An organized grouping of information within a specific structure
What is a database?
A classification model applied to existing “labeled” data (i.e., where the category or class is known). E.g., grouping patients based on a known medical history or condition.
What is classification or categorization?
A unique value assigned to observations
What is an identifier?
The discipline of extracting useful and actionable insight from data to improve the process and outcome of decision making used to be the role of this person.
What is the statistician?
A computational process of analyzing datasets using both statistical and logical methods in order to uncover hidden, previously unknown and interesting patterns that can inform organizational decision making
What is data mining?
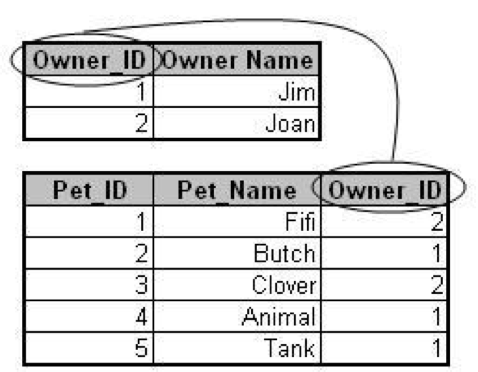
What is a relational database?
Information that is not organized or easily interpreted by traditional databases or data models, and is typically text-heavy.
What is unstructured data?
The characteristics that in combination comprise Big data.
What are the 5 V's? Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity and Value.
A system that is NOT efficient for analysis (requiring accessing multiple data sources) requiring query multiple databases at one time through joins.
What is OLTP or online transactional processing?
The intentional combination of tables which
reduces the number of joins necessary to
query related data, making it efficient for analysis.
What is OLAP or online analytical processing?
This type of data is always composed of discrete values.
What is categorical?
The process of data mining.
What is CRISP-DM: Cross Industry Standard for Data Mining?
The other TWO terms for variables, fields, columns,
characteristics.
What are attributes and features?
A large, denormalized and archived database.
What is a data warehouse?
The phase of a Data Mining project where you: Select the data (2) Cleanse the data; (3) Construct New Data; (4) Integrate the data and (5) Format the data.
What is the Data Preparation Phase or Phase 3?
The number of observations (rows) and the number of variables (columns).
What are dimensions?
Tabular data that can be stored in SQL databases in rows and columns (e.g., transactional data)
What is structured data?
The random assignment of observations
to three independent datasets to ensure each is representative of the whole.
What is partitioning?
This is known as the abstraction (or computerized representation) or a real-world phenomenon.
What is a model?