This trauma imaging technique, first described in humans, assesses the diaphragmatic-hepatic, cysto-colic, hepato-renal, and spleno-renal sites for free fluid.
What is a FAST exam?
This domestic species cannot vomit because of anatomy.
What is the horse? or What is the rabbit?
This sugar substitute is harmless in humans but deadly for dogs, causing hypoglycemia and potential liver failure.
What is xylitol (sugar-free gum and foods)?
This bedside ultrasound measurement estimates ICP in dogs, cats and horses as well as humans.
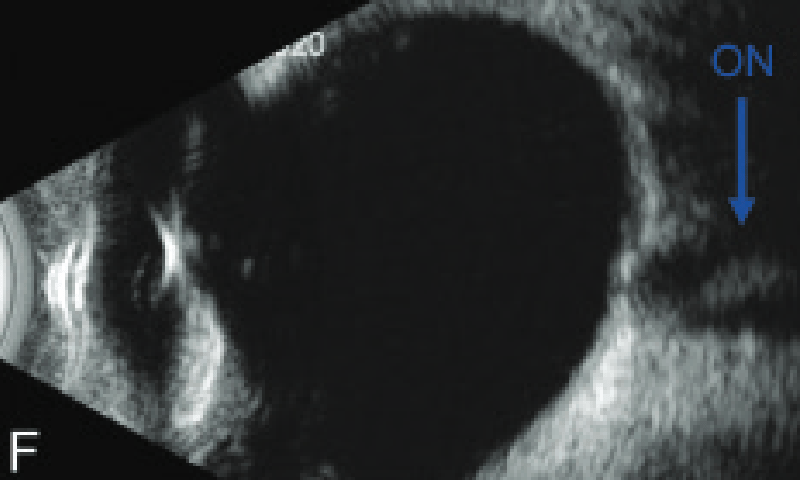
What is the optic nerve sheath diameter?
A cat with open-mouth breathing and muffled heart sounds likely has this condition.
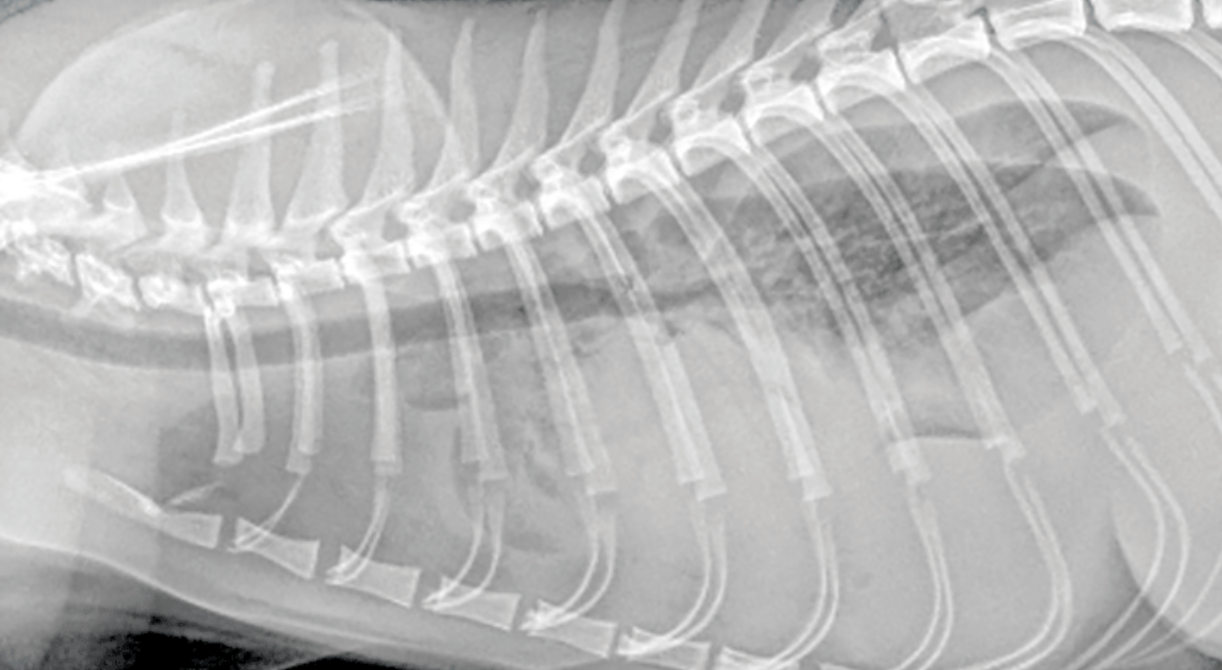
What is pleural effusion?
Unlike humans, vets typically require this test before nearly every transfusion in cats.
What is cross-matching?
Modeled after APACHE, this veterinary score predicts prognosis in critically ill dogs and cats.
What is APPLE score?
Cats with a urethral obstruction often develop an elevation of this electrolyte, which can cause a unique “sinoventricular rhythm” on ECG.
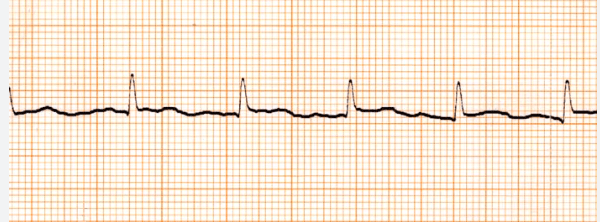
What is hyperkalemia?
Cats given acetaminophen often die from this condition.
What is methemoglobinemia (and hepatic necrosis)?
Cats that fall from 2–6 stories often survive better than from lower heights, due to terminal velocity physics and their anatomy. This phenomenon is nicknamed the “__________ syndrome.”
What is the high-rise syndrome?
This canine breed is the poster child for arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy.
What is a boxer?
Veterinary ICUs were early adopters of this point-of-care coagulation testing (TEG/ROTEM) to guide transfusion decisions, even before many human centers.
What is viscoelastic testing?
This therapy for local anesthetic overdose in humans became a lifesaver for dogs that ingest lipophilic toxins like ibuprofen and marijuana.
What is intralipids (lipid emulsion therapy)?
Rabbits restrained too suddenly may develop this fatal condition.
What is capture myocarditis leading to cardiac arrest?
This anticoagulant rodenticide causes life-threatening bleeding in both people and pets.
What are vitamin K antagonists? (Brodifacoum, Bromadiolone, Difethialone, Difenacoum, Flocoumafen)
Ferrets that present with seizures most often suffer from this endocrine disease.
What is insulinoma?
Tick-borne Ehrlichia can trigger this immune-mediated red cell disorder.
What is IMHA (immune-mediated hemolytic anemia)?
Veterinary studies on this class of fluids, raised concerns about renal injury and helped shape debate in human critical care guidelines.
What are synthetic colloids (hydroxyethyl starches)?
In 2012, veterinary medicine developed its own evidence-based CPR guidelines, modeled after AHA/ILCOR.
What is RECOVER?
Ferrets are commonly used in research for this seasonal human vaccine because they contract the same disease as humans.
What is influenza or flu?
Grape or raisin ingestion in dogs leads to failure of this organ.
What are the kidneys?
Stenotic nares, elongated soft palate, hypoplastic trachea, and everted laryngeal saccules are key findings in this syndrome that primarily affects English and French bulldogs, pugs, and other smoosh-faced dogs.
What is brachycephalic obstructive airway syndrome (BOAS)?
Closed-cervix pyometra is considered more dangerous than open-cervix because of this pathophysiologic risk.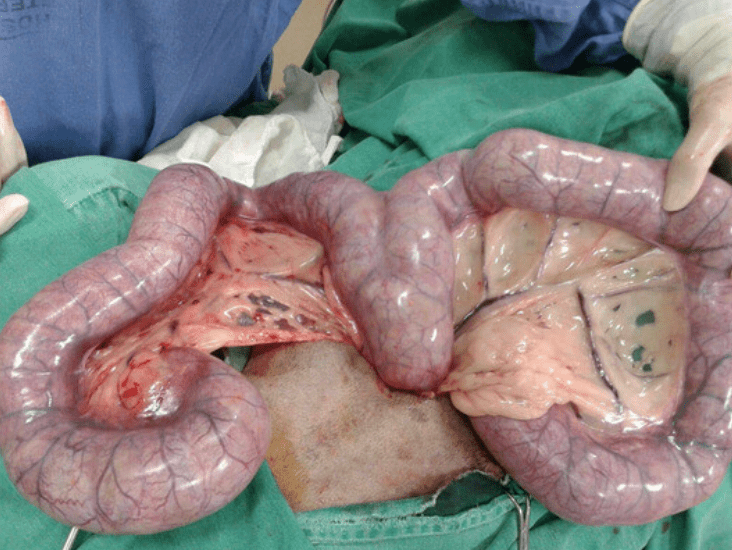
What is uterine rupture and septic peritonitis?
Veterinary medicine pioneered structured tools like the HHHHHMM scale and frank discussions about this sensitive topic, which human palliative care now cites as a model for compassionate decision-making.
What is quality of life and euthanasia?
Originally developed for use in human critical care, norepinephrine is now the first-line vasopressor in both species. But while human guidelines only recently accepted it, veterinarians have been giving it this way for decades without hesitation.
What is peripherally (through peripheral IVs)?
This organ twists in cattle and dogs, but not in humans, leading to shock and death without surgery.
What is the stomach (gastric dilatation-volvulus, abomasal displacement)?
This chelator, used in both children and parrots, treats lead poisoning.
What is EDTA?
This parasitic infection in cats can mimic stroke, seizures, or brain tumors, and in pregnant women, it poses serious risks to the fetus.
What is toxoplasmosis?
Toy breeds like Yorkies may present with a “goose-honking” cough caused by dynamic airway narrowing. This condition is often confirmed with fluoroscopy or bronchoscopy.
What is tracheal collapse?
Before it became mainstream in human trauma care, veterinary studies in dogs with hemoperitoneum supported “small-volume resuscitation” and this strategy of maintaining a lower-than-normal blood pressure until bleeding is controlled.
What is permissive hypotension?