This type of search uses both the path cost and the heuristic cost to affect the order of the search.
What is A* search?
The solution to the following Minimax Problem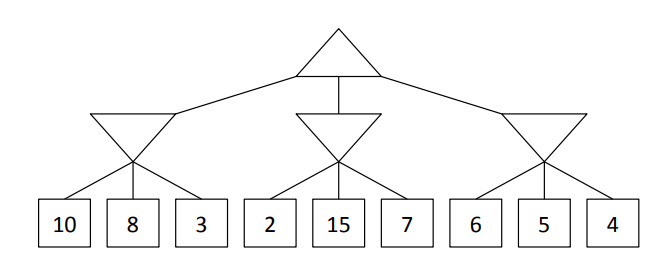
What is 4?
The reason why the Bellman equation,
V^{opt}(s) = max_a { \sum_{s'} T(s,a,s') [ R(s,a,s') + \gamma V^{opt}(s')]}
, starts with max_a
What is, "to choose the action that maximizes expected utility?"
This reinforcement learning algorithm seeks to estimate the value of a state based on rewards from the entire episode.
What is direct evaluation?
Two factors that affect the probability of acceptance in simulated annealing.
What are the difference in expected value (delta E) and the temperature?
This search uses a FIFO queue to order the search
What is a BFS (Breadth-First Search)?
The definition of the heuristic property admissibility.
What is the heuristic property that the heuristic cost must be less than or equal to the path cost from each node to the goal node?
In the Bellman equation,
V^{opt} = max_a { \sum_{s'} T(s,a,s') [ R(s,a,s') + \gamma V^{opt}(s')]}
, a concise name for the sum, which is a function of state s and action a.
What is a Q-value?
This form of reinforcement learning estimates values of T and R through experimentation, given a fixed policy.
What is model based learning?
Simulated annealing seeks to avoid converging to this solution.
What is a local optimum? (local max or min also acceptable)
To enable search on graphs with loops, this is added to the tree-search algorithm.
What is the visited set?
The heuristic properties of the following hueristic and path-cost graph: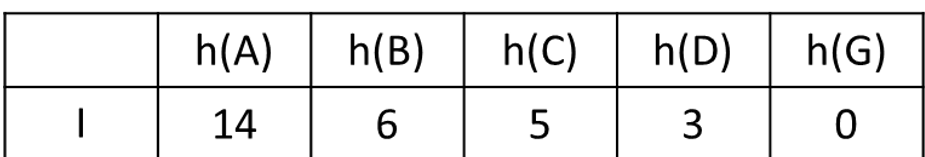
What is admissible and consistent?
Ignoring all the historical (state, action) pairs except the current one in an MDP's transition probabilities to make it tractable to solve.
What is the Markov property?
This equation is utilized in Temporal Difference Learning to estimate the value of a given state: V^(pi)(s) . This equation utilizes [sample] to represent [r-gammaV^(pi)(s')]
What is
V^{pi}(s} = (1-alpha)V^{pi}(s) + alpha[sampl\e]?
When a proposed solution to a minimization problem is smaller than the current solution, the probability of acceptance is this fixed value.
What is 1?
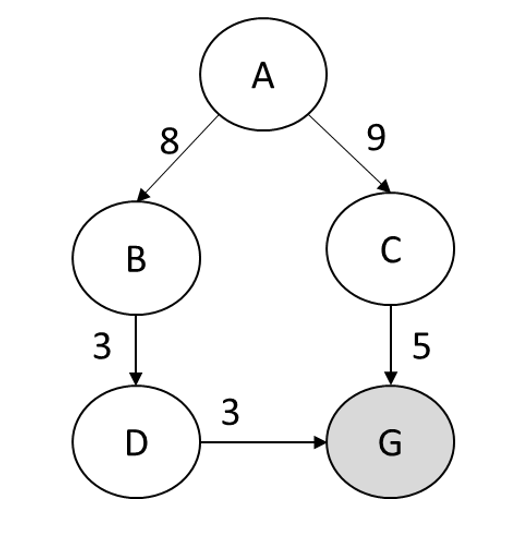
When starting at A and ending at goal G in this graph, nodes are expanded in this order using DFS.
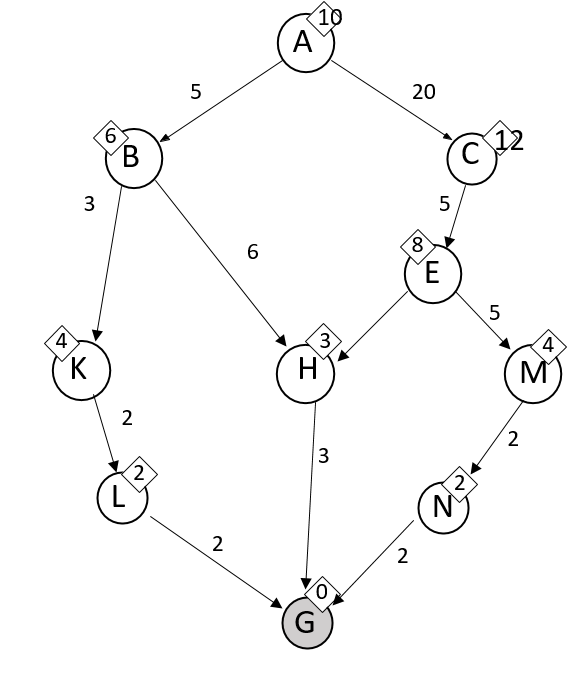
What is A, C, E, M, G?
This is the dominate heuristic, assuming all heuristics are admissible and consistent.
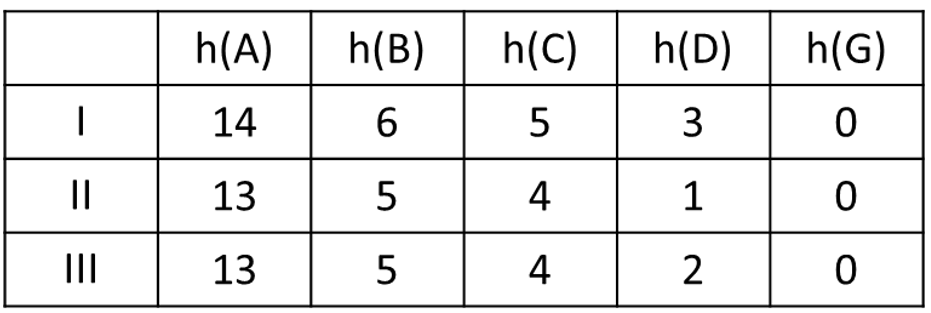
What is Heuristic I?
This algorithm avoids uses dynamic programming instead of recursion to converge to the true value of each state in an MDP. We implemented it using a spreadsheet.
What is value iteration?
This is represented by gamma
What is the discount factor that represents the exponential decrease in reward with each time step?
The equation for determining if a proposed solution is accepted in Simulated Annealing
What is
e^((\DeltaE)/T)>r ?
When starting at A and ending at goal G in this graph, nodes are expanded in this order using UCS.

What is A, B, K, L, H, G?
These nodes can be pruned from this tree when the search is conducted from left to right:
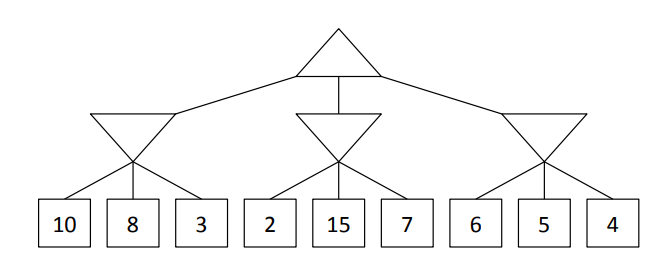
What are nodes with the expected value of 15 and 7?
The number of T(s,a,s') values needed for the center grid state in Gridworld, assuming it is not adjacent to any walls, and when the actor moves in the desired direction with probability 0.7 and the opposite direction with probability 0.3.
What is 8? (4 actions and 2 possible outcomes for each action)
This function updates feature weights in Approximate Q learning.
What is:
w_i = w_i+alpha*["difference"]*f(s,a)
Methods to prevent input features from overpowering the temperature variable in Simulated Annealing
What are normalization and scaling?