This type of thermal energy transfer moves through electromagnetic waves and doesn’t require a medium to travel.
Conduction - Touchin'
Convection - Warm up, Cool down, thats the way convection moves around
Radiation - Waves
Radiation
High-frequency wave; Can be used to sterilize medical equipment 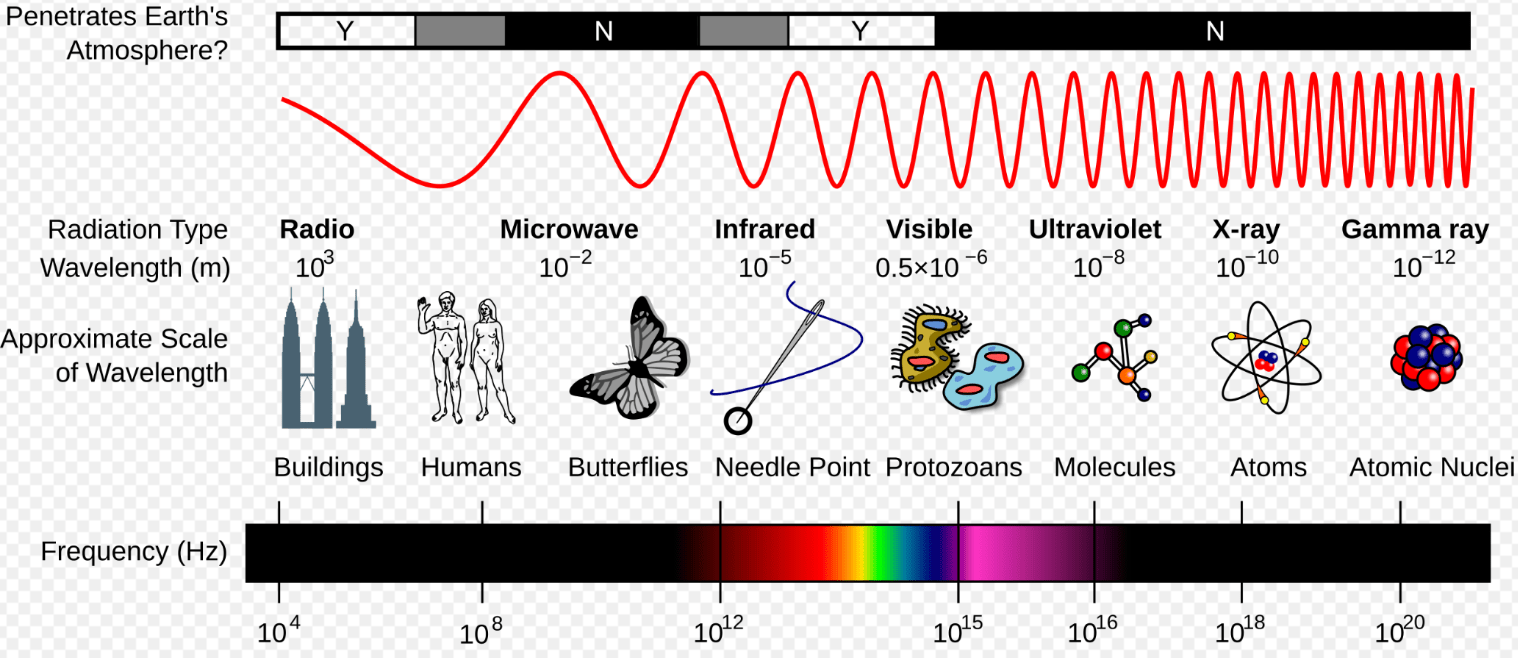
Ultraviolet (UV)
These stars stretch across the H–R Diagram from hot and bright to cool and dim, and they’re in the longest, most stable stage of a star’s life cycle — a stage that includes our Sun and about 90% of all stars.
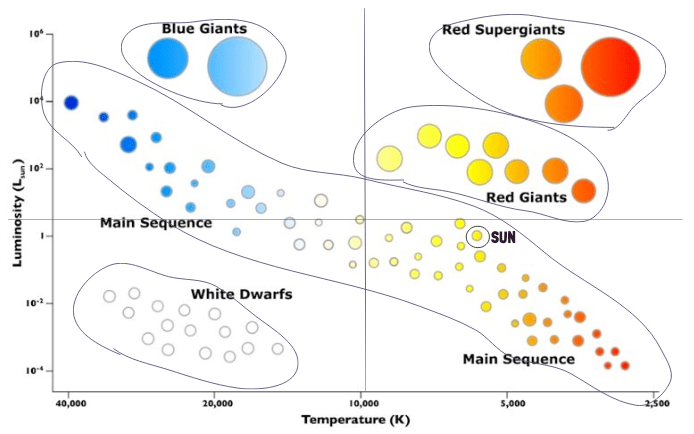
Main Sequence Stars
Our sun is a _________________ star, that is one-third of the way through its life cycle.
Main sequence
Classify this galaxy as Spiral, Elliptical or Irregular.
Elliptical
True or False
These waves carry the same amount of energy.
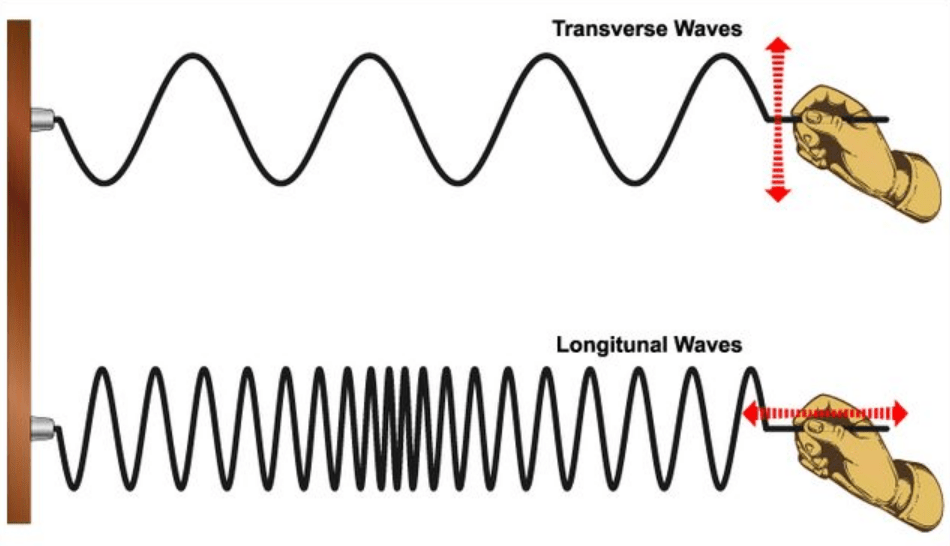
False
Long wavelength; can travel long distances with low energy for communication
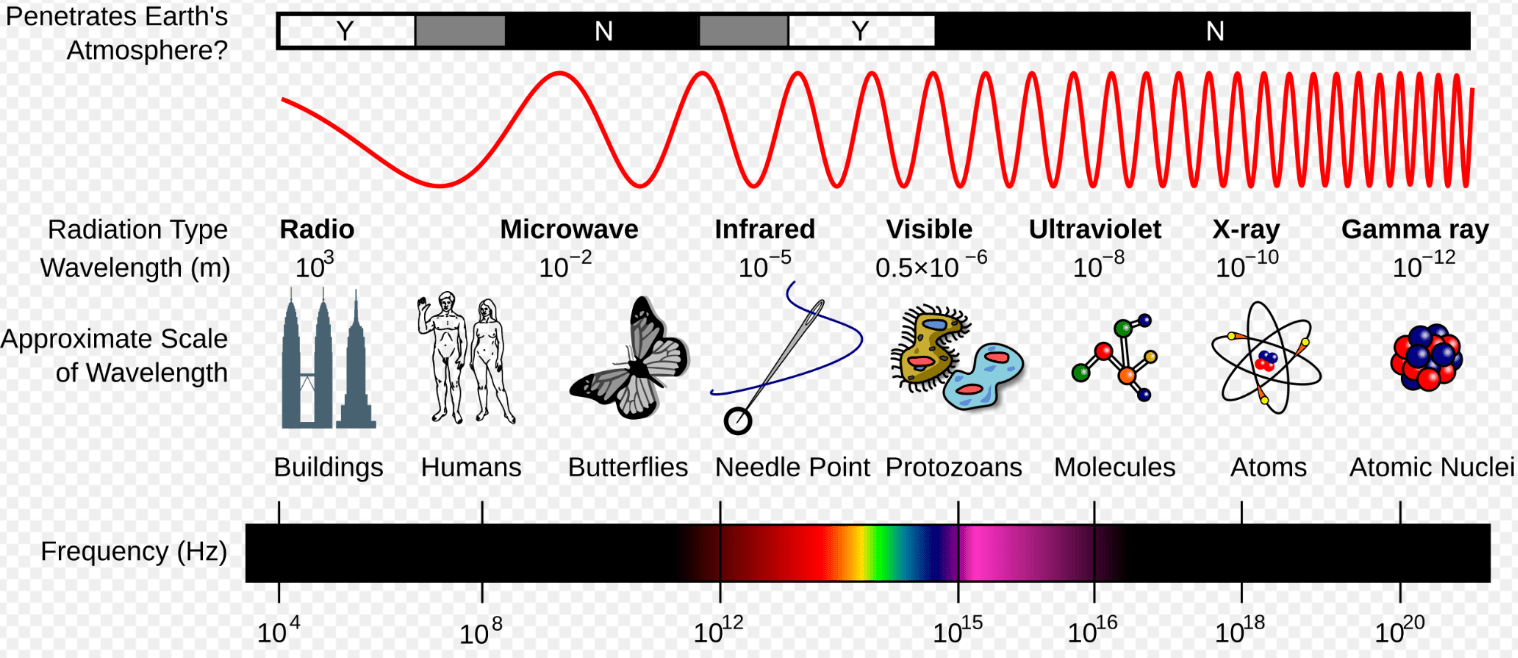
Radio
These enormous, extremely bright stars occupy the top of the H–R Diagram and form when massive stars swell to tremendous sizes late in their life cycle.
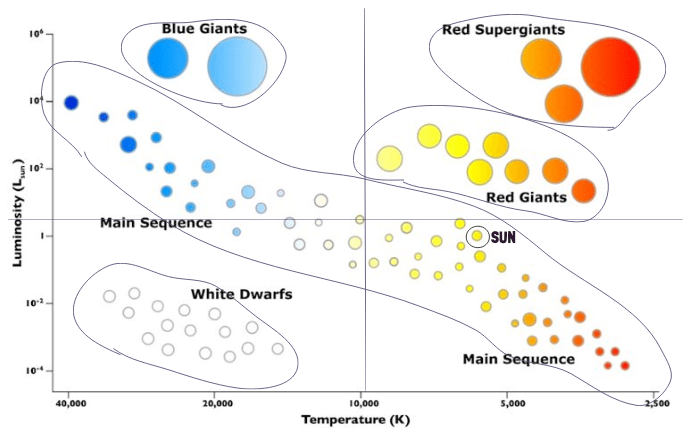
As our sun nears the end of its life and burns away, it will expand and become a __________.
Red Giant
Classify this galaxy as Spiral, Elliptical or Irregular.

The name for location A on the wave. 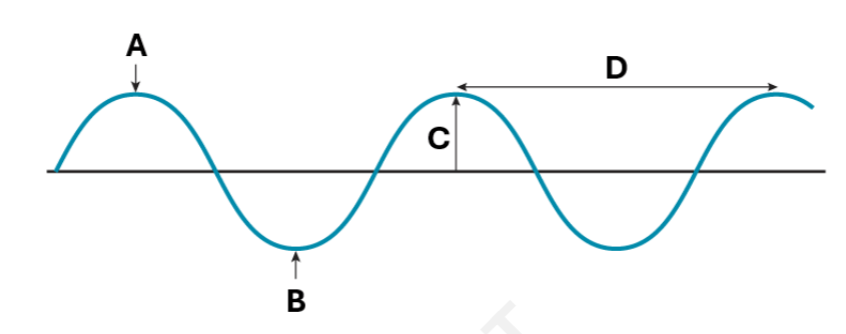
Crest
Slightly longer wavelength than visible light; can be used in heat lamps
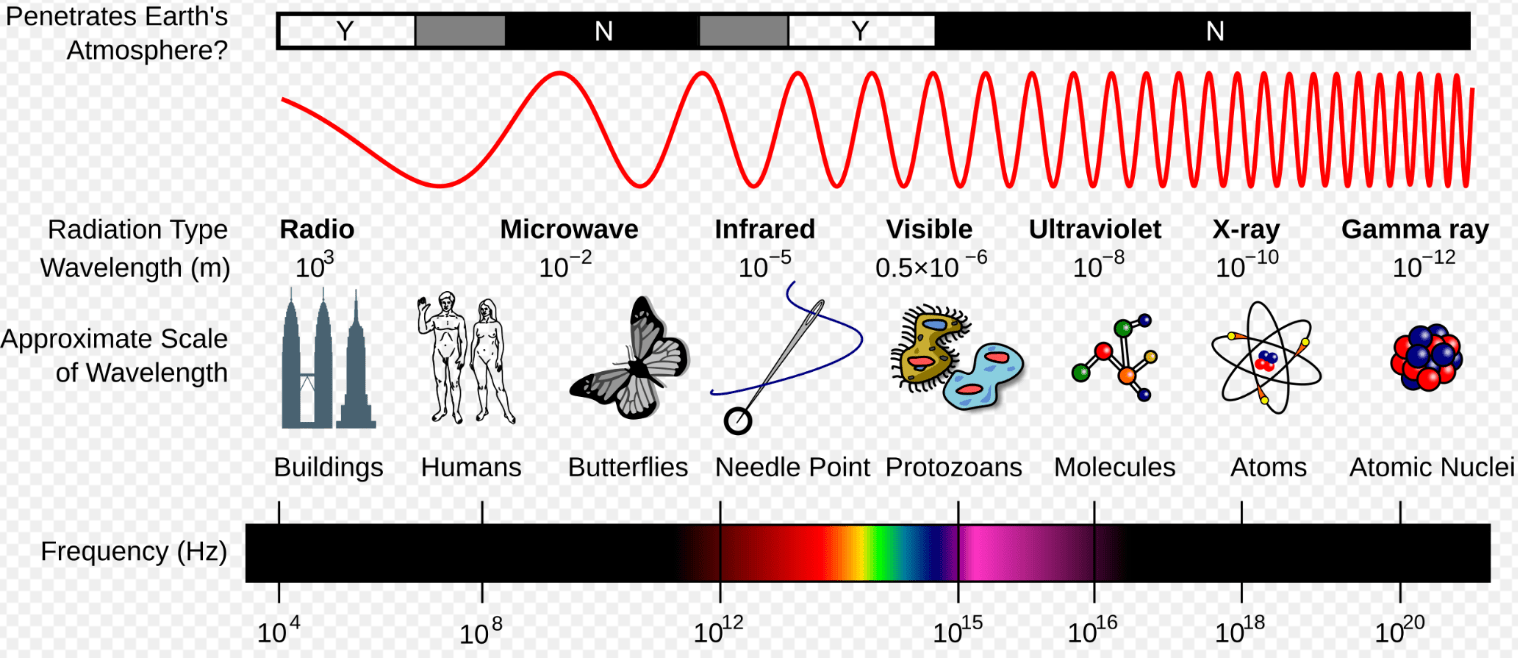
Infrared
Aldebaran is a star with a Luminosity of 102 and a temperature of 4,200K. Aldebaran would be located in this zone.
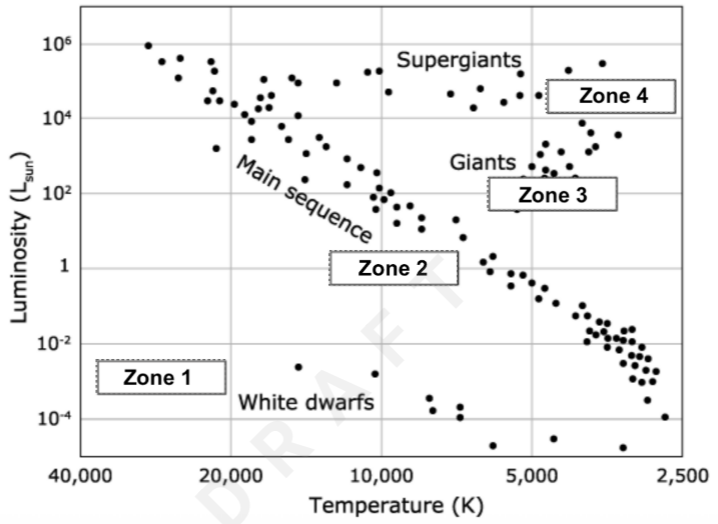
Zone 3
The end stage of our suns life cycle.
White Dwarf
The easily identifiable feature of spiral galaxies.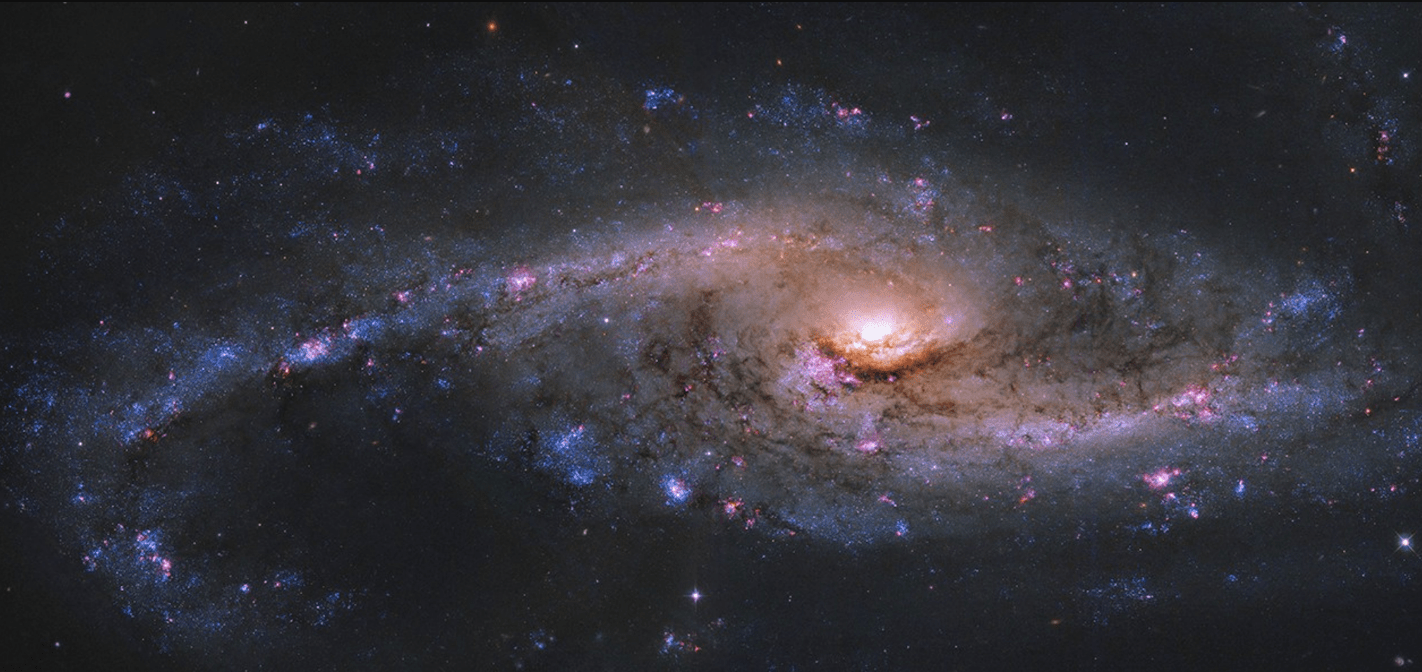 
Spiral Arms
The name for location C on the wave.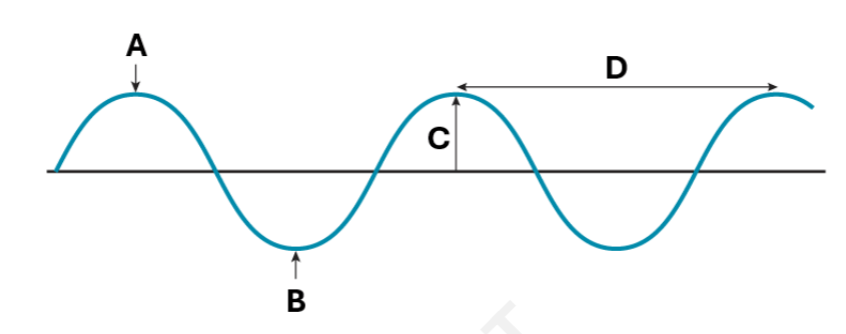
Amplitude
A frequency of 1.41 x 109 Hz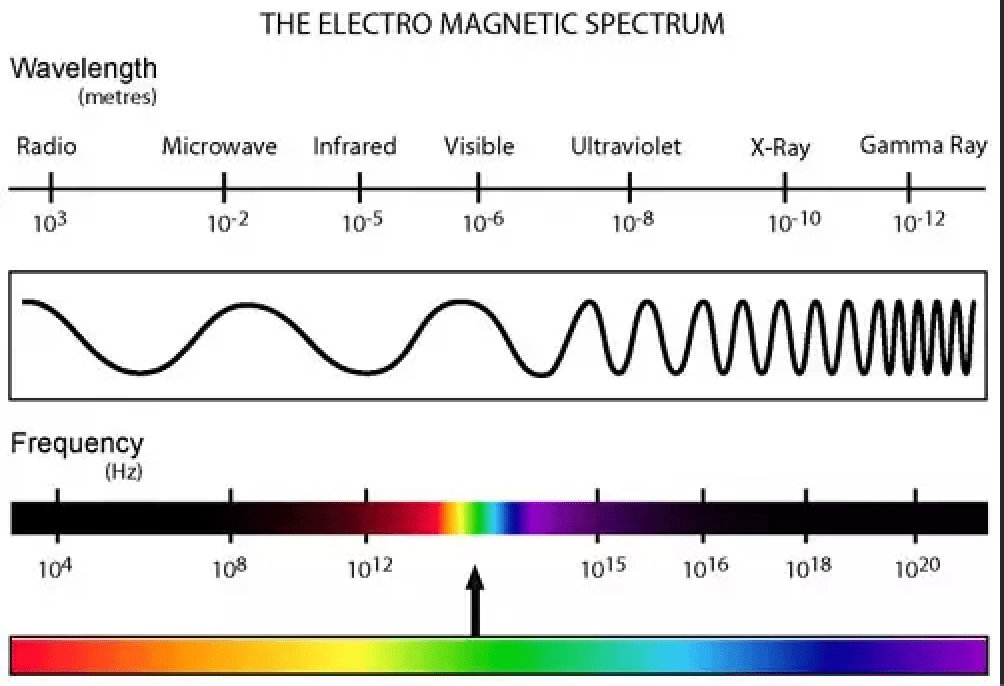
Microwaves
Sirius B is a star with a luminosity of 10-3 and a temperature of 30,000K. Sirius B would be located in this zone. 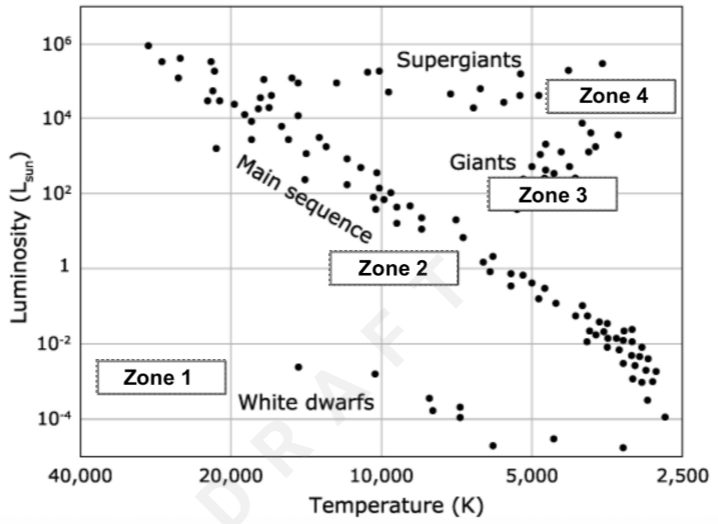
Zone 1
This dramatic event in the life of a massive star scatters dust and gas across space, helping to form new nebulae.
Supernova
The location of our solar system in the Milky Way Galaxy.
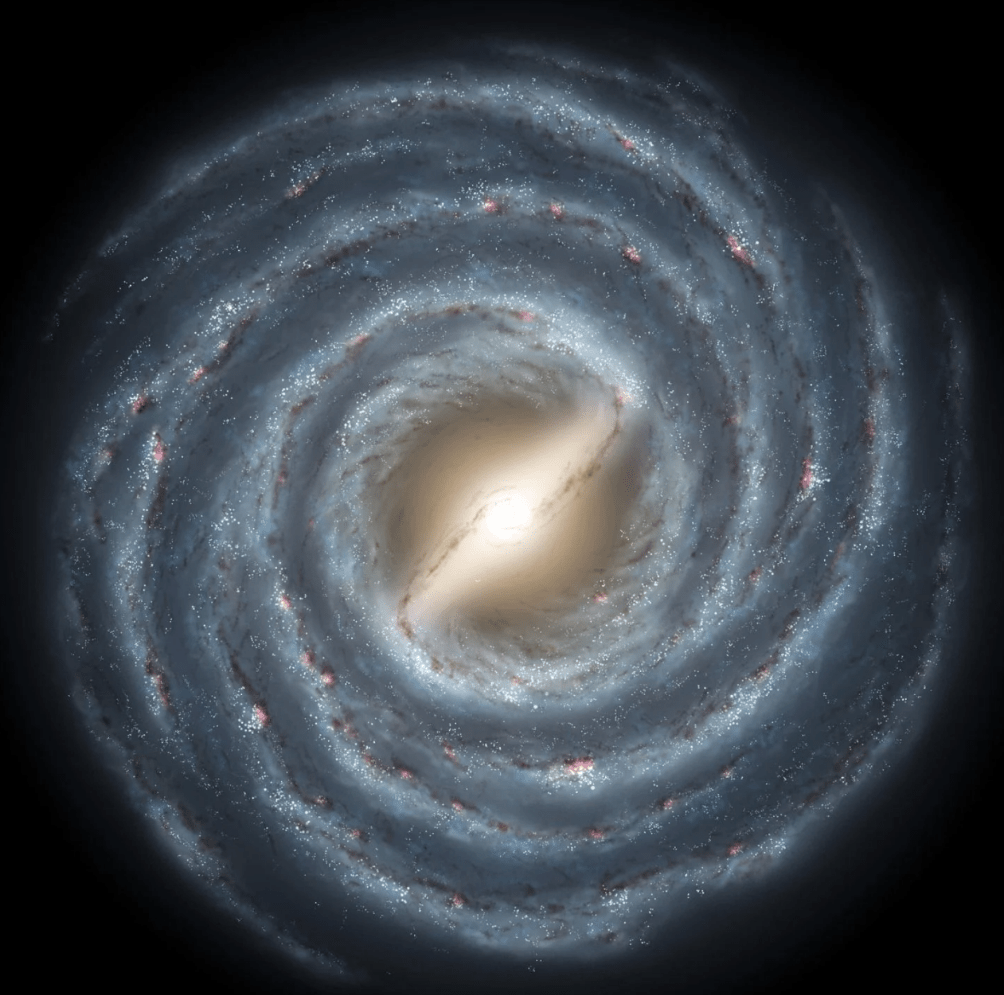
Spiral Arm
If we change the motor so the wave oscillates twice as fast, what effect will this have on the wavelength? Will the wavelength decrease/Increase?
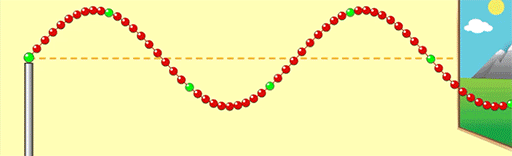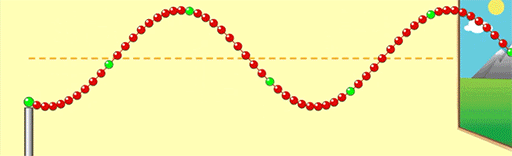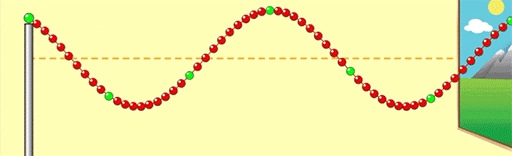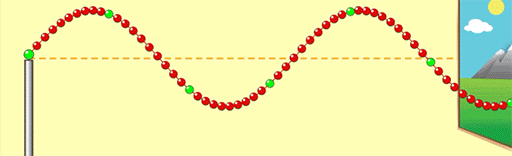
The wavelength will decrease
Energy can travel through Earth’s atmosphere as electromagnetic waves. Which type of electromagnetic wave is best for sending messages from the International Space Station to Earth?
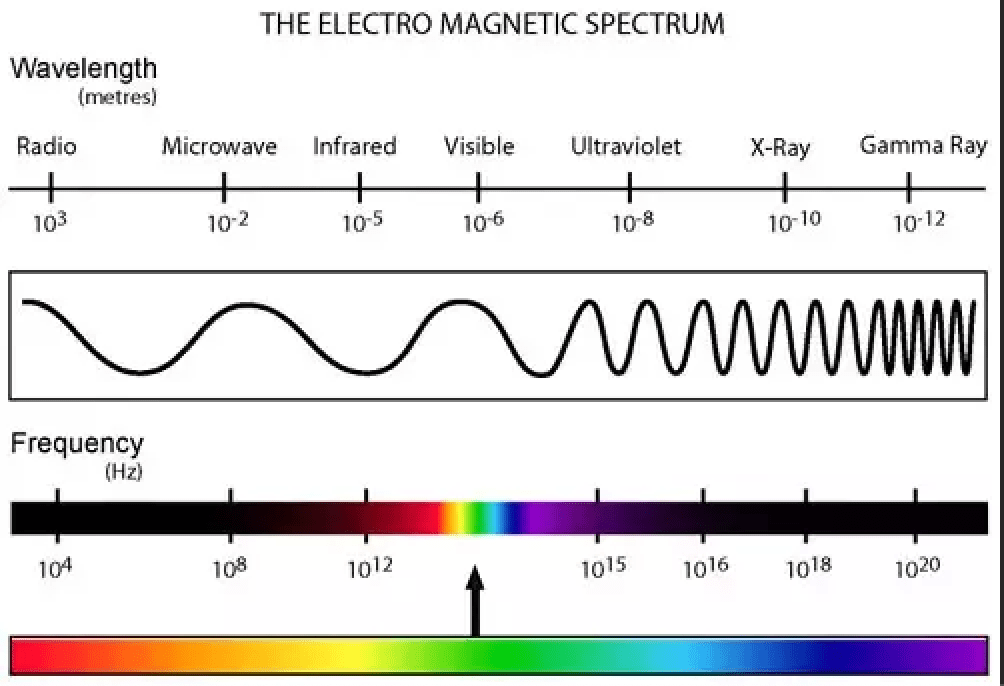
Radio waves
Accurately identify each quadrant as either: Hot/Bright, Cool/Bright, Hot/Dim, Cool/Dim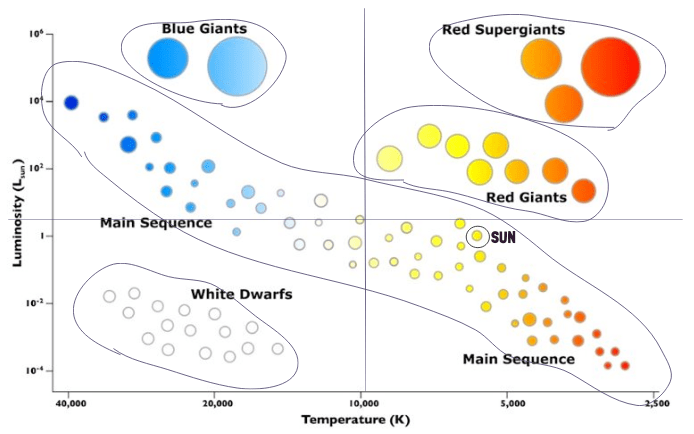
Teacher approved
The spectral class of star E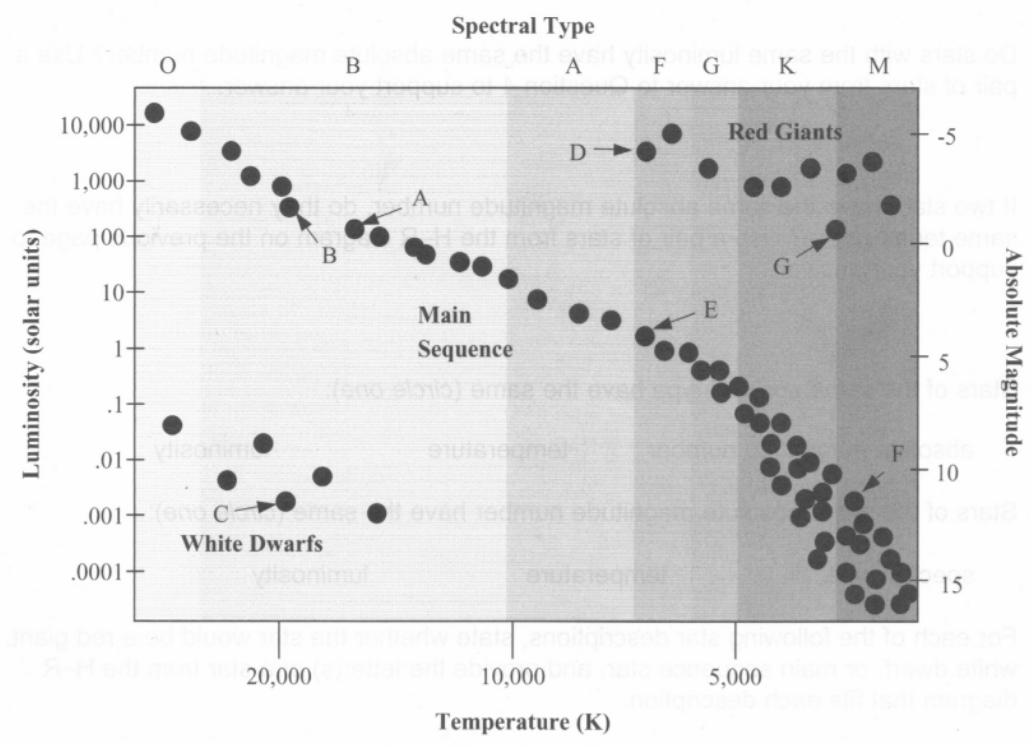
Spectral class F
What are the action and reaction forces involved when a basketball bounces off the floor?
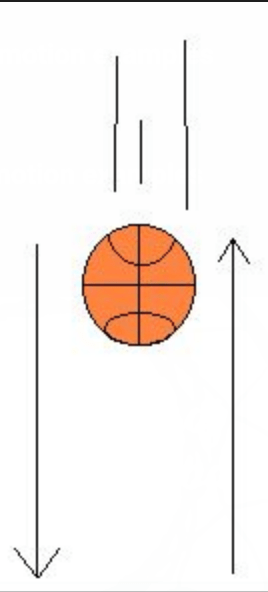
Action: The basketball exerts a force downward on the floor.
Reaction: The floor exerts an equal and opposite force upward on the b