The final node in a recursive structure that has no children.
What is a leaf node?
What is one of the primary reasons for the creation of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)?
a) To make code execution faster and more efficient by avoiding the use of classes and objects.
b) To enable better management of complex software systems by organizing code into reusable and modular units.
c) To write more code
d) To allow for the direct execution of machine code without the need for an interpreter or compiler.
b.
Python has a limit on the maximum ________ to prevent infinite ________ and stack overflow errors. By default, this limit is set to 1000, but it can be changed using a system function.
Recursion Depth
Why do bit positions matter?
Detailed Example
Consider an IPv4 header:
- Version: The first 4 bits of the header.
- Header Length: The next 4 bits.
- Type of Service: The following 8 bits.
- Total Length: The next 16 bits.
Each field has a specific bit position, and misinterpreting these positions can lead to incorrect data processing. For example, if the total length field is not correctly interpreted, the receiver might not know where the payload starts or ends.
Often used to represent memory addresses in computing. Memory locations are more efficiently and clearly represented in _______ than in decimal or binary.
Hexadecimal
How would you properly access the maximum index in an MxN matrix?
a. matrix[M][N]
b. matrix[len(mat)-1][N-1]
c. matrix[-1][N-1]
d. matrix[M-1][N]
Both B and C are correct.
Since indices are zero based, the max index will always be the number of cols/rows - 1. You can also just index the last element in any list using [-1]
What is the term that represents each of the numbers:
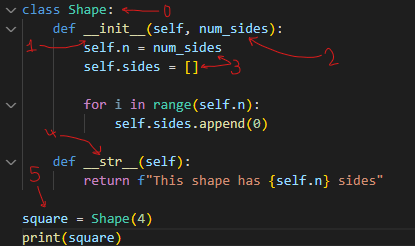
0) Class
1) Constructor
2) Arguments/Parameters
3) Attributes
4) Magic Method
5) Object
Which is the correct recursive call to make for a recursive sum implementation?
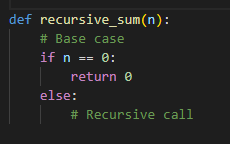
a. return 1 + recursive_sum(n)
b. return n - 1 + recursive_sum(n)
c. return n + recursive_sum(n + 1)
d. return n + recursive_sum(n - 1)
d. return n + recursive_sum(n - 1)
You are summing every value up until n-1, and then adding n to that sum.
What is 1110 >> 2 in decimal?
What is 1011 << 3 in decimal?
a) for right shifting, add 0s to the MSB (left) and take away from the LSB (right)
1110 -> 00 1110 -> 0011 = 3
b) left shift: for y = x >> n, y = x*2^n
1011 is 11, 11*2^3 = 88
also like adding 0s to the LSB (right)
Which is true about recursive algorithms?
A. Recursive algorithms are always faster than iterative algorithms.
B. Recursive algorithms utilize mathematical formulas, making them inherently faster.
C. Recursive algorithms eliminate the need for looping, reducing the number of iterations.
D. Recursive algorithms leverage previously computed results, avoiding redundant computations.
D.
By storing previously computed results, recursive algorithms can avoid redundant calculations and directly fetch the result from memory, leading to improved efficiency.
However, it's important to note that not all recursive algorithms are inherently faster than their iterative counterparts, and the efficiency depends on the specific problem and implementation details.
What is the difference between a stack and a queue? When would you use one over the other?
Stack: LIFO
Think of a stack of quizzes to be graded
Used for recursion, tasks that require backtracking or history
Could be used to implement undo functionality
Queue: FIFO
Think of the line at the bank
Used for sequential processing (one after another)
Could be used to implement a schedule of tasks
A fundamental principle of object-oriented programming that involves bundling the data (attributes) and the methods (functions) that operate on that data into a single unit called a class. It also restricts direct access to some of the object's components, which can be achieved by making attributes private and providing public getter and setter methods. This helps in protecting the integrity of the data and promotes modularity and maintainability of the code.
Encapsulation
Which of these are NOT elements of a recursive solution to a problem?
a. base case
b. accumulator pattern
c. recursive call
d. subproblem
b. accumulator.
This is an essential part of the accumulator pattern, and can be used in a recursive implementation, but is NOT an essential element of one.
x = 0b1
x ^= 0xf
What is the value of x (in decimal)?
14. Remember that a hexadecimal value of F is equivalent to the binary 1111. So performing the XOR assignment on these two looks like this.
0001
1111
-----
1110 = (8 + 4 + 2) = 14
Which of the following functions correctly calculates the bitwise OR between two binary numbers?
a. lambda x, y: ~x | y
b. lambda x, y: x || y
c. lambda x, y: x or y
d. lambda x, y: x | y
d. The bitwise OR operation in Python is represented by the `|`
the keyword `or` is a logical operator and does not perform a bitwise comparison. It can be performed on boolean values and other non binary types.
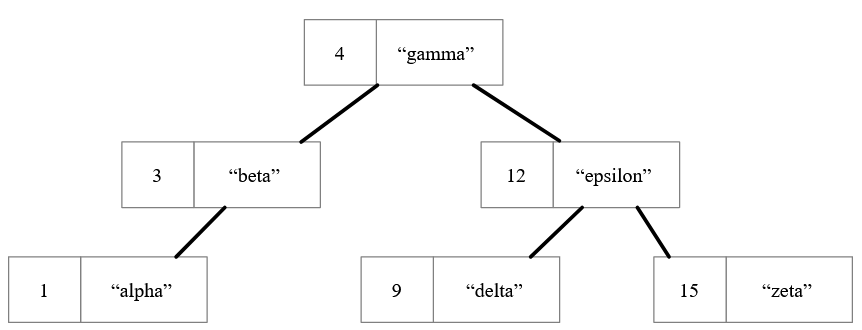
What is a BST? How is the data ordered? Draw a diagram.
Each node has a max of two children. The child on the left is smaller than the parent, and the one on the right is greater. This structure can be used to search or insert into the tree recursively.
What is the difference between private and protected attributes?
How do these terms contribute to the use of setter and getter functions?
Private attribute: self.__private = private
Can only be accessed by the class it's defined in
Protected attribute: self._protected = protected
Can only be accessed by the class it's defined in AND its subclasses
Private/protected attributes can't be accessed directly, so we need to define methods to access and mutate them. This allows for greater control over how these variables are used and makes it easier for end users to interact with your code.
The order in which Python resolves the inheritance hierarchy and determines which method implementation to invoke when a method is called on an object
The method resolution order (MRO)
x = 0b11
x <<= 0b011
x >>= 0b010
What is the final value of x (in decimal)?
6.
3 left shifts, 2 right shifts, the difference of shifts is 1 to the left. So you can just shift the original value 0b11 left once, which gives you 0b110 or 6.
These things transfer data and instructions that are being used immediately by the CPU.
What are registers?
A Quad Tree is a tree data structure commonly used to represent and efficiently store spatial data. Which of the following statements about a Quad Tree is correct?
A) A Quad Tree can only be used to store two-dimensional data.
B) A Quad Tree is a binary tree that stores elements in a balanced manner.
C) A Quad Tree divides space into quadrants, forming a hierarchical structure.
D) A Quad Tree is primarily used for searching and sorting operations on linear data.
C.
A Quad Tree is a hierarchical data structure that divides space into quadrants and is commonly used for organizing and efficiently storing spatial data.
True or False
A concrete class can serve as the base for an abstract class
True.
The abstract class can inherit and override the concrete class methods, and also define its own abstract methods.
Which line best represents the (worst case) time complexity of Binary Search?
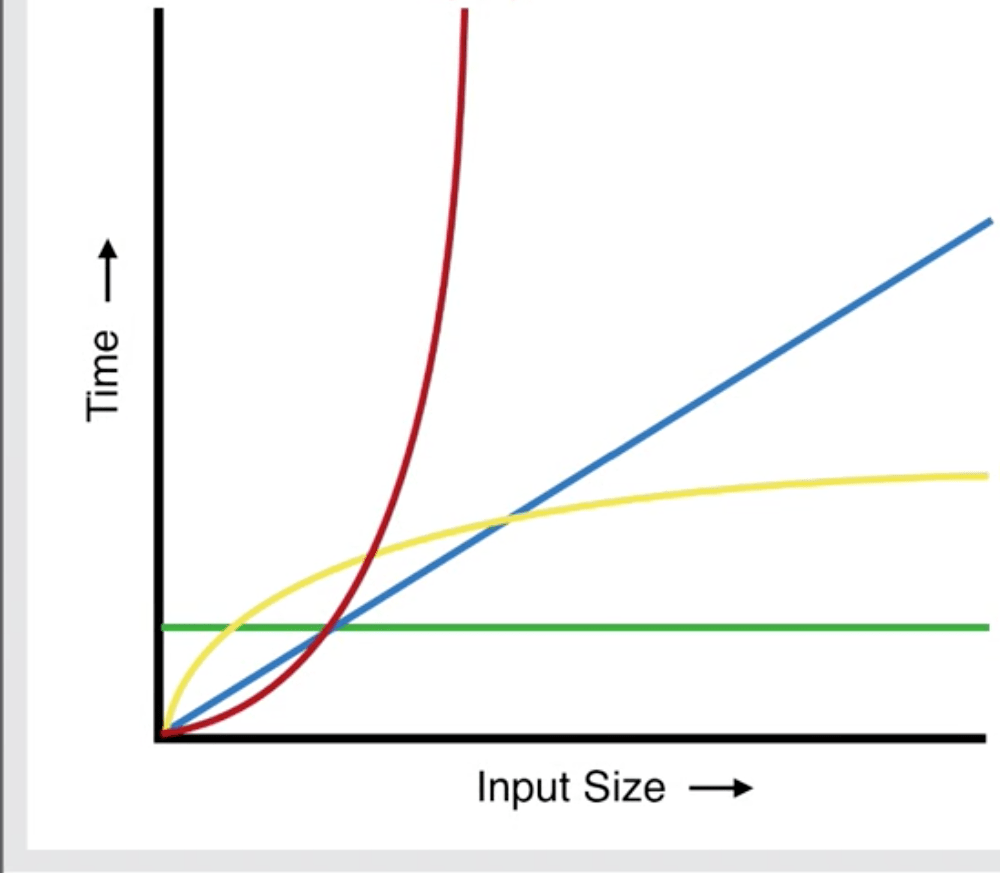
a. Green
b. Yellow
c. Red
d. Blue
Remember that the time complexity for binary search is O(logN) or logarithmic. So knowing that, you can select the line which most resembles the graph of a logarithm, which is the color Yellow in this image.
What mask could you apply to the unsigned binary number 1110 1011 to return 74 as an unsigned binary number?
74 as unsigned binary: 01001010
1110 1010 & 0101 1110 = 01001010
For AND: 1 keeps the value, 0 rejects it
What is the correct definition and description of the ALU?
A. Assembly Language Unit. The component of the CPU responsible for managing memory operations.
B. Abstract Level Usage. The component of the CPU responsible for handling input and output operations.
C. Arithmetic Logic Unit. The component of the CPU responsible for executing arithmetic and logical operations.
D. Artificial Learning Utility. The component of the CPU responsible for controlling the overall execution of instructions.
Correct Answer: C.
The ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) is a fundamental component of the CPU (Central Processing Unit). It is responsible for performing arithmetic and logical operations on data.