This chamber is most anterior in the chest.
What is the right ventricle?
Hockey stick MV suggest this disease.
What is rheumatic mitral stenosis?
This equation calculates pressure gradient from velocity.
What is the modified Bernoulli equation?
HOCM is treated with this surgical procedure
What is septal myectomy or alcohol ablation?
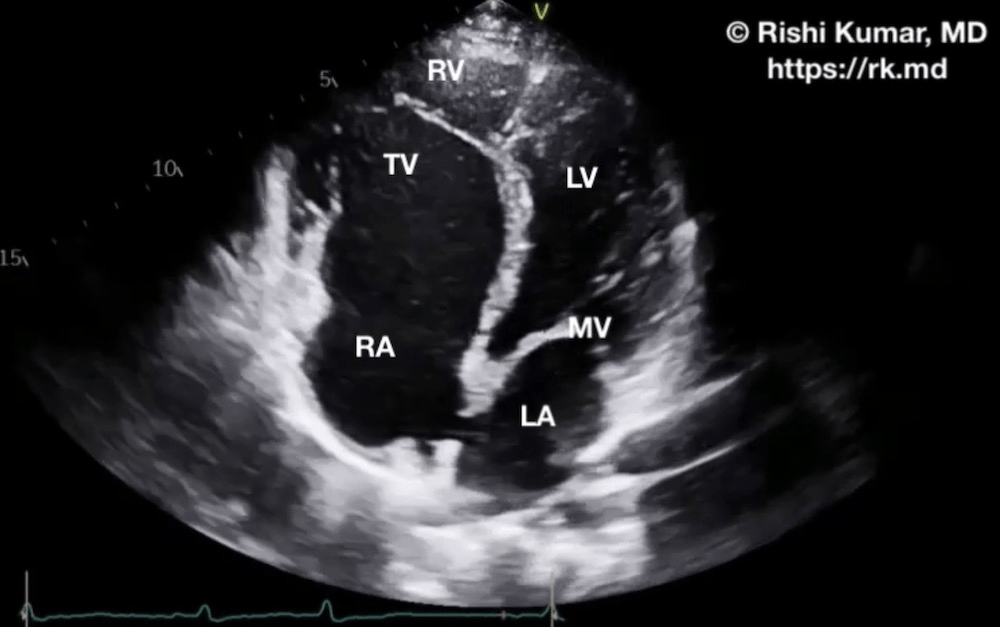 Apical displacement of the TV, atrialized RV
Apical displacement of the TV, atrialized RV
What is Ebstein's anomaly?
Moderate range for RV
What is 30-60 mL?
This measurement estimates LA size in PLAX view.
What is the anteroposterior LA dimension?
MR due to cusp or leaflet prolapse, flail, and tethered all show this type of jet on color Doppler
What is an eccentric jet?
This Doppler method detects high velocities without aliasing.
What is CW?
A gene mutation causes this thick CM
What is hypertrophic CM?
Shunts are normally L->R. When they switch due to high pulmonary/right sided pressures, it's called this
What is Eisenmenger's syndrome?
Moderate range for RF
What is 30-49?
This chamber shows earliest collapse in tamponade.
What is the right atrium?
Aortic sclerosis differs from AS by this feature.
What is a normal transvalvular gradient?
This "effect" explains frequency shift in Doppler.
What is Doppler effect?
"Speckled" myocardium with a "ground glass" appearance is a classic presentation of this
What is amyloidosis?
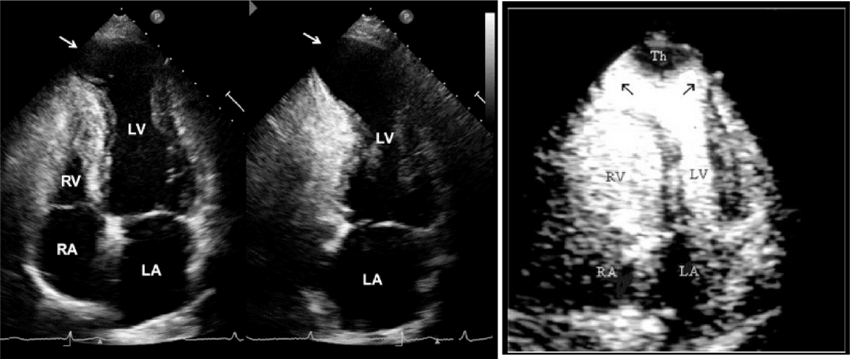
Highlighted with the arrows
What is LV apical aneurysm?
The a3 and p3 scallops of the MV are nearest to this easily identifiable structure
What is the interventricular septum?
This apical 4 chamber view, this wall is on the far right of the image
What is the anterolateral wall?
TR is most often secondary to and a good measure of this
What is pulmonary hypertension?
Aliasing in PW indicates this
What is a velocity exceeding the Nyquist limit
Apical wall segments in A4C
What are apical septal and apical lateral?
How poor EF impacts AS quantification
What is underestimation?
This is the pap that usually ruptures
What is the posteromedial papillary muscle?
LV hypertrophy is most commonly due to this
What is systemic hypertension - HBP.
PS is best evaluated in this echo window.
What is PSAX?
Spectral Doppler displays this on the x-axis
What is time?
Apical wall segments in A3C
What are apical lateral and apical anterior?
RV diastolic collapse
What is cardiac tamponade?
First tell that there's a blocked coronary
What are MV inflow changes?
RA pressure is estimated using this vein
What is the IVC?
Flail mitral leaflet usually causes this, to this degree
What severe MR?
Gain affects this visual aspect of Doppler signal
What is signal brightness/intensity?
SAM is seem in this disease
M-mode diastolic fluttering of AMVL is likely due to this
What is aortic regurgitation?
Very rare, always congenital
What is PS?
The basal segments of this chamber are usually sampled with TDI.
What is the LV?
This disorder usually presents with concurrent MVP
What is Marfan's syndrome?
This must be lowered when assessing PISA
What is color baseline?
Global hypokinesis and increase LVID
What is dilated CM?
RVSP = this
when IVC=2.7cm, no collapse
and TR velocity is 4 m/s
What is 79 mmHg?
What is the pedoff/blind probe?
This chamber dilates first in MR and MS
What is the LA?
M-mode of BAV in PLAX displays this feature
What is eccentric closure line?
TDI measures movement of this
What is myocardium?
LV thombus most common with this CM
What is ICM?
Formula for regurgitant fraction
What is RV /SVav * 100 (%)
RV = (SVav - SVmv)
AVA Moderate stenosis range
What is 1.0 - 1.5 cm2?
This chamber's contraction is measured with M-mode at the free wall annulus
What is the RV?
Doming of MV leaflets is a sign of
E and A waves are measured during this phase
What is diastole?
Impacts coronary arteries causing aneurysms; makes jet skis on the side
What is Kawasaki Disease?
The reason our mitral inflow might be missing a wave
What is atrial fibrillation?
The value that is squared in the Continuity Equation
What is LVOTd?
Apply: Apical two chamber demonstrates thinning and akinesis in the wall along the right side of the image, wrapping around the tip of the heart to include the top segment of the wall along the left of the image.
THIS VESSEL IS BLOCKED.
What is the LAD?
When you think of thick retracted leaflets, think of this valve being attacked by an endocrine tumor.
What is the tricuspid valve?
This is a normal E:A ratio
What is 0.8 - 1.5?
Affects large vessels, particularly the aorta
What is Takayasu arteritis?
This ______stream side of the valve is where IE vegs happen
What is upstream?
IE veg on this side of the heart embolizes to the lungs
What is right side?