The beliefs and practices of small, homogenous groups of people, often living in rural areas that are relatively isolated and slow to change.
What is Folk culture?
The language spoken by the greatest number of non-native speakers.
What is English?
The difference between a nation and a state.
A nation is a group of people with similar beliefs and customs, a common heritage, claims to a particular homeland, and desire to become a state.
The boundary between Libya and Egypt
What is superimposed and/or geometric?
one effect of centrifugal forces
What is:
Failed states
Uneven development
Stateless nations
Ethnic nationalist movements
Separatist movements
Ethnic tension or violence
facilitated the global diffusion of plants, animals, diseases, human population, culture, technology, and ideas between Afro-Eurasia and the Americas
What is the Columbian Exchange?
improved methods of cultivation, harvesting, and storage of food that started in the 1700s and then benefited from the Industrial Revolution with the use of machines and new technology
What is the Second Agricultural Revolution?
activities involved in the creation of a product: design, production of raw materials, manufacturing and assembly, distribution
What is a complex commodity chain?
category of country the relies on more developed countries for money but exploits less developed countries for natural resources.
What is semi-periphery?
As technology improves, the amount of time it takes for ideas to diffuse across a space becomes smaller.
What is space-time compression?
The two most wide spread language families.
What are Indo-European and Sino-Tibetan?
Korean is an example
What is a multistate nation?
occurs after reapportionment, is when state legislatures redraw the district boundaries so that each district contains roughly the same number of people
What is redistricting?
External conflict is an example of this force
the agricultural practice located in the marked areas on the map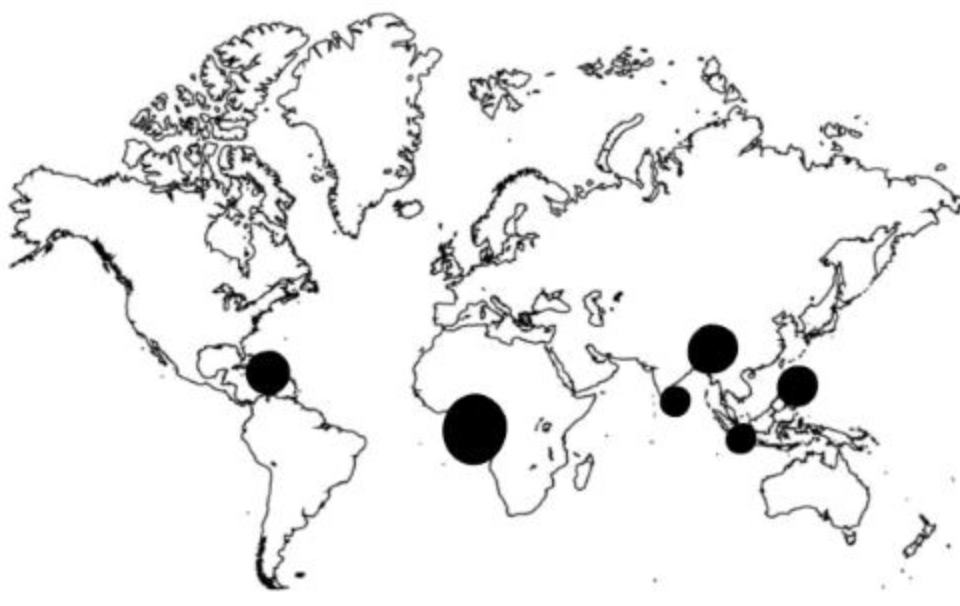
What is plantation agriculture?
the job of the majority of people before the 2nd Agricultural Revolution, but after the start of the Neolithic Revolution
What is farmer?
the use of economic, political, cultural, or other pressures to control or influence other countries, especially former dependencies
What is neocolonialism?
urban areas that lack places to buy affordable, good-quality, fresh food
What are food deserts?
The spread of Christianity in the Roman Empire after Emperor Theodosius declares it to be the state religion.
What is Hierarchical diffusion?
The religion that originated in South Asia and spread throughout much of Southeast and East Asia.
What is Buddhism?
What is a stateless nation?
The idea that Germany should annex any land in Europe with German speakers.
What is Irredentism?
This organization is focused on expanding the economic growth in Southeast Asia.
What is ASEAN?
US state and Canadian province where sections of land, perpendicular to river can be found (2 parts)
What are Louisiana and Quebec?
led to a reduced need for human labor
What is mechanized agriculture?
the number of these has decreased as the number of corporate farms has increased
What are small family farms?
Women in MDCs have more access to this which allows them to participate in other economic sectors
What is education and training?
The universalizing religion with places of worship usually located in the center of a town and surrounded by minarets.
What is Islam?
Language that has diffused throughout East Africa and become a lingua franca for the region.
What is Swahili?
The effort by one country to establish settlements in a territory and to impose its political, economic, and cultural principles on that territory
What is colonialism?
List the four zones established by UNCLOS in order from most sovereignty to least.
1. Territorial sea
2. Contiguous sea
3. Exclusive economic zone (EEZ)
4. High Seas
What is
1. Territorial sea
2. Contiguous sea
3. Exclusive economic zone (EEZ)
4. High Seas
the forced removal of a minority ethnic group from a territory, often through violence.
What is ethnic cleansing?
Horticulture agriculture and plantations would be considered this type of farming, while ranching and nomadic herding would be considered this type of farming. (2 parts)
What is intensive and extensive?
two positive consequences of the Green Revolution
What are higher crop yields, increased nutritional value, and decrease in food prices?
these large enterprises that have been able to occupy an increasing share of US farming largely because they are able to take advantage of this, which enables them to sell products at a lower price. (2 parts)
What are agribusinesses taking advantage of economies of scale?
two examples of value-added specialty crops
What are organic, non-GMO, free range, and artisanal foods (turning berries into jam, turning milk into cheese, turning tomatoes and peppers into salsa)?
The belief that your own cultural group is more important and superior to other cultures.
What is Ethnocentric?
The idea of a neighborhood or community whose landscape reflects evidence of multiple cultures as a result of immigrants forming ethnic enclaves.
What is sequent occupancy?
______________ is a geographical feature on land or sea that has to be traversed by the armed forces to reach their target destination. An example is _______________. (Two parts)
What is a choke point and what is the Panama Canal, Strait of Gibraltar, Cape of Good Hope, Bosphorous Strait, Suez Canal, Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, Strait of Hormuz, Strait of Malacca, and the Spratly Islands?
Two examples of autonomous regions
What are
Catalan region in Spain
Native American Reservations in the US
Hong Kong + Macau of China
Quebec of Canada
Aland Islands of Finland
Svalbard of Norway
Cook Islands of New Zealand
What is
physical isolation
ethno-linguistic divisions
terrorism
economic inequity
the agricultural practice found in the shaded areas and the method often used with the practice (2 parts)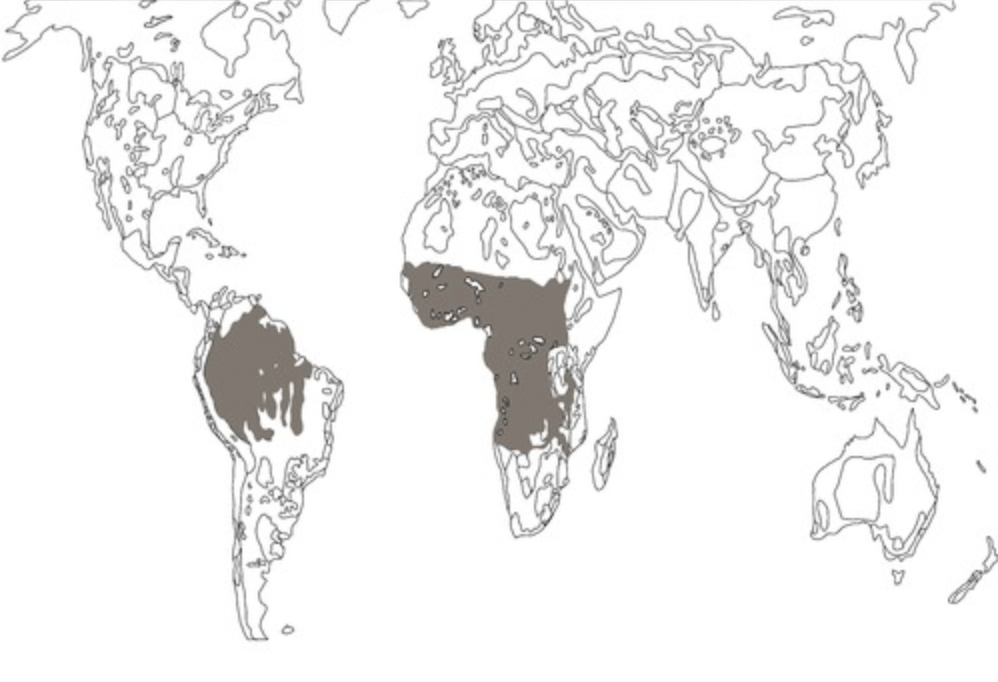
What is shifting cultivation and slash and burn?
two advancements of the Second Agricultural Revolution
What are the Iron/Steel Plough, Mechanized Seed Drilling, McCormick Reaper/Harvester, Grain Elevator, Barbed Wire, and Mixed Nitrogen and Nitric Acid Fertilizer?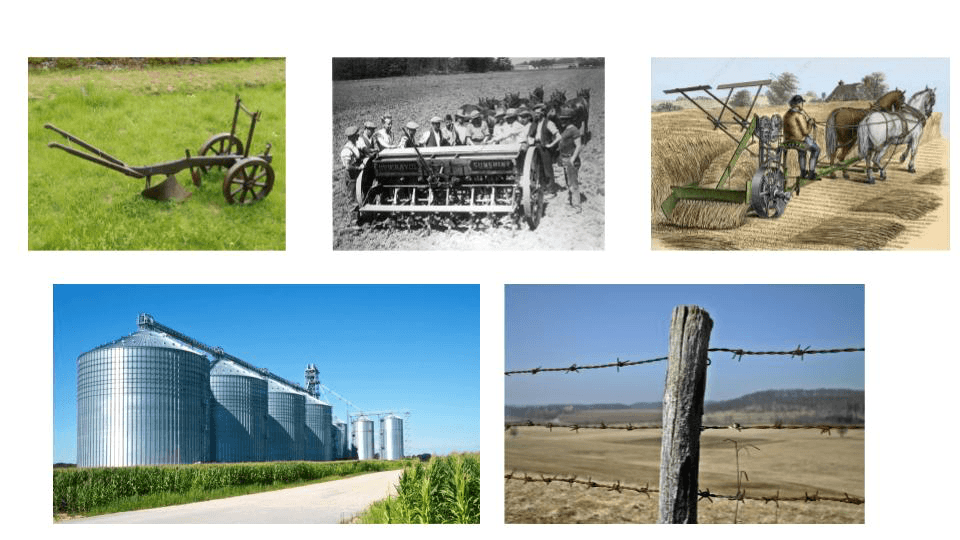
two examples of economic supranational organizations created to encourage global or regional trade
What are OPEC, ASEAN, EU, USMCA, AU, WTO, Mercosur?
two examples of how evolving agricultural practices impact society
What are changing diets (new food preferences), role of women (excluded from revolutions, training, and land ownership), and economic purpose (food supply is affected by changing technology)?