This type of study is experimental and subjects undergo an intervention
Clinical trail
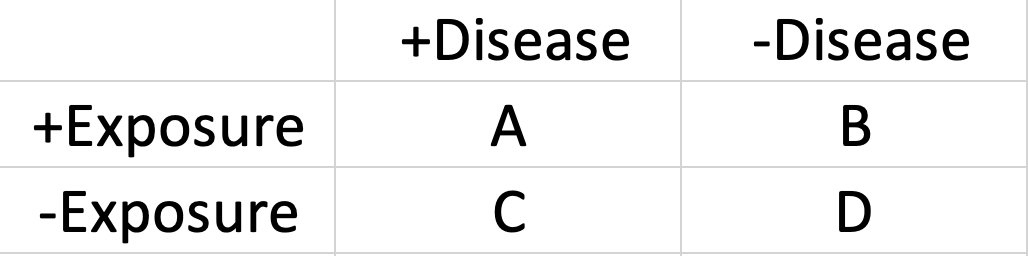
Calculate sensitivity and specificity
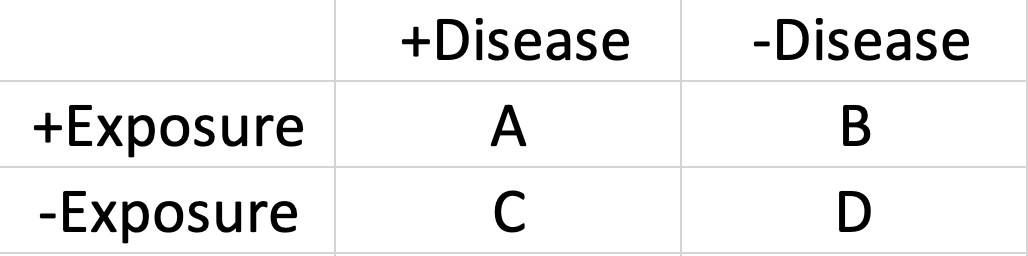
Sensitivity=A/(A+C)
Specificity=D/(D+B)
You are testing drugs for insomnia and more OB/gyn residents want to sign up than the general population
Selection bias
The _________ variable is sometimes called the “response,” the “symptoms”, or the “outcome”. These variables are not affected by other variables the study measures. In contrast, the _______ variable is often the focus of the research study.
independent and dependent variables
This type of variable influences both the dependent variable and independent variables, causing a spurious association
Confounder or confounding variable
A ___________ study looks back at past data to analyze an outcome, while a ___________ study follows a group of individuals forward in time to observe how an exposure might influence a future outcome
Retrospective, prospective
Describe the calculation of relative risk (RR)
RR = [A/(A+B)] / [C/(C+D)]
A patient reports that they got chicken pox shortly after receiving the HPV vaccine
Recall bias aka reporting bias
Mild, moderate, and severe pain
Categorical ordinal variables (have a specific order)
This type of statistical error occurs when you state there is a difference observed, when in reality there is not
Type I error (alpha) aka p-value
This type of observational study choses subjects based on the presence or absence of risk factors to see if they develop a disease/condition. Yields incidence and relative risk
Observational cohort study
Calculate odds ratio (OR)

OR = (A/B)/(C/D)=(A*D)/(B*C)
A surgeon who typically doesn't wash their hands, does so before surgery after the hospital started a SSI prospective observational study
Observation bias aka Hawthorne effect
Ca-125 values of 17.36, 364.4, and 3,489.3
Numerical continuous variables (cannot be counted)
This type of error occurs when you report there is no difference, when in actuality there is a difference between the groups
Type II error (beta)
Power=1-beta
In this type of observational study, subjects are chosen based on presence or absence of disease/condition. Yields odds ratios
Case control
Calculate attributable risk (AR)

AR=[A/(A+B)] - [C/(C+D)]
A participant doesn't report their full sexual history on a research survey
Response bias
Dysgerminoma, high-grade serous, and sertoli-leydig ovarian cancers
Categorical nominal variables - have no logical order
This measures of the ability of an experimental design to detect a particular effect based on a percent difference observed
Power
This type of randomized clinical trial compares a new treatment to an existing standard treatment to determine if the new treatment is not significantly less effective
Non-inferiority trial
This type of risk is calculated the same way as attributable risk (AR), but the term refers to the probability of a disease increasing due to an exposure or a risk factor
Absolute risk reduction (ARR)
AR=ARR=[A/(A+B)] - [C/(C+D)]
Doing these 4 things in your study can reduce bias
1. Blinding
2. A control group
3. Crossover (everyone is their own control)
4. Randomization
Para 1, para 2, para 3, para 4, para 5, para 6
Numeric discrete variables (can be counted)
A child is born to parents who are both carriers of achondroplasia. What are the odds (in a fraction or %) that the offspring is a carrier?
2/3 or 67%