Arrest rhythm characterized by a "flatline," with no associated electrical or mechanical activity.
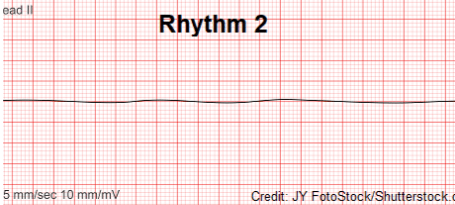
What is Asystole?
The two medical interventions that constitute BLS (Basic Life Support).
What are chest compressions and ventilation?
A sodium channel blocker, used in treating tachyarrhythmia's.
What is Lidocaine?
The initial dose in joule/kg when defibrillating.
What is 2 joule/kg?
The three medical interventions that constitute ALS (Advanced Life Support).
What is composed of monitoring, IV access, and reversal/arrest medications?
Arrest rhythm characterized by visible electrical activity with no mechanical activity.
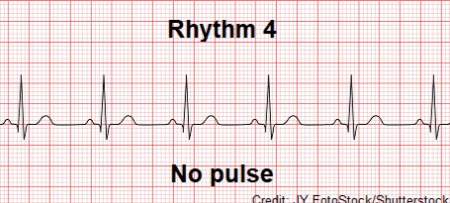
What is Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA)?
The recommended ventilation rate during BLS.
1 breath every 6 seconds (10 breaths/minute)
An anticholinergic medication most effective when used for vagally mediated arrests, dosed once as early as possible (not repeated).
What is Atropine?
CPA rhythm(s) where defibrillation is indicated.
What is ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia?
The two pieces of monitoring equipment needed to monitor CPR efforts.
What is ECG and ETCO2?
Arrest rhythm characterized by rapid and uncoordinated activity of the ventricles, with electrical impulses beginning in multiple locations of the heart.
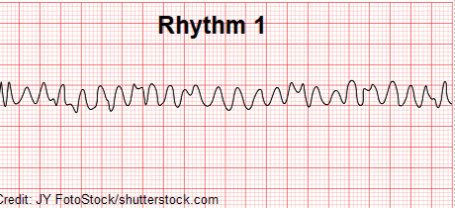
What is Ventricular Fibrillation?
What is 100-120 chest compressions/minute?
Reversal agent for benzodiazepines.
What is flumazenil?
CPA rhythm(s) where defibrillation is NOT indicated.
What is asystole and pulseless electrical activity?
Minimum ETCO2 value that is associated with proper compression (and ventilation) technique.
What is 18mmHg?
Arrest rhythm characterized by rapid movements of the ventricles with a consistent ectopic pacemaker.
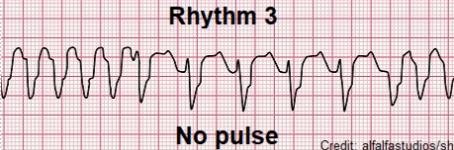
What is Ventricular Tachycardia?
The ABC's of CPR, checked rapidly when CPA has occurred or will likely occur soon.
What is composed of airway, breathing, and circulation?
Reversal agent for opioid medications.
What is naloxone?
What is alcohol?
Alternate medication administration route(s) that can be used during CPR if IV access cannot be rapidly obtained.
What are the intratracheal and intraosseous route(s)?
Three medications that can be used during CPR to treat arrhythmias.
What is Lidocaine, Esmolol, and Amiodarone?
The ideal compression depth during CPR (excluding barrel chested patients).
What is 1/3 to 1/2 (33%-50%) of the chest circumference?
A medication that causes intense vasoconstriction and increased HR/contractility through alpha/beta activity, useful for increasing cerebral and coronary perfusion.
What is epinephrine?
The goal of defibrillation during CPR when associated "shockable" rhythms are present.
What is the intentional termination of abnormal heart rhythms (through depolarization) via dosed electrical currents?
A monitorable value that when suddenly/greatly increased can indicate ROSC.
What is ETCO2?