Which level of biological organization is directly above organ system?
Organism
The smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element is a(n):
A) Proton
B) Atom
C) Neutron
D) Molecule
B) Atom
What type of bond connects two water molecules?
Hydrogen bond
Carbon can form four covalent bonds. Which property of carbon allows it to build large and complex molecules?
A) Its ability to bond with many different elements
B) Its ability to only bond with itself
C) Its inability to form double bonds
D) Its electronegativity
A) Its ability to bond with many different elements
All living organisms share certain characteristics. Which of the following is an example of one of these shared traits?
A) They all perform photosynthesis
B) They all maintain internal balance
C) They all move from place to place
D) They all produce oxygen
B) They all maintain internal balance
Which of the following is not shared by all living organisms?
A) Ability to regulate internal environment
B) Containing genetic information
C) Reproducing genetic information in the same manner
D) Being multicellular
D) Being multicellular
When two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons, what type of bond is formed?
Extra 100 points : Name one molecule that forms this type of bond.
Which property of water explains why lakes don’t freeze solid from the bottom up?
A) Adhesion
B) Cohesion
C) Expansion upon freezing
D) High surface tension
C) Expansion upon freezing
Testosterone and estradiol are both steroids. Which of the following explains why they have different effects in the body?
A) They contain different numbers of carbon atoms
B) They have different functional groups attached
C) They are both proteins, not steroids
D) They are identical molecules
B) They have different functional groups attached
How many covalent bonds can carbon form up to?
4
Which of the following shows the correct hierarchy of life from smallest to largest?
A) Muscle cell → Muscle tissue → Heart → Circulatory system
B) Heart → Muscle tissue → Muscle cell → Circulatory system
C) Circulatory system → Heart → Muscle tissue → Muscle cell
D) Muscle tissue → Circulatory system → Heart → Muscle cell
A) Muscle cell → Muscle tissue → Heart → Circulatory system
Living organisms are primarily composed of just a few key elements. Which four elements together make up about 96% of the human body’s mass?
CHON
C - Carbon
H - Hydrogen
O - Oxygen
N - Nitrogen
The hydrogen ion concentration [H+] of a solution is 1×10^5 M. What is the pH of this solution, and is it acidic, neutral, or basic?
pH 5 ; acidic
ATP stores energy in its phosphate groups. What happens when ATP is hydrolyzed (broken down to ADP)?
A) A phosphate group is removed, and energy is released for cellular work
B) Two phosphate groups attach, storing extra energy
C) ATP is converted into a lipid for long-term energy storage
D) The sugar in ATP is replaced by glucose
A) A phosphate group is removed, and energy is released for cellular work
Define hydrophobic and hydrophilic
Hydrophobic hates water
Hydrophilic likes water
If two species share 95% of their genes, what does this suggest about their evolutionary relationship?
A) They diverged recently from a common ancestor
B) They cannot interbreed
C) They are unrelated
D) They share many similarities in traits
A) They diverged recently from a common ancestor
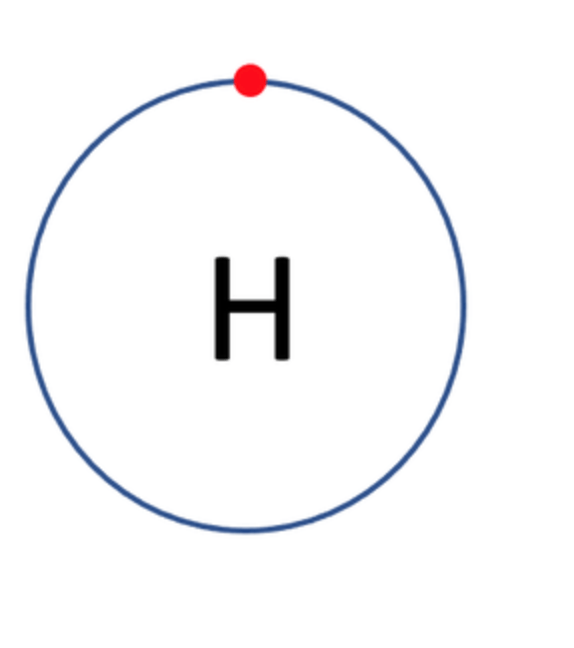
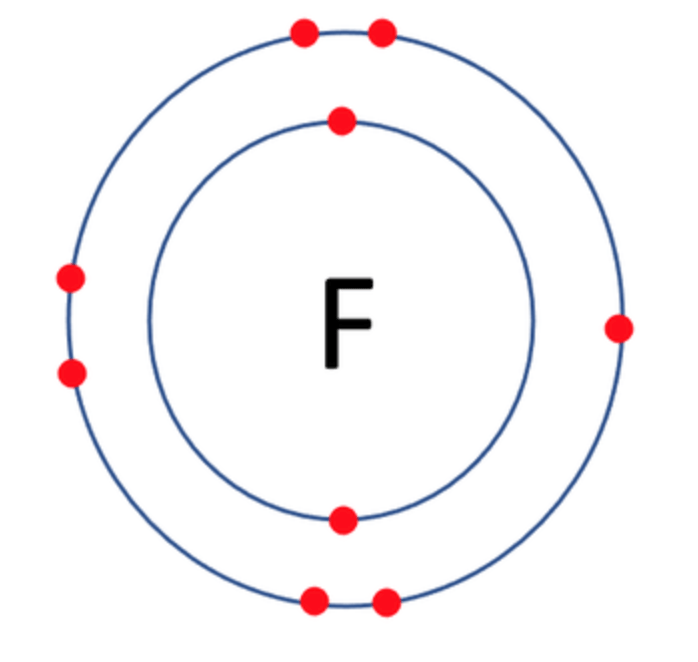
Which one of the following atoms would be most likely to form an anion with a charge of –2? AND WHY
A)
B)
 C)
C)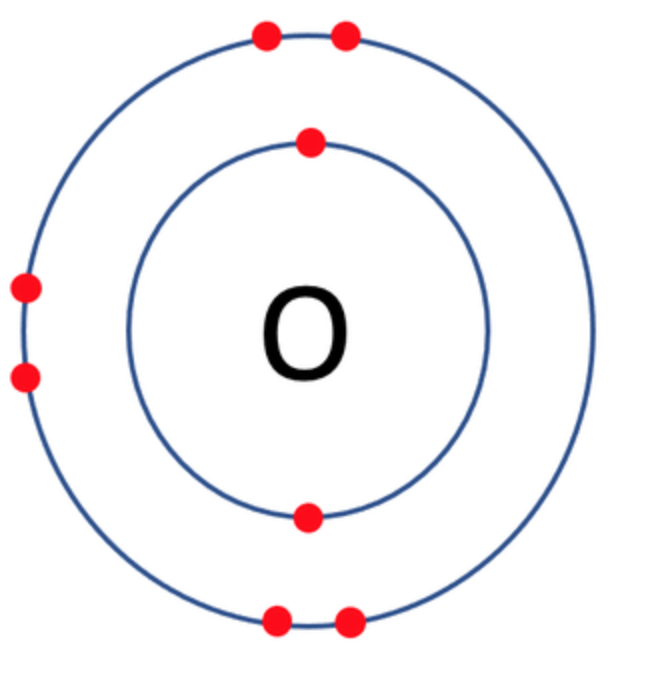
D)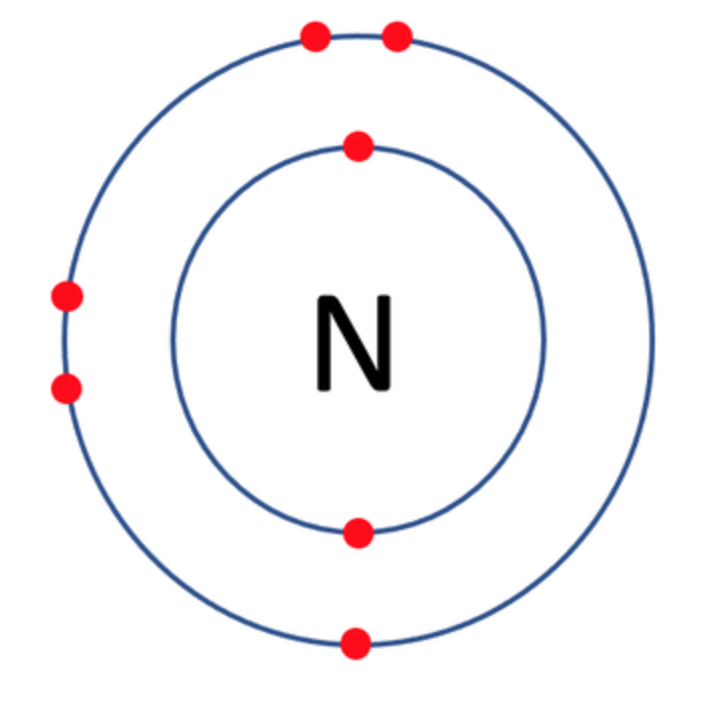
C)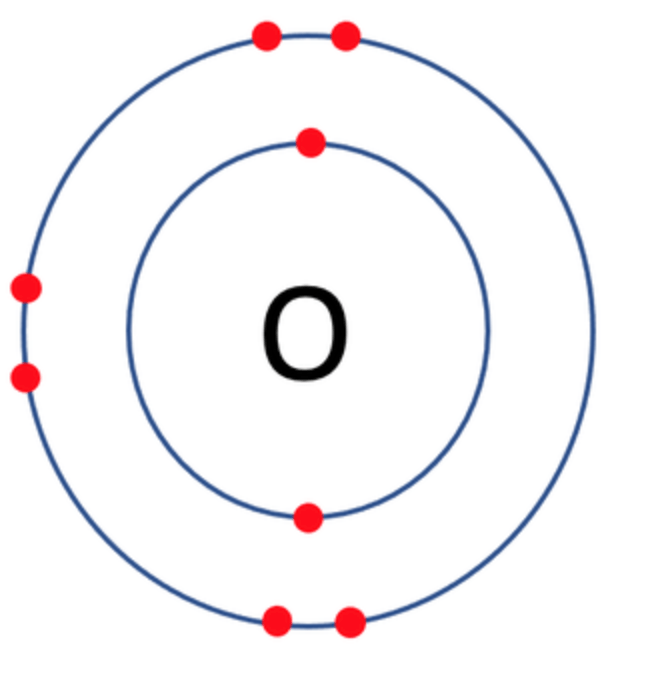
A plant relies on both cohesion and adhesion to move water upward. Which is the best explanation?
A) Cohesion holds water molecules together, while adhesion helps water stick to cell walls
B) Cohesion pushes water into leaves, adhesion prevents evaporation
C) Cohesion helps dissolve minerals, adhesion makes water hydrophobic
D) Cohesion lowers pH, adhesion raises pH
A) Cohesion holds water molecules together, while adhesion helps water stick to cell walls
The carboxyl group (–COOH) is common in amino acids. Which property does this group give to molecules?
Acts as an acid
Ice floats on liquid water because of the way hydrogen bonds form when water freezes. Why is this important for life on Earth?
It keeps lakes and oceans from freezing solid, allowing organisms to survive beneath the ice
State at least 2 differences and similarities of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotes - multicellular(most), have membraned enclosed organelles
Prokaryotes - unicellular, don't have membraned enclosed organelles
Oxygen has 6 valence electrons and needs 2 more to fill its outer shell. When two oxygen atoms bond together, which type of bond forms, and how many pairs of electrons are shared?
A) Single covalent bond; 1 pair shared
B) Double covalent bond; 2 pairs shared
C) Ionic bond; 2 electrons transferred
D) Hydrogen bond; 2 pairs of electrons attracted
B) Double covalent bond; 2 pairs shared
Why coastal areas have milder climates than inland areas?
Water absorbs and releases large amounts of heat with only slight temperature change.
Absorb the heat when it's hot, releasing when it's cold
Identify all of the functional groups present in this molecule
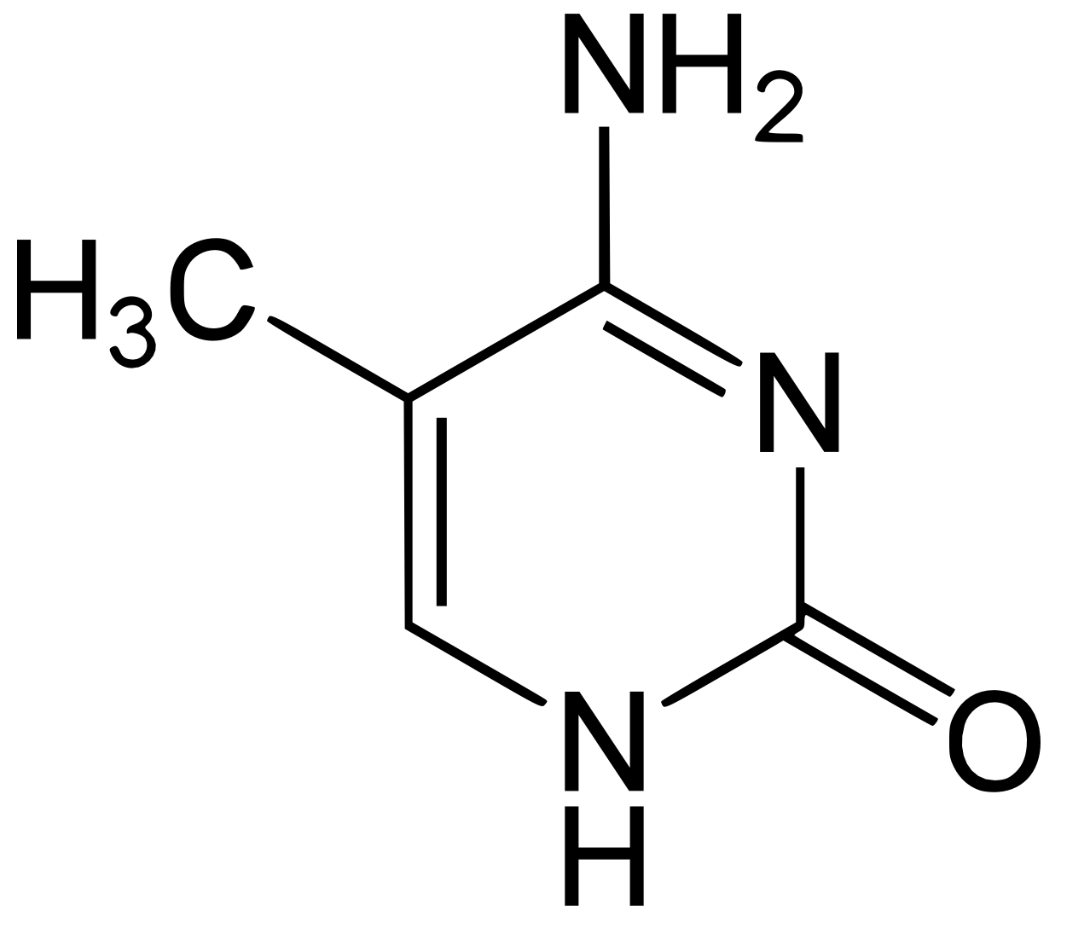
NH2 - Amino
CH3 - Methyl
C=O - Carbonyl
Identify all of the functional groups present in this molecule
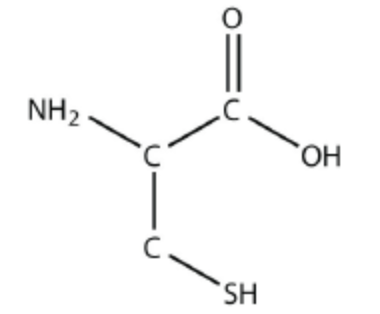
C=O-OH - Carboxyl
NH2 - Amino
SH - Sulfhydryl