Designed for efficient, life-saving interventions. Also may have sensory overload and deprivation.
What is critical care environment?
This cardiac rhythm has P waves with every QRS but has a rate less than 60. If symptomatic, patients would receive Atropine IVP.
What is sinus bradycardia?
This type of Pneumonia is developed during a patient's admission to the hospital.
What is hospital-acquired pneumonia?
This is when your head has contact on impact of an object, surface, etc.
What is direct injury?
This acute process is common in patients with extemity fractures and monitored with frequent neurovascular checks and pain assessments using the 5 Ps.
What is compartment syndrome?
This is inadequate tissue perfusion that has 4 different types, and 4 stages.
What is shock?
What are antibiotics and NSAIDs?
Competence, voluntariness, disclosure of information.
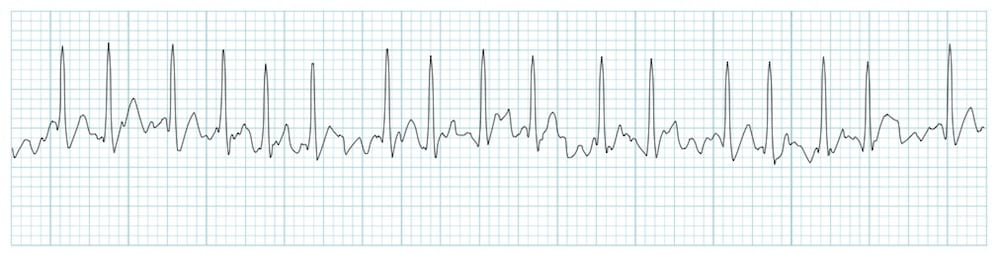 This rhythm is identified as.
This rhythm is identified as.
What is Atrial Fibrillation?
Auscultating the epigastric area and bilateral breath, ETCO2 detector, and CXR are all ways to check this.
What is the ET tube placement?
This is when your kidneys suddenly stop working. This is a sudden onset.
What is an Acute Kidney Injury?
This tool is used to determine how severe a patient's head injury maybe during the triaging.
What is the GCS score?
Patients that are declared brain dead and are in good health. No existing diseases such as diabetes, CAD, cancer, kidney disease, HIV, or COVID are good candidates for this.
What is organ donation?
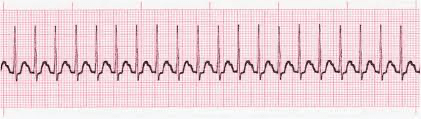 This rhythm can be converted with nonpharmalogical ways such as vagal manuvers, but if not successful, can be converted using Adenosine.
This rhythm can be converted with nonpharmalogical ways such as vagal manuvers, but if not successful, can be converted using Adenosine.
What is Supraventricular Tachycardia?
This alarms when there is a loss of connection. This usually means an air leak in circuit, disconnection in the system, or ET tube displacement.
What is the low-pressure alarm?
What is Prerenal?
This is a result of the initial trauma or injury.
What is a Secondary TBI?
Lights, noises, loss of privacy, and emotional and physical pain are all happening in this particular environment.
What is the critical care environment?
On a Rhythm strip, this is where atrial depolarization is happening, and the atrials are contracting?
What is the P wave?
Standard sizes for females are: 7.5-8.0 mm.
Males: 8.0 mm to 9.0 mm.
What is Endotracheal tubes?
What is the Maintenance phase?
Alleviating distress symptoms that negatively affect the patient or family.
What is Palliative care?
This is the artery that is best to use for a CABG patient.
What is the internal mammery artery?
This is an alarm usually alarms when there is some type of blockage or obstruction in the ET tube.
What is a high pressure alarm?
What is Glomerular Filtration Rate?
This is the largest specialty organization in the world.
What is the American Association of Critical Care?
Elevated troponin and ST elevation are diagnostics used to diagnose this.
What is a Myocardial Infarction?
Elevating the HOB 30-45 degrees, preventing condensation back to the patient, hand hygiene, oral hygiene, and repositioning the patient all prevents this.
What are ways to prevent VAP?
This takes 4 to 6 months for your BUN and creatinine levels to return to normal and to return to tubular function.
What is the Recovery phase?
During this process, you have to assess the situation, consider all options, collaborate with the care team and the patient, act on the plan, and then evaluate the plan.
What is Ethical Decision-Making?
What is left-sided heart failure?
Older patients, previous PMHx of clots, or diseases like COPD and CHF are at greater risk for this.
What is a Pulmonary Embolism?
This results in obstruction of flow, which leads to increased intratubular pressure.
What is Postrenal?
Severing the professional relationship with the patient when that patient is in need.
What is abandonment?
What is stable angina?
Worsening V/Q mismatch. These type of patients are also CO2 retainers.
What is COPD?
Vasopressors, abx, blood, nutritional support, and ICDs are therapies that are.
What is commonly withheld therapies?
Friction rub of the heart that makes this area of the heart inflammed. This may lead to cardiac tamponade and scarring if not treated.
What is Pericarditis?
This pneumonia is usually developed outside of the hospital setting but within a healthcare setting. Such as a nursing home.
What is healthcare-Acquired pneumonia?
We finally made.
What is ABOUT TIME!!!!
Dilation or thinning of the vessel wall that can lead to a disection, which is described as a sudden painfully sharp pain.
What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm?
This is the most dangerous type of pneumonia. Infection and aspiration preventions are key.
What is Ventilator-Associated pneumonia?