Get Physiological With It
Bloodygood Histology
Blaze Your Own Pathology
Can-cer You Dig It?
Pesky Little Buggers
100
The preganglionic nerve fibers from this branch of the extrinsic nervous system synapse outside of the myenteric and submucosal plexuses in the GI tract.
What is the sympathetic nervous system.
100
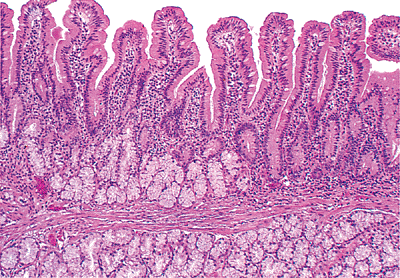 The mucosal epithelium in this image originates from this portion of the small bowel.
The mucosal epithelium in this image originates from this portion of the small bowel.What is the duodenum.
100
A patient presenting with ulcerated esophageal lesions containing histological "owl eye" inclusions likely suffers from an infection from this microbe.
What is CMV.
100
Patients presenting with refractory celiac sprue disease should be evaluated for this type of cancer.
What is T cell lymphoma.
100
This microbe, which accounts for roughly 20% of childhood diarrhea, is also a leading cause of chronic diarrhea in patients with AIDS.
What is cryptosporidium.
200
This peptide hormone increases both pancreatic secretions and gallbladder contractions, and is up-regulated by the entry of fatty acids and amino acids into the duodenum.
What is cholecystokinin.
200
 The lymphoid nodules seen here can be found in this specific portion of the GI tract.
The lymphoid nodules seen here can be found in this specific portion of the GI tract. What is the ileum.
200
An infant presenting with failure to pass meconium/stool within first few days of life is likely to possess this congenital anomaly.
What is Hirschsprung disease.
200
This form of cancer arises from a cirrhotic background in roughly 70% of cases.
What is hepatocellular carcinoma.
200
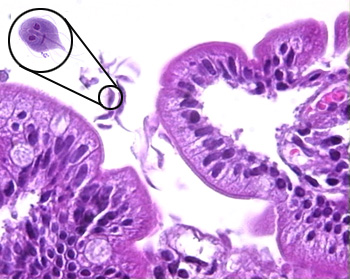 The diagnostic test of choice for the parasite in the image -- which often leaves hikers with fatty, foul-smelling diarrhea -- is this.
The diagnostic test of choice for the parasite in the image -- which often leaves hikers with fatty, foul-smelling diarrhea -- is this.What is antigen detection (ELISA, immunofluorescence) test.
300
Acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter which causes the contraction of GI smooth muscle, shares that excitatory effect with this neuropeptide.
What is substance P.
300
 The image shown is typical of this gland type.
The image shown is typical of this gland type.What is submandibular (mixed) salivary gland.
300
This biliary disorder is often associated with other autoimmune conditions including Sjögren syndrome, Hashimoto thyroiditis, RA, and celiac disease.
What is primary biliary cirrhosis.
300
,_ileum/gastrointestinal-stromnal-tumor-gist-ileum-4-il015-4.jpeg?Width=600&Height=450&Format=4) The neoplasm associated with this histological image would likely stain positive following immunohistochemical analysis targeting this protein.
The neoplasm associated with this histological image would likely stain positive following immunohistochemical analysis targeting this protein.What is c-kit.
300
Clonorchis sinensis, a trematode commonly transmitted in undercooked fish and treated effectively with praziquantel, is primarily associated with this malignancy.
What is cholangiocarcinoma.
400
Before food enters the duodenum, this process propels gastric contents back into the stomach for further mixing and reduction of particle size.
What is retropulsion.
400
 The region here labeled "2" image is responsible for endocrine release of these two important hormones.
The region here labeled "2" image is responsible for endocrine release of these two important hormones.What are insulin and glucagon.
400
Mutations in this gene can lead to abnormal iron sensing and absorption, resulting in widespread iron accumulation in the liver, pancreas, skin, heart, and joints.
What is HFE gene.
400
 This premalignant lesion is a precursor to roughly 20% of cases of sporadic colorectal cancer.
This premalignant lesion is a precursor to roughly 20% of cases of sporadic colorectal cancer. What is a sessile serrated polyp.
400
This bacteria is often carried by animal hosts and puts infants at a substantial risk for invasive disease with bacteremia.
What is yersinia enterocolitica.
500
A decrease in parietal cell concentration or function will result in deficient intrinsic factor secretion, which can lead to malabsorption of an important vitamin. The major hematological upshot of that deficiency goes by this name.
What is pernicious (megaloblastic) anemia.
500
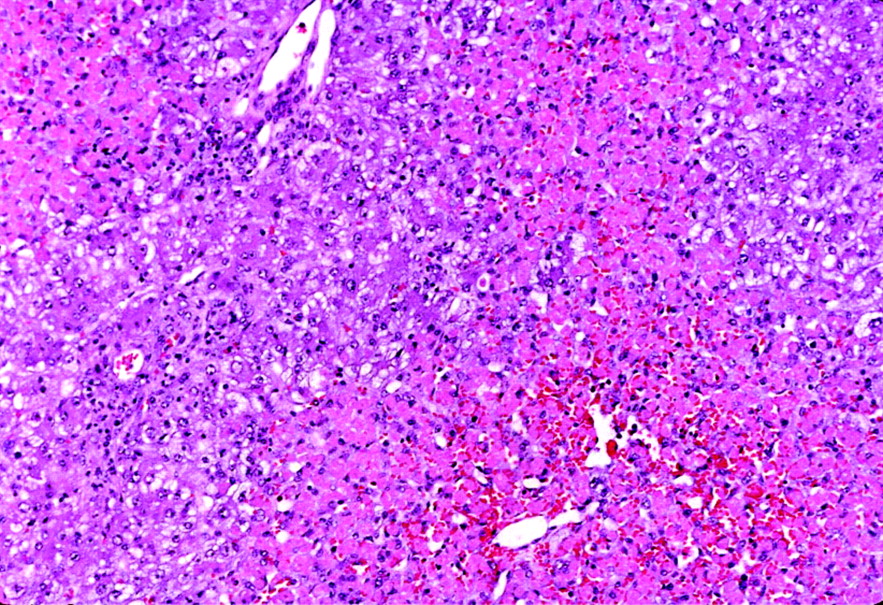 The liver damage seen here is caused by an overload of a toxic metabolite of acetaminophen, which leads to a depletion of this important antioxidant normally found in hepatocytes.
The liver damage seen here is caused by an overload of a toxic metabolite of acetaminophen, which leads to a depletion of this important antioxidant normally found in hepatocytes.What is glutathione.
500
The most common congenital anomaly of the pancreas (3-10%), which presents with failure of fusion of the fetal duct systems of the dorsal and ventral pancreatic primordia, is knows as this.
What is pancreatic divisum.
500
This cancer -- often associated with familial malignant melanoma (caused by p16 mutation) and/or familial breast cancer syndrome type 2 (caused by mutation in BRCA2) -- is the fourth deadliest cancer in the US.
What is pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
500
This microbe, which replicates in macrophages, puts patients at an increased risk of developing bacteremia by targeting reticuloendothelial cells throughout the body.
What is salmonella typhi/paratyphi.