Usually consists of a Physician, Critical Care/ER Nurse, Nursing Supervisor, Anesthetist, RT, Pharmacist, & Chaplain.
What is a code team?
In a healthy individual process of digestion begins here.
What is the mouth? (Mastication)
The functional unit of the kidney.
What is the nephron?
Pressure= flow x resistance
What is the Hemodynamic Formula/Concept?
A life-threatening condition that results when you lose more than 20 percent (one-fifth) of your body's blood or fluid supply.
What is hypovolemic shock?
This begins after 4 to 6 minutes without adequate oxygen.
What is brain damage?
is a muscular tube connecting the throat (pharynx) with the stomach.
What is the esophagus?
Is a vibratory sensation felt on the skin overlying an area of turbulence over a graft or fistula.
What is a Thrill?
Volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute (4-8L/min).
What is Cardiac Output?
A serious condition that occurs when your heart cannot pump enough blood and oxygen to the brain, kidneys, and other vital organs.
What is cardiogenic shock?
Needs to be verified in at least 2 EKG leads.
What is asystole?
total length is roughly 20 feet, begins at the pyloric sphincter of the stomach.
What is the small intestine?
Is an audible vascular sound associated with turbulent blood flow in a dialysis graft of fistula.
What is a bruit?
The opposition to blood flow exerted by the blood vessels. The resistance that the ventricle has to pump against.
What is Systemic Vascular Resistance?
Associated with physical blocking of the great vessels or the heart itself. Pulmonary embolism and cardiac tamponade are examples of this.
What is Obstructive shock?
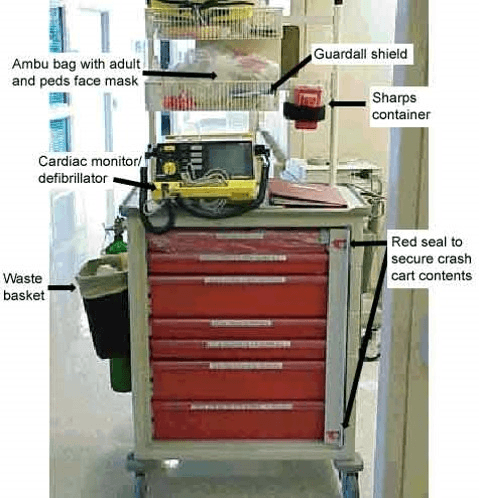 Centralized location for emergency equipment and medication.
Centralized location for emergency equipment and medication.
What is a crash cart?
What is chyme?
The waste product of the kidney.
What is urine?
States that the stroke volume of the heart increases in response to an increase in the volume of blood filling the heart (the end diastolic volume) when all other factors remain constant.
What is the Frank Sterling law?
A medical condition in which abnormal distribution of blood flow in the smallest blood vessels results in inadequate supply of blood to the body's tissues and organs.
What is distributive shock?
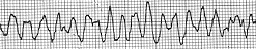 Shockable rhythm.
Shockable rhythm.
What is VFIB?
Plays a major role in bile secretion, iron metabolism, plasma-protein production and detoxification of drugs & other substances.
What is the liver?
What is the glomerulus?
Is the blood pressure in the venae cava, near the right atrium of the heart. It reflects the amount of blood returning to the heart and the ability of the heart to pump the blood back into the arterial system. Normal range is 2-6 mmHg.
What is Central Venous Pressure?
Neurogenic, Anaphylatic and Septic are examples of this type of shock.
What is distributive shock?