more random
more random
Partial Charges
& Lewis Structures
What is...
a metallic bond
What is the electronegativity difference for the bond below?
C -- Cl
What is:
0.5
T/F: Intermolecular forces are stronger than Covalent and Ionic bonds
What is...
False
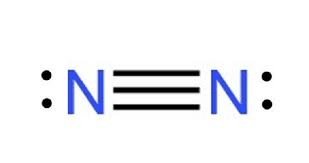
Draw the Lewis Structure for N2.
What is...
What is the total number of electrons that would be present in a CBr3H molecule?
What is...
26 electrons
Which type of compound will be able to conduct electricity when it is dissolved in water? (metallic, ionic, covalent)
What is...
Ionic compound
Which of the following bonds is a polar covalent bond?
N -- Br C -- F C -- S
What is...
C -- F
In order for hydrogen bonding to occur, what are the three atoms that a hydrogen could be bonded to?
What is...
Nitrogen, Oxygen, or Fluorine
Draw the Lewis Structure for:
C2H2
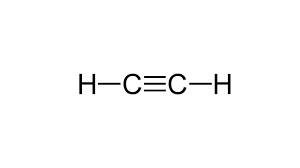 What is...
What is...
Is the following bond ionic, polar covalent, nonpolar covalent, or metallic?
Fe -- Cl
What is...
ionic
Write partial positive and partial negative charges over the atoms in both of the following two bonds.
H -- N O -- H
THEN, if the two bonds were to interact, the Nitrogen in the bond on the left will be attracted to which atom in the bond on the right?
What is...
Both hydrogens are partially positively charged. The Nitrogen in the bond on the left would be attracted towards the hydrogen in the bond on the right.
For the following bond below, which atom is partially negatively charged and which is partially positively charged? Also, draw the dipole arrow correctly if it is necessary.
N --- H
What is...
The nitrogen atom is negatively charged.
The hydrogen atom is positively charged.
Dipole arrow points towards the Nitrogen
What is the strongest IMF between molecules of the following compound?
What is...
Dipole-Dipole interactions
How many lone pairs and how many electron groups are around the central atom of the following molecule?
NBr3
What is...
1 LP which makes a total of 4 electron groups
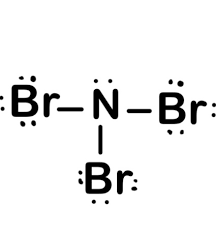
Which intermolecular force is present between molecules of ANY compound?
What is...
London Dispersion
Name ALL of the intermolecular forces that could exist between the two compounds: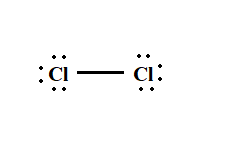
What is...
London Dispersion Forces
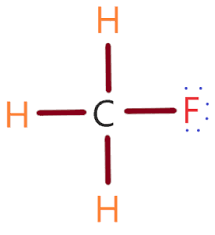
Draw the Lewis structure of CH3F. Then determine whether the molecule is polar or not.
What is...
Drawing should be on your whiteboard.
The molecule is polar.
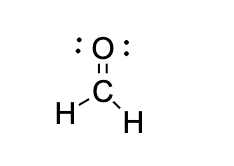
Can the following molecule hydrogen bond with water? 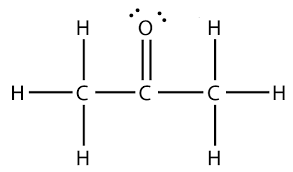
What is...
Yes they can hydrogen bond. While acetone does not have a H covalently bonded to an O, the O atom in acetone can form a hydrogen bond intermolecular attraction to either of the Hydrogens on water.
What is the molecular geometry around either of the carbon atoms in the following compound?
What is...
trigonal planar
In the following bond, are the electrons shared evenly or unevenly?
F --- C
What is...
Unevently because it is a polar covalent bond.
Explain:
Why was the lightbulb able to light up when placed in a solution of salt (NaCl) but was not able to light up when placed in a solution of sugar (C6H12O6) or a beaker of pure water?
What is...
Because when soluble, ionic compounds break up into ions which can help facilitate the flow of electrons (electrical current)
Explain: Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Ammonia (NH3) are two common covalent compounds, both with polar bonds. CO2 has a molar mass of 44.01 g/mol whereas NH3 has a molar mass of 17.04 g/mol. Despite having a larger molar mass, CO2 has a significantly lower boiling point (-78ºC compared to -34ºC).
Using principles of covalent compounds, explain why this is.
What is...
Carbon Dioxide is a non-polar molecule as it is symmetrical (and its dipoles cancel out). The strongest IMF for CO2 is London Dispersion whereas the strongest IMF for NH3 is hydrogen bonding. As a result, the BP of NH3 is significantly higher.
Which of the following compounds has the highest boiling point? And why?
FeCl3 HCl H2O Br2
What is..
FeCl3
It is an ionic compound which is a much stronger intramolecular attraction than the intermolecular forces of the other three compounds.
Which of the following molecules has trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry around the central atom?
NH3 H2O CO2
What is...
NH3
(4 electron groups and 1 lone pair)
What part of the ammonia (NH3) molecule would be attracted to the following ion? 
What is...
The Nitrogen because it is partially negatively charged and will be attracted to the positively charged ion.