This chemical bond results from sharing electrons
This is the name for the formula N2O4
Dinitrogen Tetroxide
In this figure dots represent lone pairs and a line is used to symbolize a single covalent bond
Lewis Structures
The shape of a molecule is determined by this model
VSEPR Model
This is the term for an unequal sharing of electrons
Polar Covalent Bond
Non-metals
This is the formula for sulfur hexafluoride
SF6
This term is used if there is more than one correct Lewis Structure for a molecule
Resonance
This shape is represented below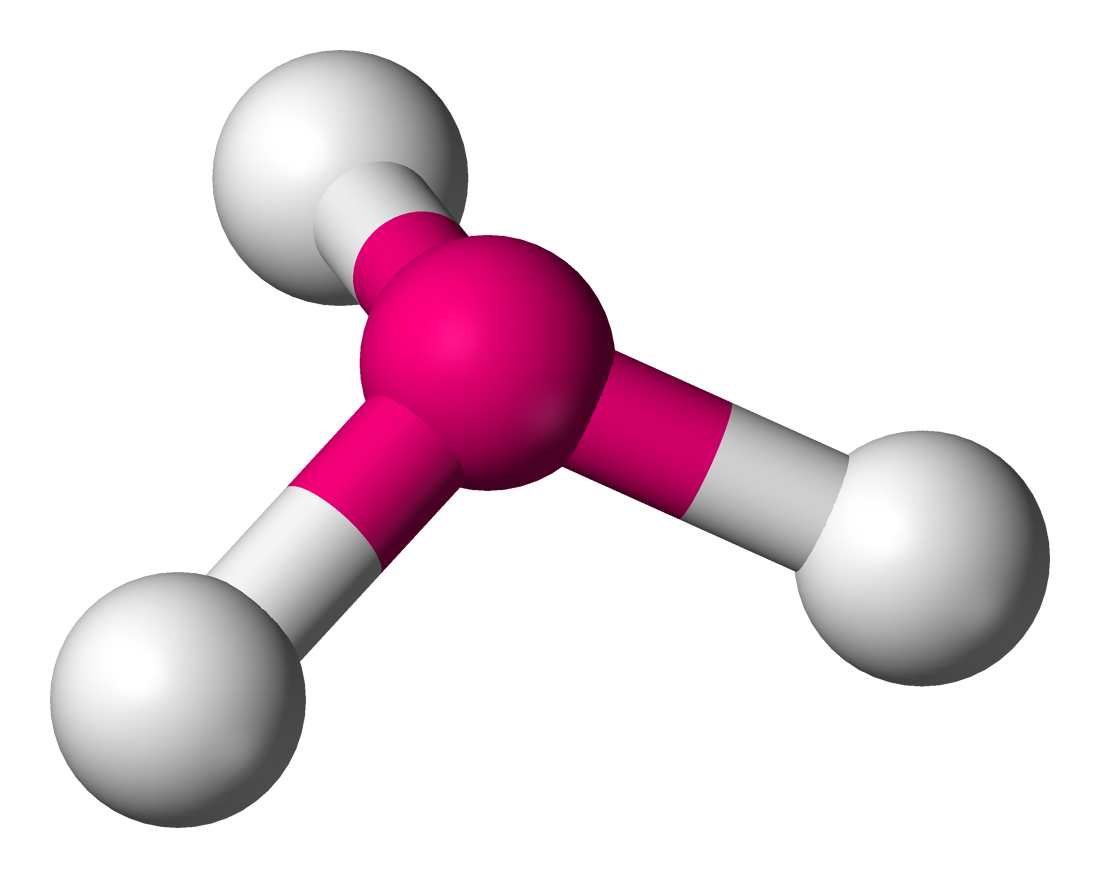
Trigonal Pyramidal
The polarity of a bond is decided by this property of an atom.
Electronegativity
This is the name used for a substance containing only covalent bonds
Molecule
This is the name for the formula C2H5
Dicarbon pentahydride
This drawing is the Lewis Structure for NH3

This shape is represented below.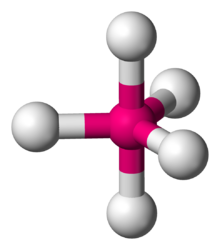
Trigonal bipyramidal
This type of bond has the biggest difference in electronegativity between the two elements.
ionic bond
This refers to the amount of energy required to break a covalent bond
Bond dissociation energy
This is the formula for the name hydrochloric acid
HCl
The Lewis Structure shown below represents this exception to the octet rule
Expanded Octet
This shape is represented below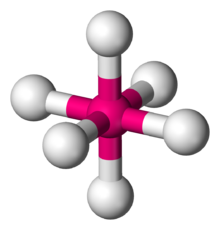
Octahedral
The polarity of a molecule is based upon these two characteristics.
Shape (Molecular Geometry)
Polarity of its bonds
In this type of reaction more energy is absorbed during breaking bonds, than is released when bonds are formed.
Endothermic Reaction
This is the name for the formula H3PO4
Phosphoric acid
This drawing represents the correct Lewis structure for BF3

This is the correct shape for the molecule SeO2
Bent
This molecule is the most polar between CH4 and NH3.
NH3