?
Hint - use X-ray data booklet
8979 eV - 932.7 eV = 8046.3 eV
Why do the peaks in an XAS spectrum appear as sharp "edges"?
Because once the energy of the x-ray hits the binding energy of a particular orbital, all X-rays with energy higher than that will be able to excite an electron from that orbital as well.
What is an Auger electron?
"low-energy electrons ejected from an atom during the Auger effect, a process where an inner-shell vacancy (created by X-rays or radioactive decay) is filled by an outer-shell electron, with the atom's excess energy transferred to another outer-shell electron, causing its emission"