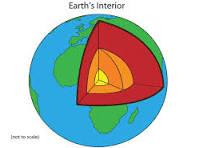
In the image, the yellow coloration represents this.
What is the inner core?
A geologist rubs minerals on a white tile to observe the color of the powder left behind. This is the name of the test he performed.
What is a streak test?
These are the basic building blocks that make up rocks.
What is a mineral?
This process involves the movement of weathered rock and soil by wind, water, ice, or gravity.
What is erosion?
At this type of plate boundary, two tectonic plates slide past each other without creating or destroying crust.
What is a transform boundary?
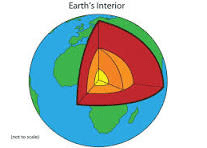
In the image, the orange coloration represents this.
What is outer core?
This term refers to a solid, inorganic substance of natural occurrence.
What is a mineral?
This process, driven by energy from Earth’s interior, is responsible for the continuous changes in the rock cycle.
What are convection currents?
This process occurs when a solid rock is heated until it becomes molten magma.
what is melting?
At this type of plate boundary, tectonic plates move away from each other, allowing magma to rise and form new crust.
What is a divergent boundary?
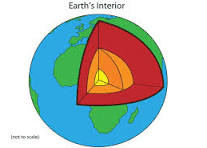
In the image, the top layer represents this.
What is the crust?
This property of a mineral describes how light reflects off its surface, making it appear shiny or dull.
What is luster?
These two conditions deep within Earth can transform existing rocks into metamorphic rocks.
What are extreme heat and pressure?
Rivers, glaciers, and wind all contribute to this process, in which sediments accumulate in a new location.
What is deposition?
At this type of plate boundary, tectonic plates move toward each other, often causing mountains, volcanoes, or subduction zones.
What is a convergent boundary?
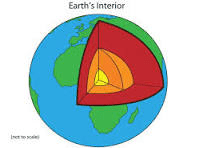
In the image, the red coloration represents this.
What is the mantel?
This mineral property measures a mineral’s resistance to being scratched.
What is hardness?
This type of rock forms from the compaction and cementation of sediments, often containing layers and fossils.
What is a sedimentary rock?
This term describes the eruption of magma, gases, and ash from Earth’s interior to the surface.
What is volcanic activity?
At this location, one tectonic plate is forced beneath another, often leading to earthquakes and volcanic activity.
What is a subduction zone?
The diagram below represents a cross section of a portion of Earth's interior. The arrows in the diagram represent a heat-transfer process that moves tectonic plates across Earth's surface.
Convection currents in this layer of Earth are believed to drive the movement of tectonic plates.
What is the mantle?
True or False: A mineral is a solid, inorganic substance that occurs naturally.
What is true?
This type of rock forms when molten rock cools and solidifies, either beneath Earth’s surface or after a volcanic eruption.
What is an igneous rock?
This large-scale motion of Earth’s lithospheric plates is responsible for earthquakes, mountain building, and volcanic activity.
What is the movement of Earth’s tectonic plates?
These two forces deep within Earth can transform existing rocks into metamorphic rocks.
What is heat and pressure?
