Calculate the map for a BP of 80/40
2(DBP) + SBP / 3
MAP = 53 mmHg
The depolarizing agent that causes hypersalivation and laryngospasm
Ketamine
Your patient is on a ventilator and they present with a decline in SaO2, hypotension, agitation and your high pressure alarm is going off what are these signs of?
Tension Pneumothorax
Is epidural an arterial or venous bleed?
Arterial
You have a patient with complaints of chest pain you do an EKG and notice prolonged QT and ST elevation patient has negative troponins you have a high suspicion that the patient is
Hypoglycemic
Inferior Wall MI is an occlusion of what artery
Right Coronary Artery
This medication is used in traumas. Its indication is hemorrhagic shock. It is an antifibrinolytic that reduces clot breakdown. Name the med and dose
TXA
1g over 10 mins
1g over Hrs
Form of Non invasive ventilation that reduces preload, reduces volume coming back to the heart
CPAP/BiPAP
What is the only clinical indication in ICP management to hyperventilate a patient with a head injury?
Brainstem Herniation
You have a CHF patient they are on loop diuretics you know with they patients that they need what organ to be perfused for the medication to be effective
Kidneys
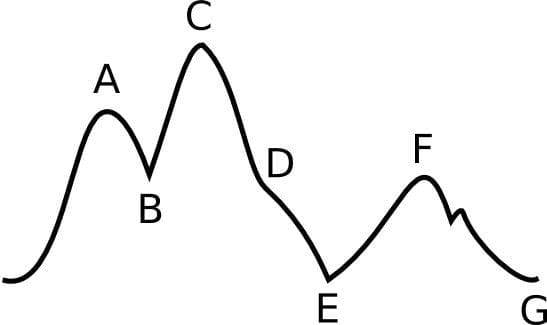 What type of deflation error does this image represent in IABPs?
What type of deflation error does this image represent in IABPs?
Late Deflation
(most detrimental form of timing error)
This medication is a positive inotrope can be used to counter citric acid with PRBCS and massive transfusions
Calcium
Your patient has a chest tube you notice tidaling on INSP/EXP but you have a constant bubbling are these normal?
Tidaling is normal
Bubbling can be a sign of a leak
Vertigo is the hallmark symptom of
Vertebro Basilar Artery Occlusion/Rupture
A 55yoM presents to the ER with generalized weakness and stomach pains. Pt has a hx of alcoholism. With this information what do you expect his BUN to be and why?
Low
BUN measures proteins in the liver
What's the target HR and BPs for someone with an Aortic Dissection?
HR 60 bpm
BP 100-120 mmHg
Name the three most common causes of shock in children
Hypovolemia
Sepsis
Cardiogenic
This goal is to produce a rapid loss of consciousness immediately prior to the administration of neuromuscular blocking agents. Paralysis with induction
Rapid Sequence Intubation
Whats anisocoria
causes asymmetric pupil sizes
This patient is a 65yoF came in with weakness. Vitals: Temperature: 102.7°F (39.3°C) Heart Rate: 118 bpm Blood Pressure: 86/52 mmHg Respiratory Rate: 24 breaths/min O2 Saturation: 93% on room air Mental Status: Confused (GCS: 13)
Labs:
WBC 19.4 x10⁹/L
Lactate 4.2 mmol
Creatinine 2.3 mg/dL
BUN 48 mg/dL
Glucose 156 mg/dL
Given the following information you have a high suspicion for what?
Septic Shock
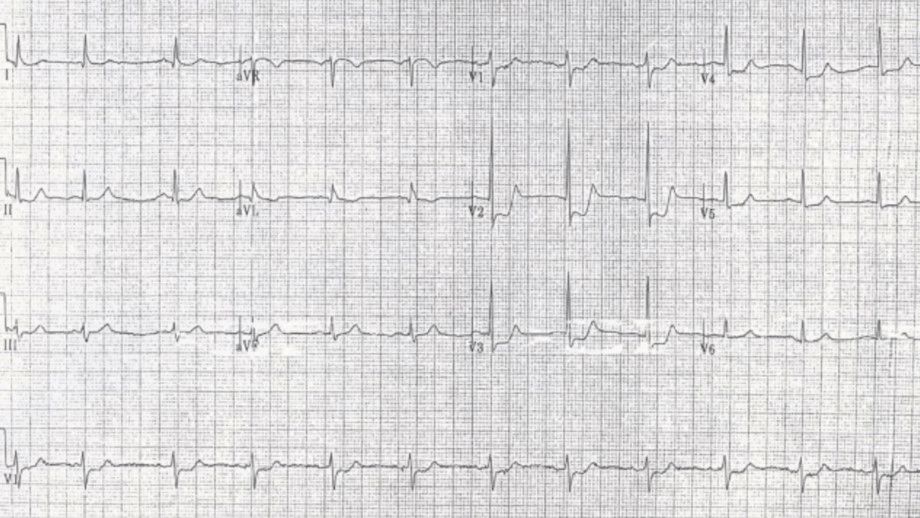
52 yo M with chest pain and shortness of breath, ECG as shown, do you activate cath lab?
Yes
Consider posterior MI as a cause. You need to then obtain an ECG with posterior leads. If there is 0.5 mm elevation in any posterior lead this is diagnostic of posterior MI.
This is secondary to Sepsis or multi organ failure. It has an acute onset. Causes hypoxemia secondary to a V/Q mismatch. Its characterized as a systemic inflammation response effecting capillaries in the lungs.
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Your patient has just been RSI'd whats an ARDsnet compliant ventilation settings?
TV 5-8ml/kg
Plateau Pressures <30cm H20
Peak Pressures < 35 cm H20
Peep 5cm H20
Type of hematoma with a brief period of unconsciousness followed by lucid interval and then progressively deteriorating consciousness
Epidural Hematoma
You have a pt on a vent with an ABG
pH 7.23
PaCo2 67
PaO2 58
SaO2 89%
Mode: Assist-Control (A/C) Volume
Tidal Volume (Vt): 500 mL
Rate: 10 breaths/min
FiO₂: 40%
PEEP: 5 cm H₂O
What are some things you can change with the vent settings and what is this patient currently presenting with?
Increase RR
Increase FiO2
Uncompensated Respiratory Acidosis