Pulmonary circuit meaning
to and from the lungs
How many sulci does the heart have?
The heart has 3 sulci.
what are the 2 primary layers of pericardium?
1. Fibrous pericardium
2. Serous pericardium
Where will you find the epicardium?
what divides the left and right ventricles (internally)?
the interventricular septum
what artery carries deoxygenated blood?
pulmonary artery (slide 7/47)
describe the location of the coronary sulcus.
The coronary sulcus runs between the atria and the ventricles
Which layer of the pericardium is dense, irregular tissue?
The fibrous pericardium is dense, irregular tissue.
what is the myocardium?
the myocardium is the muscular layer of the heart.
True or False:
the right ventricle is thicker than the left ventricle.
False, the left ventricle is thicker.
systemic circuit meaning
to and from body tissues
describe the location of the anterior interventricular sulcus
the anterior interventricular sulcus runs between the left and right ventricles
True or False:
The heart is encased within a membranous fluid-filled sac, the pericardium.
True
What is the endocardium?
The endocardium makes up the inner surface of the heart.
What is the name of the ridges inside the anterior right atrium?
pectinate muscles
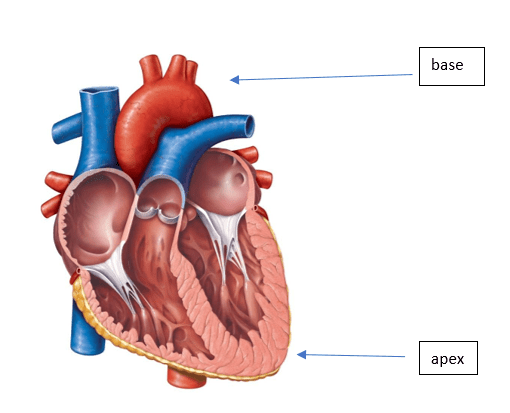
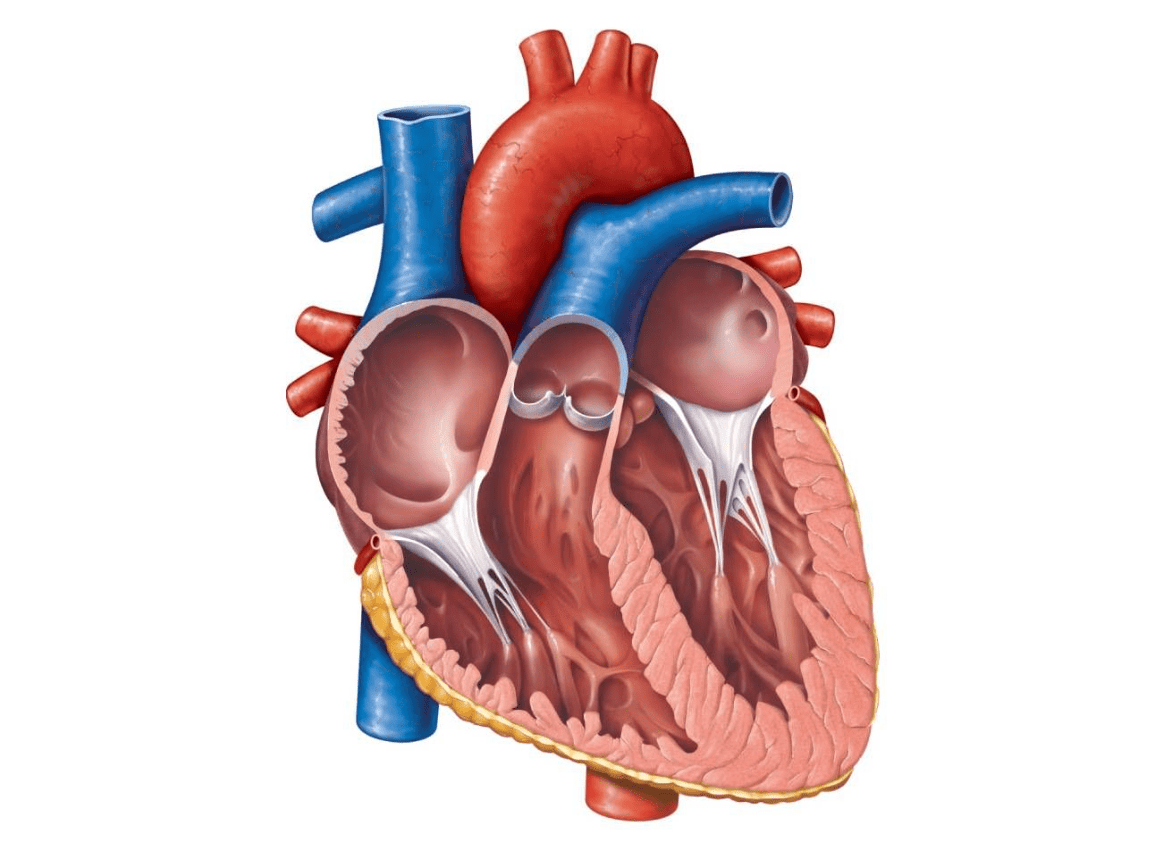 Where is the apex of the heart? Where is the base?
Where is the apex of the heart? Where is the base?
describe the location of the posterior interventricular sulcus
the posterior interventricular sulcus lies between the ventricles.
What is the purpose of pericardial fluid?
Lubrication
How is the myocardium arranged?
The myocardium (muscle) is arranged in spiral and circular patterns.
what is the fossa ovalis?
a depression in interatrial septum
[remnant of foramen ovale]
True or False:
blood vessels anchor the apex of the heart.
False: Blood vessels anchor the base of the heart.
The heart is enclosed and held in place by what?
Pericardium
What are the three layers of the heart wall?
1. Epicardium
2. Myocardium
3. Endocardium
how many chambers are there in the human heart?
4 chambers: 2 atria, 2 ventricles.
These three things make of the internal walls of the right ventricle
Trabeculae carneae
papillary muscles
chordae tendineae